Abstract
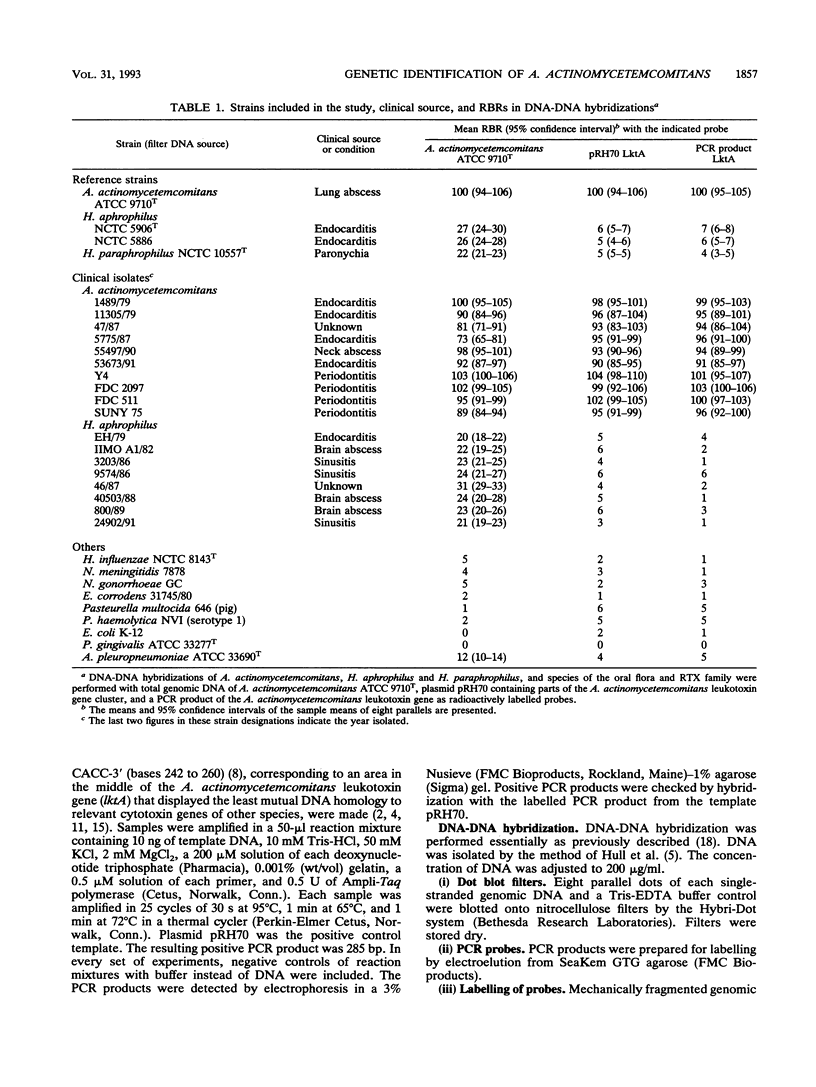
Eleven strains of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans isolated from cases of systemic infections, local abscesses, and periodontitis were identified by genetic assays using the leukotoxin gene as the target. We have developed a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay, based on the leukotoxin structural gene of this pathogen, which clearly identified all tested strains of A. actinomycetemcomitans and separated them from the closely related Haemophilus aphrophilus as well as other bacterial species. Furthermore, DNA-DNA hybridization was performed with the cloned partial leukotoxin structural gene (lktA) as a probe, which again clearly distinguished A. actinomycetemcomitans from H. aphrophilus, parts of the normal oral flora, and species harboring RTX (repeats in toxin) family-related cytotoxins. The PCR fragment amplified from the leukotoxin structural gene gave results similar to those given by the cloned leukotoxin gene when used as a probe in hybridization experiments. The hybridization and PCR assays described here are fundamental improvements for the identification of A. actinomycetemcomitans.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caugant D. A., Selander R. K., Olsen I. Differentiation between Actinobacillus (Haemophilus) actinomycetemcomitans, Haemophilus aphrophilus and Haemophilus paraphrophilus by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Oct;136(10):2135–2141. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-10-2135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Young R., Struck D. K. Cloning and characterization of a hemolysin gene from Actinobacillus (Haemophilus) pleuropneumoniae. DNA. 1989 Nov;8(9):635–647. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran D. L. Bacteriologic monitoring of periodontal diseases: cultural, enzymatic, immunologic, and nucleic acid studies. Curr Opin Dent. 1991 Feb;1(1):37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Pellett S., Welch R. A. Nucleotide sequence of an Escherichia coli chromosomal hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):94–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.94-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R. A., Gill R. E., Hsu P., Minshew B. H., Falkow S. Construction and expression of recombinant plasmids encoding type 1 or D-mannose-resistant pili from a urinary tract infection Escherichia coli isolate. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):933–938. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.933-938.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., TATUM H. W. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Hemophilus aphrophilus. J Infect Dis. 1962 Sep-Oct;111:85–94. doi: 10.1093/infdis/111.2.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraig E., Dailey T., Kolodrubetz D. Nucleotide sequence of the leukotoxin gene from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans: homology to the alpha-hemolysin/leukotoxin gene family. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):920–929. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.920-929.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lally E. T., Golub E. E., Kieba I. R., Taichman N. S., Rosenbloom J., Rosenbloom J. C., Gibson C. W., Demuth D. R. Analysis of the Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin gene. Delineation of unique features and comparison to homologous toxins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15451–15456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson D. A., Haas R., Meyle J., Meyer T. F. Molecular analysis of periodontal pathogens. Arch Oral Biol. 1990;35 (Suppl):101S–105S. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(90)90138-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lian C. J., Rosendal S., MacInnes J. I. Molecular cloning and characterization of a hemolysin gene from Actinobacillus (Haemophilus) pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3377–3382. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3377-3382.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Listgarten M. A., Slots J., Nowotny A. H., Oler J., Rosenberg J., Gregor B., Sullivan P. Incidence of periodontitis recurrence in treated patients with and without cultivable Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Prevotella intermedia, and Porphyromonas gingivalis: a prospective study. J Periodontol. 1991 Jun;62(6):377–386. doi: 10.1902/jop.1991.62.6.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savitt E. D., Kent R. L. Distribution of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas gingivalis by subject age. J Periodontol. 1991 Aug;62(8):490–494. doi: 10.1902/jop.1991.62.8.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J., Jr, Kraig E., Kolodrubetz D. Regulation of leukotoxin in leukotoxic and nonleukotoxic strains of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1394–1401. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1394-1401.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Extensive homology between the leukotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica A1 and the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3233–3236. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3233-3236.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strzempko M. N., Simon S. L., French C. K., Lippke J. A., Raia F. F., Savitt E. D., Vaccaro K. K. A cross-reactivity study of whole genomic DNA probes for Haemophilus actinomycetemcomitans, Bacteroides intermedius, and Bacteroides gingivalis. J Dent Res. 1987 Oct;66(10):1543–1546. doi: 10.1177/00220345870660100601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. C., Visconti R. A., Socransky S. S., Holt S. C. Classification and identification of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and haemophilus aphrophilus by cluster analysis and deoxyribonucleic acid hybridizations. J Periodontal Res. 1982 Nov;17(6):585–596. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb01180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tønjum T., Bukholm G., Bøvre K. Identification of Haemophilus aphrophilus and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans by DNA-DNA hybridization and genetic transformation. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1994–1998. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1994-1998.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]