Abstract
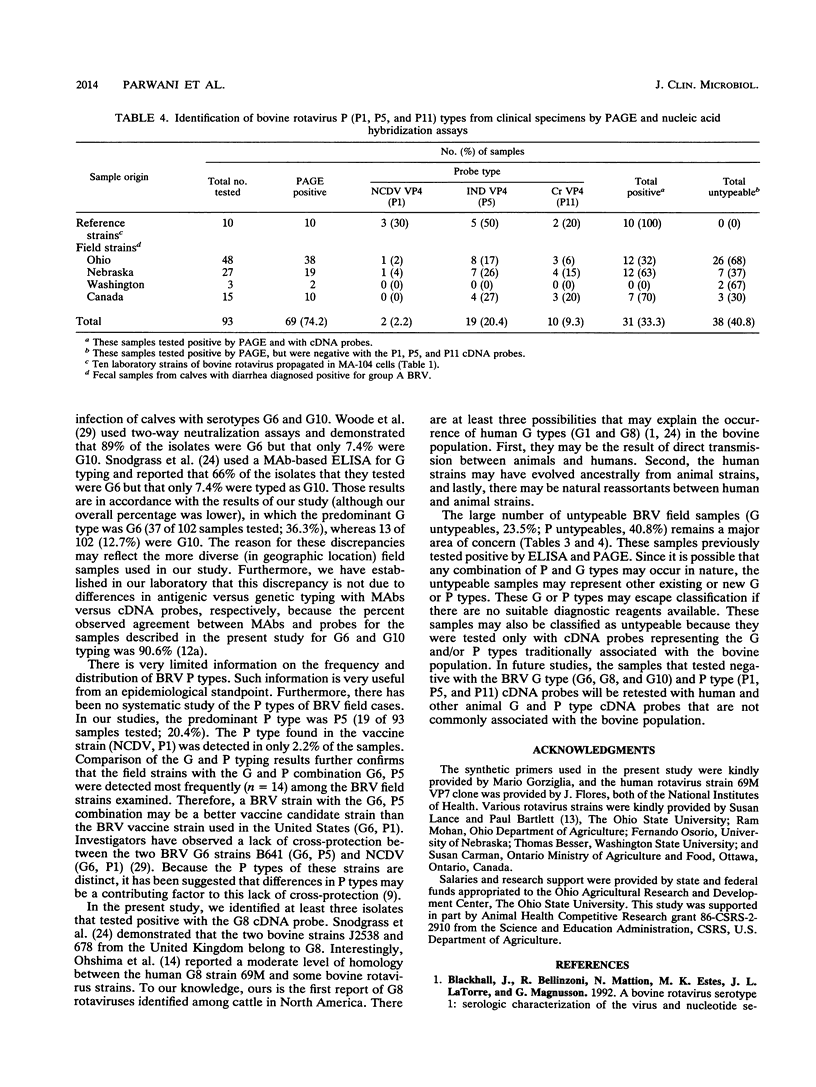
Dot and Northern blot hybridization assays were used to analyze field strains of group A bovine rotaviruses (BRVs) by using nucleic acid probes representing P and G type specificities. The probes were prepared by polymerase chain reaction amplification of hyperdivergent regions of the cloned VP4 (nucleotides 211 to 686) and VP7 (nucleotides 51 to 392) genes from four serotypically distinct (in P or G types) strains of rotaviruses: NCDV (G6, P1), IND (G6, P5), 69M (G8, P10), and Cr (G10, P11). The P and G type cDNA probes were radiolabeled with [32P]dCTP and hybridized with RNA extracted from reference cell culture-passaged rotavirus strains or the field samples. The field samples were obtained from young diarrheic calves from Ohio, Nebraska, Washington State, and Canada. The cDNA probes were specific for their respective G or P types on the basis of analysis of known P and G type reference strains. The G typing analysis of 102 field samples revealed that 36.3% (37 of 102) were G6, 2.9% (3 of 102) were G8, 12.7% (13 of 102) were G10, and 23.5% (24 of 102) were untypeable. The P typing results for 93 samples indicated that 2.2% (2 of 93) were P1 (NCDV-like), 20.4% (19 of 93) were P5 (UK-like), 9.3% (10 of 93) were P11 (B223-like), and 40.8% (38 of 93) were untypeable. This is the first report of the identification among BRV strains in North America of a G type other than G6 or G10. Our report further confirms that G6, P5 rotaviruses are predominant among the BRV field strains that we examined, and the P types of these strains differ from that of the BRV vaccine strain used in the United States (G6, P1). The large number of untypeable G (23.5%) and P (40.8%) types suggests that other or new P and G types exist among BRV field strains.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Browning G. F., Chalmers R. M., Fitzgerald T. A., Snodgrass D. R. Serological and genomic characterization of L338, a novel equine group A rotavirus G serotype. J Gen Virol. 1991 May;72(Pt 5):1059–1064. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-5-1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning G. F., Fitzgerald T. A., Chalmers R. M., Snodgrass D. R. A novel group A rotavirus G serotype: serological and genomic characterization of equine isolate FI23. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):2043–2046. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.2043-2046.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Cohen J. Rotavirus gene structure and function. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):410–449. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.410-449.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Greenberg H. B., Myslinski J., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Use of transcription probes for genotyping rotavirus reassortants. Virology. 1982 Sep;121(2):288–295. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Sears J., Schael I. P., White L., Garcia D., Lanata C., Kapikian A. Z. Identification of human rotavirus serotype by hybridization to polymerase chain reaction-generated probes derived from a hyperdivergent region of the gene encoding outer capsid protein VP7. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):4021–4024. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.4021-4024.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass R. I., Keith J., Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Askaa J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M., Flores J. Nucleotide sequence of the structural glycoprotein VP7 gene of Nebraska calf diarrhea virus rotavirus: comparison with homologous genes from four strains of human and animal rotaviruses. Virology. 1985 Mar;141(2):292–298. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90260-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy M. E., Woode G. N., Xu Z. C., Gorziglia M. Comparative amino acid sequence analysis of VP4 for VP7 serotype 6 bovine rotavirus strains NCDV, B641, and UK. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5535–5538. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5535-5538.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Serotypic similarity and diversity of rotaviruses of mammalian and avian origin as studied by plaque-reduction neutralization. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):694–702. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantharidis P., Dyall-Smith M. L., Tregear G. W., Holmes I. H. Nucleotide sequence of UK bovine rotavirus segment 4: possible host restriction of VP3 genes. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):308–315. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90501-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larralde G., Flores J. Identification of gene 4 alleles among human rotaviruses by polymerase chain reaction-derived probes. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):469–473. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90317-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchelli A., Lance S. E., Bartlett P. B., Miller G. Y., Saif L. J. Prevalence of bovine group A rotavirus shedding among dairy calves in Ohio. Am J Vet Res. 1992 Feb;53(2):169–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima A., Takagi T., Nakagomi T., Matsuno S., Nakagomi O. Molecular characterization by RNA-RNA hybridization of a serotype 8 human rotavirus with "super-short" RNA electropherotype. J Med Virol. 1990 Feb;30(2):107–112. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890300206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parwani A. V., Rosen B. I., Flores J., McCrae M. A., Gorziglia M., Saif L. J. Detection and differentiation of bovine group A rotavirus serotypes using polymerase chain reaction-generated probes to the VP7 gene. J Vet Diagn Invest. 1992 Apr;4(2):148–158. doi: 10.1177/104063879200400206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parwani A. V., Rosen B. I., McCrae M. A., Saif L. J. Development of cDNA probes for typing group A bovine rotaviruses on the basis of VP4 specificity. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2717–2721. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2717-2721.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. I., Parwani A. V., Gorziglia M., Larralde G., Saif L. J. Characterization of full-length and polymerase chain reaction-derived partial-length Gottfried and OSU gene 4 probes for serotypic differentiation of porcine rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2644–2652. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2644-2652.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. I., Saif L. J., Jackwood D. J., Gorziglia M. Hybridization probes for the detection and differentiation of two serotypes of porcine rotavirus. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Sep;24(3-4):327–339. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90181-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Redman D. R., Smith K. L., Theil K. W. Passive immunity to bovine rotavirus in newborn calves fed colostrum supplements from immunized or nonimmunized cows. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1118–1131. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1118-1131.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Fitzgerald T., Campbell I., Scott F. M., Browning G. F., Miller D. L., Herring A. J., Greenberg H. B. Rotavirus serotypes 6 and 10 predominate in cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):504–507. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.504-507.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Hoshino Y., Fitzgerald T. A., Smith M., Browning G. F., Gorziglia M. Identification of four VP4 serological types (P serotypes) of bovine rotavirus using viral reassortants. J Gen Virol. 1992 Sep;73(Pt 9):2319–2325. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-9-2319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Morita Y., Urasawa T., Urasawa S. Cross-reactive neutralization epitopes on VP3 of human rotavirus: analysis with monoclonal antibodies and antigenic variants. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1726–1730. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1726-1730.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunemitsu H., Saif L. J., Jiang B. M., Shimizu M., Hiro M., Yamaguchi H., Ishiyama T., Hirai T. Isolation, characterization, and serial propagation of a bovine group C rotavirus in a monkey kidney cell line (MA104). J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2609–2613. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2609-2613.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Kelso N. E., Simpson T. F., Gaul S. K., Evans L. E., Babiuk L. Antigenic relationships among some bovine rotaviruses: serum neutralization and cross-protection in gnotobiotic calves. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):358–364. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.358-364.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]