Abstract
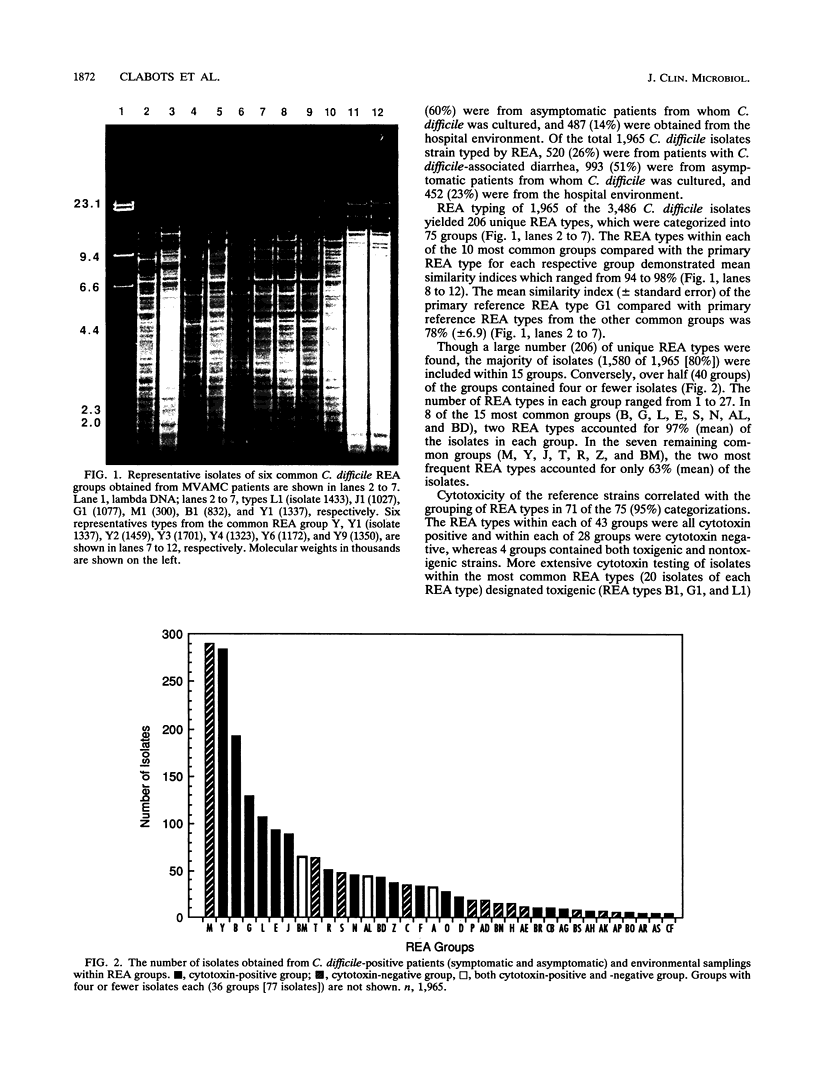
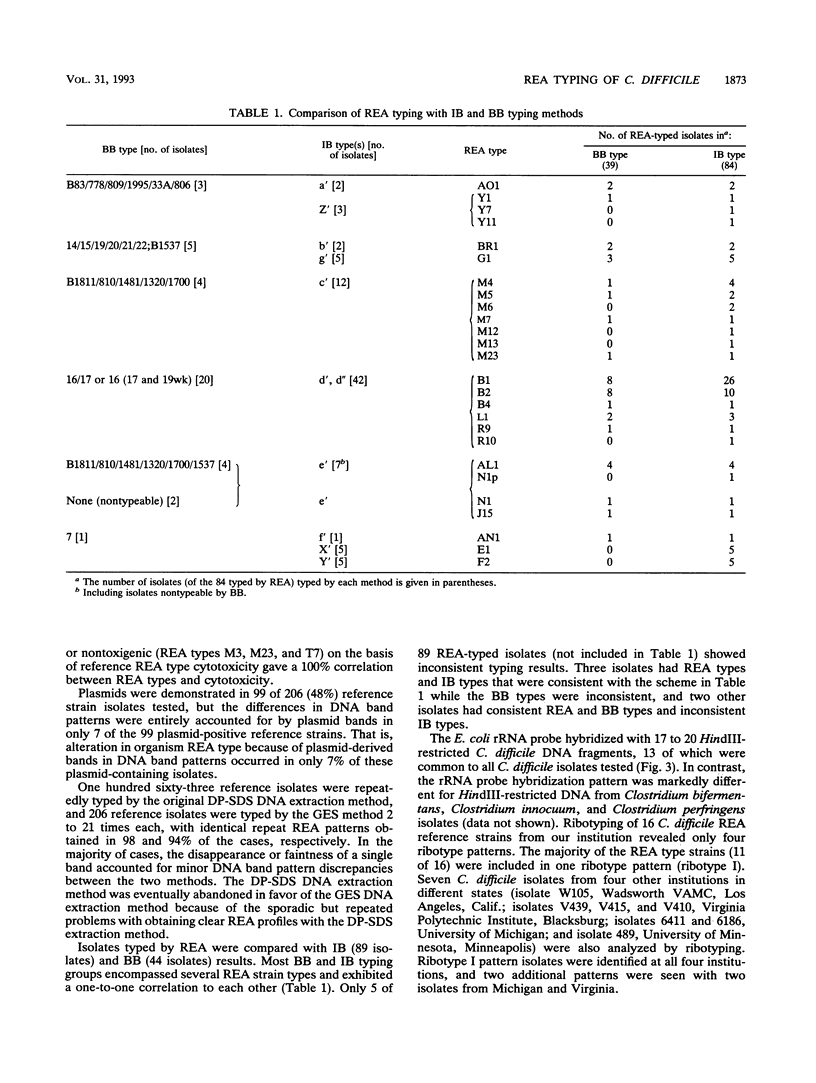
A HindIII restriction endonuclease analysis (REA) typing system for total genomic Clostridium difficile DNA including a rapid and efficient method of DNA extraction and a scheme for organizing unique electrophoretic DNA band patterns was developed. REA typing was performed by two extraction methods for 1,965 C. difficile isolates obtained from patients with symptomatic C. difficile disease, asymptomatic patients who were C. difficile culture positive, and environmental surfaces. This isolate collection yielded 206 unique REA types, which were organized into 75 groups. A reference strain representing each unique REA type was chosen for DNA band pattern comparisons, cytotoxin testing, and plasmid analysis. The DNA band patterns utilizing a guanidine thiocyanate-EDTA-Sarkosyl DNA extraction method were 94% reproducible, while the original and sporadically problematic diethyl pyrocarbonate-sodium dodecyl sulfate DNA extraction method was 98% reproducible when readable patterns were obtained. Reference strains from 43 of the 75 groups were cytotoxin positive, 28 groups were cytotoxin negative, and 4 groups included both toxigenic and nontoxigenic strains. Cytotoxicity of isolates with a particular REA type was always consistent with the toxicity of the reference strain for that type. REA typing was able to discriminate strain differences within types identified by the immunoblot (89 isolates), bacteriophage-bacteriocin (44 isolates), and ribotyping (23 isolates) methods. REA typing is a sensitive, discriminating, reproducible, and rapid method for differentiating C. difficile strains and is suitable for large-scale epidemiologic studies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschek H. P., Klacik M. A. Role of DNase in recovery of plasmid DNA from Clostridium perfringens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):178–181. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.178-181.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clabots C. R., Bettin K. M., Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Evaluation of cycloserine-cefoxitin-fructose agar and cycloserine-cefoxitin-fructose broth for recovery of Clostridium difficile from environmental sites. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2633–2635. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2633-2635.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clabots C. R., Johnson S., Olson M. M., Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Acquisition of Clostridium difficile by hospitalized patients: evidence for colonized new admissions as a source of infection. J Infect Dis. 1992 Sep;166(3):561–567. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.3.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clabots C. R., Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Characterization of a nosocomial Clostridium difficile outbreak by using plasmid profile typing and clindamycin susceptibility testing. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):731–736. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary P. P., Kaplan E. L., Livdahl C., Skjold S. DNA fingerprints of Streptococcus pyogenes are M type specific. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1317–1323. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin H. R., Au W., Foux L., Bradbury W. C. Restriction endonuclease analysis of nosocomial isolates of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2168–2172. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2168-2172.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L., Sutter V. L., Citron D., Finegold S. M. Selective and differential medium for isolation of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):214–219. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.214-219.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerding D. N., Olson M. M., Peterson L. R., Teasley D. G., Gebhard R. L., Schwartz M. L., Lee J. T., Jr Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea and colitis in adults. A prospective case-controlled epidemiologic study. Arch Intern Med. 1986 Jan;146(1):95–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izard N. C., Hächler H., Grehn M., Kayser F. H. Ribotyping of coagulase-negative staphylococci with special emphasis on intraspecific typing of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):817–823. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.817-823.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S., Adelmann A., Clabots C. R., Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Recurrences of Clostridium difficile diarrhea not caused by the original infecting organism. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):340–343. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S., Clabots C. R., Linn F. V., Olson M. M., Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Nosocomial Clostridium difficile colonisation and disease. Lancet. 1990 Jul 14;336(8707):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91605-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S., Homann S. R., Bettin K. M., Quick J. N., Clabots C. R., Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Treatment of asymptomatic Clostridium difficile carriers (fecal excretors) with vancomycin or metronidazole. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Aug 15;117(4):297–302. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-4-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Gitlin S. D., Schaberg D. R., Wilson K. H., Kauffman C. A., Seo S. M., Fekety R. Acquisition of Clostridium difficile from the hospital environment. Am J Epidemiol. 1988 Jun;127(6):1289–1294. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijper E. J., Oudbier J. H., Stuifbergen W. N., Jansz A., Zanen H. C. Application of whole-cell DNA restriction endonuclease profiles to the epidemiology of Clostridium difficile-induced diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):751–753. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.751-753.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland L. V., Elmer G. W., Stamm W. E., Mulligan M. E. Correlation of immunoblot type, enterotoxin production, and cytotoxin production with clinical manifestations of Clostridium difficile infection in a cohort of hospitalized patients. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2456–2462. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2456-2462.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland L. V., Mulligan M. E., Kwok R. Y., Stamm W. E. Nosocomial acquisition of Clostridium difficile infection. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jan 26;320(4):204–210. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198901263200402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Peterson L. R., Kwok R. Y., Clabots C. R., Gerding D. N. Immunoblots and plasmid fingerprints compared with serotyping and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for typing Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):41–46. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.41-46.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Holter J. J., Shanholtzer C. J., Garrett C. R., Gerding D. N. Detection of Clostridium difficile toxins A (enterotoxin) and B (cytotoxin) in clinical specimens. Evaluation of a latex agglutination test. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Aug;86(2):208–211. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.2.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvi R. J., Ahroon W., Saunders S. S., Arnold S. A. Evoked potentials: computer-automated threshold-tracking procedure using an objective detection criterion. Ear Hear. 1987 Jun;8(3):151–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell T. L., Schaberg D. R., Fekety F. R. Bacteriophage and bacteriocin typing scheme for Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1148–1152. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1148-1152.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., LiPuma J. J., Edlind T. D. A broad-spectrum probe for molecular epidemiology of bacteria: ribosomal RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S., Holland D., O'Farrell S., Silman R. Typing scheme for Clostridium difficile: its application in clinical and epidemiological studies. Lancet. 1984 Apr 28;1(8383):935–938. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92392-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toma S., Lesiak G., Magus M., Lo H. L., Delmée M. Serotyping of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):426–428. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.426-428.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wren B., Heard S. R., Tabaqchali S. Association between production of toxins A and B and types of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Dec;40(12):1397–1401. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.12.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





