Abstract
Repetitive element sequence-based polymerase chain reaction (rep-PCR) enables the generation of DNA fingerprints which discriminate bacterial species and strains. We describe the application of whole-cell methods which allow specimens from broth cultures or colonies from agar plates to be utilized directly in the PCR mixture. The rep-PCR-generated DNA fingerprints obtained with whole-cell samples match results obtained with genomic DNA templates. Examples with different gram-negative bacteria (e.g., Citrobacter diversus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and gram-positive bacteria (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae) are demonstrated. Rapid specimen preparation methods enable rep-PCR-based fingerprinting to be completed in several hours and, therefore, allows the timely analysis of epidemiological relationships.
Full text
PDF
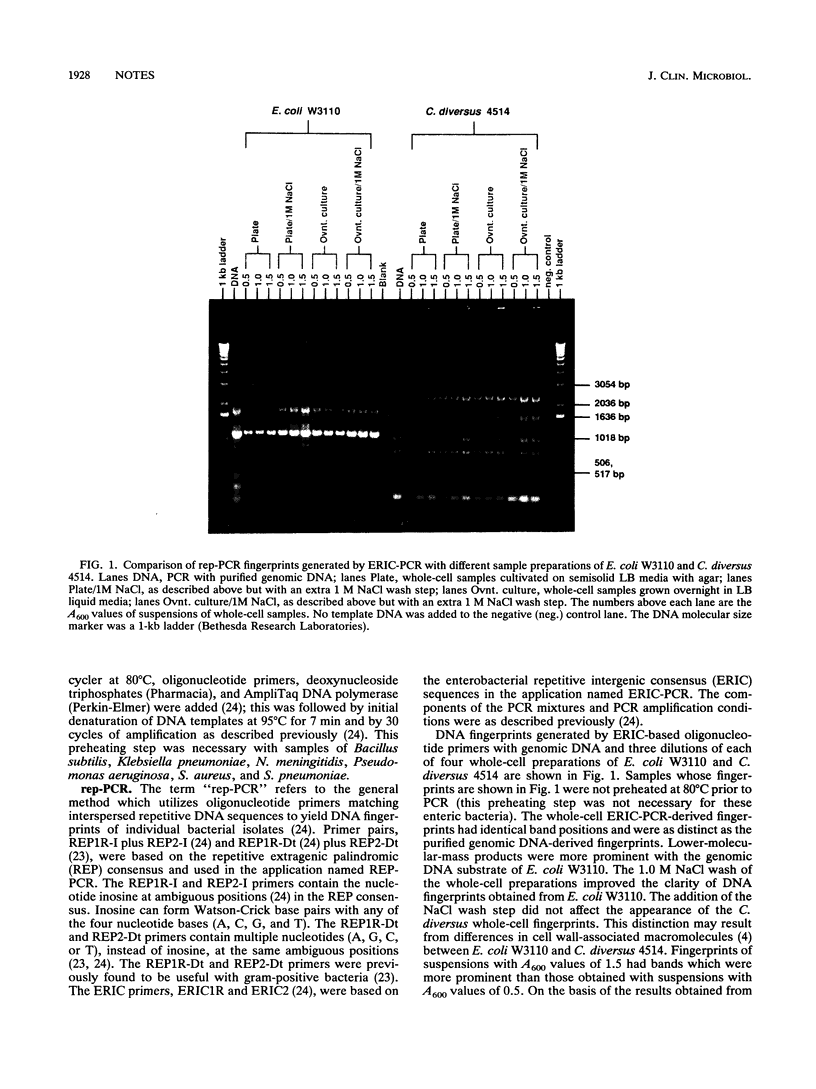
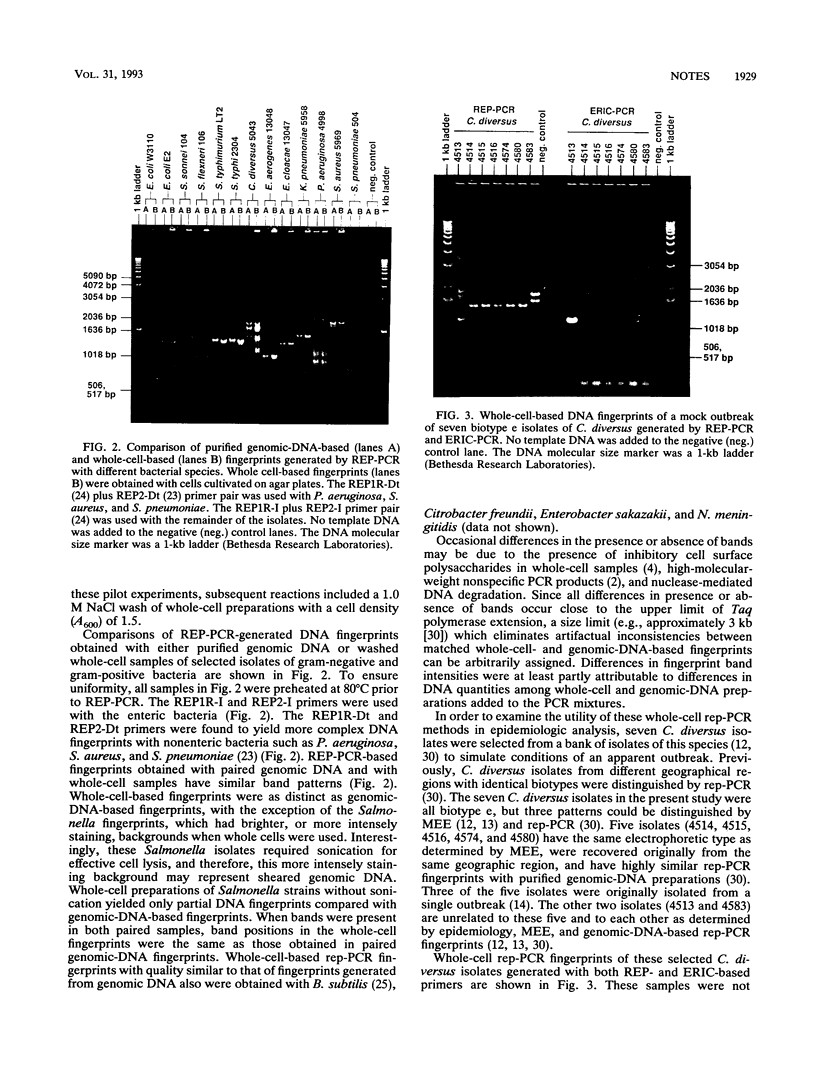


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aufauvre-Brown A., Cohen J., Holden D. W. Use of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers to distinguish isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2991–2993. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2991-2993.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell D. A., DeMarini D. M. Excessive cycling converts PCR products to random-length higher molecular weight fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):5079–5079. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.5079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domenico P., Marx J. L., Schoch P. E., Cunha B. A. Rapid plasmid DNA isolation from mucoid gram-negative bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2859–2863. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2859-2863.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkiner F. R. Epidemiological typing: a user's view. J Hosp Infect. 1988 May;11(4):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(88)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. E., Jr Molecular analysis of plasmids in epidemiologic investigation. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):1–6. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faruque S. M., Haider K., Rahman M. M., Abdul Alim A. R., Ahmad Q. S., Albert M. J., Sack R. B. Differentiation of Shigella flexneri strains by rRNA gene restriction patterns. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2996–2999. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2996-2999.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goering R. V., Ehrenkranz N. J., Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Long term epidemiological analysis of Citrobacter diversus in a neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1992 Feb;11(2):99–104. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199202000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irino K., Grimont F., Casin I., Grimont P. A. rRNA gene restriction patterns of Haemophilus influenzae biogroup aegyptius strains associated with Brazilian purpuric fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1535–1538. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1535-1538.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J. F., Jr, Twitty J. A. Plasmids as epidemiologic markers in nosocomial gram-negative bacilli: experience at a university and review of the literature. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Sep-Oct;8(5):693–704. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.5.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline M. W., Mason E. O., Jr, Kaplan S. L. Characterization of Citrobacter diversus strains causing neonatal meningitis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):101–105. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Musser J. M., Beltran P., Kline M. W., Selander R. K. Genotypic heterogeneity of strains of Citrobacter diversus expressing a 32-kilodalton outer membrane protein associated with neonatal meningitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1760–1765. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1760-1765.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. C., Devoe W. F., Morrison C., Libonati J., Powers P., Gross R. J., Rowe B., Israel E., Morris J. G., Jr Outbreak of neonatal Citrobacter diversus meningitis in a suburban hospital. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Jan;6(1):50–55. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198701000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupski J. R., Weinstock G. M. Short, interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in prokaryotic genomes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4525–4529. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4525-4529.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J., Beck A., Dayal P. A., Dawson C. Detection of genomic variation in Providencia stuartii clinical isolates by analysis of DNA restriction fragment length polymorphisms containing rRNA cistrons. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2161–2166. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2161-2166.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N., Mills S. D., Bradbury W. C. Application of serotyping and chromosomal restriction endonuclease digest analysis in investigating a laboratory-acquired case of Campylobacter jejuni enteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1427–1428. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1427-1428.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. C., Raios K., Jackson K., Dwyer B. Molecular cloning of a highly repeated DNA element from Mycobacterium tuberculosis and its use as an epidemiological tool. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):942–946. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.942-946.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versalovic J., Kapur V., Mason E. O., Jr, Shah U., Koeuth T., Lupski J. R., Musser J. M. Penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae strains recovered in Houston: identification and molecular characterization of multiple clones. J Infect Dis. 1993 Apr;167(4):850–856. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.4.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versalovic J., Koeuth T., Lupski J. R. Distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in eubacteria and application to fingerprinting of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6823–6831. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth K. Molecular epidemiology of bacterial infections: examples of methodology and of investigations of outbreaks. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Sep-Oct;8(5):682–692. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.5.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7213–7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams W. W., Mariano J., Spurrier M., Donnell H. D., Jr, Breckenridge R. L., Jr, Anderson R. L., Wachsmuth I. K., Thornsberry C., Graham D. R., Thibeault D. W. Nosocomial meningitis due to Citrobacter diversus in neonates: new aspects of the epidemiology. J Infect Dis. 1984 Aug;150(2):229–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods C. R., Jr, Versalovic J., Koeuth T., Lupski J. R. Analysis of relationships among isolates of Citrobacter diversus by using DNA fingerprints generated by repetitive sequence-based primers in the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2921–2929. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2921-2929.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods T. C., Helsel L. O., Swaminathan B., Bibb W. F., Pinner R. W., Gellin B. G., Collin S. F., Waterman S. H., Reeves M. W., Brenner D. J. Characterization of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup C by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and ribosomal DNA restriction profiles (ribotyping). J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):132–137. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.132-137.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn F. J. Use of repetitive (repetitive extragenic palindromic and enterobacterial repetitive intergeneric consensus) sequences and the polymerase chain reaction to fingerprint the genomes of Rhizobium meliloti isolates and other soil bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jul;58(7):2180–2187. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.7.2180-2187.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belkum A., Bax R., Peerbooms P., Goessens W. H., van Leeuwen N., Quint W. G. Comparison of phage typing and DNA fingerprinting by polymerase chain reaction for discrimination of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Apr;31(4):798–803. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.4.798-803.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






