Abstract
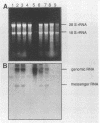
Vesicular stomatitis virus of the New Jersey serotype (VSV-NJ) causes vesicular disease in cattle, pigs, and horses throughout the Americas. Vesicular disease is clinically indistinguishable from foot-and-mouth disease (FMD). Therefore, outbreaks of vesicular disease in FMD-free areas must be rapidly diagnosed by laboratory methods and affected farms must be quarantined until laboratory results confirm the absence of FMD. Diagnosis is currently performed in high-containment (biosafety level 3) laboratories by using complement fixation and virus isolation in tissue culture. We describe here an alternative method for the detection of VSV-NJ RNA in clinical samples. This method includes a rapid acid guanidine-phenol RNA extraction procedure coupled with a one-tube polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using reverse transcriptase. By using this test, we were able to detect the largest number of positive samples (53 of 58), followed by complement (48 of 58) and isolation in tissue culture (43 of 58). The primers chosen for this assay amplify a 642-nucleotide region of the phosphoprotein gene of VSV-NJ but not of VSV-IN. Sequencing of the PCR product enables genetic typing of virus isolates and epidemiological studies. Since no infectious materials are necessary to perform this test and any infectious virus in clinical samples is destroyed by acid guanidine-phenol treatment, diagnosis can be safely performed in regular diagnostic laboratories.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad I., Finkelstein J. A., Steggles A. W. The analysis of RNA by in situ agarose gel hybridization is more sensitive than the equivalent northern blot analysis. Biotechniques. 1990 Feb;8(2):162–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilsel P. A., Rowe J. E., Fitch W. M., Nichol S. T. Phosphoprotein and nucleocapsid protein evolution of vesicular stomatitis virus New Jersey. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2498–2504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2498-2504.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodger W. J., Thurmond M., Nehay J., Mitchell J., Smith P. Economic impact of an epizootic of bovine vesicular stomatitis in California. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1985 Feb 15;186(4):370–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiroz E., Moreno N., Peralta P. H., Tesh R. B. A human case of encephalitis associated with vesicular stomatitis virus (Indiana serotype) infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Sep;39(3):312–314. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.39.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez L. L., Vernon S., Morales A. I., Letchworth G. J. Serological monitoring of vesicular stomatitis New Jersey virus in enzootic regions of Costa Rica. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Mar;42(3):272–281. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.42.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh R. B., Peralta P. H., Johnson K. M. Ecologic studies of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Prevalence of infection among animals and humans living in an area of endemic VSV activity. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Sep;90(3):255–261. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon S. D., Rodriguez L. L., Letchworth G. J. Vesicular stomatitis New Jersey virus glycoprotein gene sequence and neutralizing epitope stability in an enzootic focus. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):209–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90474-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Miyada C. G. Oligonucleotide probes for the screening of recombinant DNA libraries. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:432–442. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship P. R. An improved method for directly sequencing PCR amplified material using dimethyl sulphoxide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1266–1266. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]