Abstract
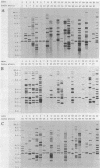
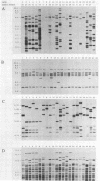
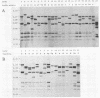
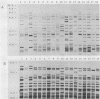
Five different genetic elements have been found to be associated with genetic rearrangements in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains. Of these elements, the insertion sequence IS6110 is presently the most frequently used genetic marker for strain differentiation of M. tuberculosis. In the present study we compared five genetic elements for their potentials to differentiate a given cluster of M. tuberculosis strains. Because of the presence of only a single copy of IS6110 or two IS6110 copies at the same chromosomal locus, a large number of strains could not be differentiated by IS6110 fingerprinting. Most strains, including the low-copy-number IS6110 strains, could be differentiated by fingerprinting with the 36-bp direct repeat or the polymorphic GC-rich repetitive DNA element. Less discriminative power was obtained with the major polymorphic tandem repeat and the insertion element IS1081. One strain which did not contain IS6110 DNA was encountered. Until now, this element has invariantly been found to be present in all M. tuberculosis complex strains. On the basis of classical taxonomic criteria and sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene, this strain was shown to be a genuine M. tuberculosis strain. Therefore, the use of this element as a target for polymerase chain reaction-facilitated detection of M. tuberculosis should be reconsidered.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck-Sagué C., Dooley S. W., Hutton M. D., Otten J., Breeden A., Crawford J. T., Pitchenik A. E., Woodley C., Cauthen G., Jarvis W. R. Hospital outbreak of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections. Factors in transmission to staff and HIV-infected patients. JAMA. 1992 Sep 9;268(10):1280–1286. doi: 10.1001/jama.1992.03490100078031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cave M. D., Eisenach K. D., McDermott P. F., Bates J. H., Crawford J. T. IS6110: conservation of sequence in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and its utilization in DNA fingerprinting. Mol Cell Probes. 1991 Feb;5(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(91)90040-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. M., Stephens D. M. Identification of an insertion sequence, IS1081, in Mycobacterium bovis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Sep 15;67(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90435-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daley C. L., Small P. M., Schecter G. F., Schoolnik G. K., McAdam R. A., Jacobs W. R., Jr, Hopewell P. C. An outbreak of tuberculosis with accelerated progression among persons infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. An analysis using restriction-fragment-length polymorphisms. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jan 23;326(4):231–235. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199201233260404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley S. W., Villarino M. E., Lawrence M., Salinas L., Amil S., Rullan J. V., Jarvis W. R., Bloch A. B., Cauthen G. M. Nosocomial transmission of tuberculosis in a hospital unit for HIV-infected patients. JAMA. 1992 May 20;267(19):2632–2634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlin B. R., Tokars J. I., Grieco M. H., Crawford J. T., Williams J., Sordillo E. M., Ong K. R., Kilburn J. O., Dooley S. W., Castro K. G. An outbreak of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among hospitalized patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jun 4;326(23):1514–1521. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199206043262302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlin B. R., Tokars J. I., Grieco M. H., Crawford J. T., Williams J., Sordillo E. M., Ong K. R., Kilburn J. O., Dooley S. W., Castro K. G. An outbreak of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among hospitalized patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jun 4;326(23):1514–1521. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199206043262302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenach K. D., Crawford J. T., Bates J. H. Repetitive DNA sequences as probes for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2240–2245. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2240-2245.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischl M. A., Uttamchandani R. B., Daikos G. L., Poblete R. B., Moreno J. N., Reyes R. R., Boota A. M., Thompson L. M., Cleary T. J., Lai S. An outbreak of tuberculosis caused by multiple-drug-resistant tubercle bacilli among patients with HIV infection. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Aug 1;117(3):177–183. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-3-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey-Faussett P., Mortimer P. R., Jenkins P. A., Stoker N. G. Evidence of transmission of tuberculosis by DNA fingerprinting. BMJ. 1992 Jul 25;305(6847):221–223. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6847.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans P. W., van Soolingen D., Bik E. M., de Haas P. E., Dale J. W., van Embden J. D. Insertion element IS987 from Mycobacterium bovis BCG is located in a hot-spot integration region for insertion elements in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2695–2705. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2695-2705.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans P. W., van Soolingen D., Dale J. W., Schuitema A. R., McAdam R. A., Catty D., van Embden J. D. Insertion element IS986 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a useful tool for diagnosis and epidemiology of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2051–2058. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2051-2058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans P. W., van Soolingen D., van Embden J. D. Characterization of a major polymorphic tandem repeat in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and its potential use in the epidemiology of Mycobacterium kansasii and Mycobacterium gordonae. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):4157–4165. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.4157-4165.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurek G. H., Cave M. D., Eisenach K. D., Wallace R. J., Jr, Bates J. H., Crawford J. T. Chromosomal DNA fingerprint patterns produced with IS6110 as strain-specific markers for epidemiologic study of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):2030–2033. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.2030-2033.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdam R. A., Hermans P. W., van Soolingen D., Zainuddin Z. F., Catty D., van Embden J. D., Dale J. W. Characterization of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis insertion sequence belonging to the IS3 family. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1607–1613. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendiola M. V., Martín C., Otal I., Gicquel B. Analysis of the regions responsible for IS6110 RFLP in a single Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain. Res Microbiol. 1992 Oct;143(8):767–772. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90104-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otal I., Martín C., Vincent-Lévy-Frebault V., Thierry D., Gicquel B. Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis using IS6110 as an epidemiological marker in tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jun;29(6):1252–1254. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.6.1252-1254.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi N., Ross B. C., Dwyer B., Goh K. S., Clavel-Sérès S., Jeantils V., Cruaud P. Emergence during unsuccessful chemotherapy of multiple drug resistance in a strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 Oct;11(10):901–907. doi: 10.1007/BF01962370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogall T., Wolters J., Flohr T., Böttger E. C. Towards a phylogeny and definition of species at the molecular level within the genus Mycobacterium. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;40(4):323–330. doi: 10.1099/00207713-40-4-323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B. C., Raios K., Jackson K., Dwyer B. Molecular cloning of a highly repeated DNA element from Mycobacterium tuberculosis and its use as an epidemiological tool. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):942–946. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.942-946.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöningh R., Verstijnen C. P., Kuijper S., Kolk A. H. Enzyme immunoassay for identification of heat-killed mycobacteria belonging to the Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium complexes and derived from early cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):708–713. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.708-713.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Nagata A., Ono Y., Yamada T. Complete nucleotide sequence of the 16S rRNA gene of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2886–2889. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2886-2889.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry D., Brisson-Noël A., Vincent-Lévy-Frébault V., Nguyen S., Guesdon J. L., Gicquel B. Characterization of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis insertion sequence, IS6110, and its application in diagnosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Dec;28(12):2668–2673. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.12.2668-2673.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdall P. A., DeYoung D. R., Roberts G. D., Anhalt J. P. Identification of clinical isolates of mycobacteria with gas-liquid chromatography: a 10-month follow-up study. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):400–402. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.400-402.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zainuddin Z. F., Dale J. W. Polymorphic repetitive DNA sequences in Mycobacterium tuberculosis detected with a gene probe from a Mycobacterium fortuitum plasmid. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Sep;135(9):2347–2355. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-9-2347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., Cave M. D., Crawford J. T., Dale J. W., Eisenach K. D., Gicquel B., Hermans P., Martin C., McAdam R., Shinnick T. M. Strain identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by DNA fingerprinting: recommendations for a standardized methodology. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):406–409. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.406-409.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., van Soolingen D., Small P. M., Hermans P. W. Genetic markers for the epidemiology of tuberculosis. Res Microbiol. 1992 May;143(4):385–391. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90051-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Soolingen D., Hermans P. W., de Haas P. E., Soll D. R., van Embden J. D. Occurrence and stability of insertion sequences in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains: evaluation of an insertion sequence-dependent DNA polymorphism as a tool in the epidemiology of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2578–2586. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2578-2586.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Soolingen D., Hermans P. W., de Haas P. E., van Embden J. D. Insertion element IS1081-associated restriction fragment length polymorphisms in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex species: a reliable tool for recognizing Mycobacterium bovis BCG. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1772–1777. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1772-1777.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]