Abstract
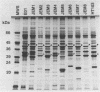
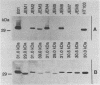
Eight spirochetal isolates (JEM1 to JEM8) were obtained from cutaneous lesions of patients with Lyme disease in Hokkaido, Japan, and were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, reactivities with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, and Southern blot hybridization. The protein profiles of these borrelial isolates were variable and differed markedly from that of Borrelia burgdorferi B31. The 41-kDa flagellin protein was present in all isolates, but the outer surface protein A that reacted with monoclonal antibody H5332 was absent from four clinical isolates (JEM1, JEM5, JEM7, and JEM8). Genomic hybridization with rRNA gene probes demonstrated the genetic divergences among those isolates. These findings indicate that the borrelial isolates from patients in Japan are quite characteristically unique.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baranton G., Postic D., Saint Girons I., Boerlin P., Piffaretti J. C., Assous M., Grimont P. A. Delineation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, Borrelia garinii sp. nov., and group VS461 associated with Lyme borreliosis. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;42(3):378–383. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-3-378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Heiland R. A., Schrumpf M. E., Tessier S. L. A Borrelia-specific monoclonal antibody binds to a flagellar epitope. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):549–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.549-554.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Todd W. J. Lyme disease spirochetes and ixodid tick spirochetes share a common surface antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):795–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.795-804.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Hayes S. F., Corwin D. Pathophysiology of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, in ixodid ticks. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Sep-Oct;11 (Suppl 6):S1442–S1450. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_6.s1442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Lane R. S., Barbour A. G., Gresbrink R. A., Anderson J. R. The western black-legged tick, Ixodes pacificus: a vector of Borrelia burgdorferi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Sep;34(5):925–930. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B. E., MacDougall J., Saint Girons I. Physical map of the linear chromosome of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi 212, a causative agent of Lyme disease, and localization of rRNA genes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3766–3774. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3766-3774.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga M., Mifuchi I. Unique organization of Leptospira interrogans rRNA genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5763–5767. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5763-5767.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga M., Sohnaka M. Tandem repeat of the 23S and 5S ribosomal RNA genes in Borrelia burgdorferi, the etiological agent of Lyme disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 31;183(3):952–957. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80282-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga M., Sohnaka M., Yanagihara Y. Analysis of Borrelia species associated with Lyme disease by rRNA gene restriction fragment length polymorphism. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Jun;139(Pt 6):1141–1146. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-6-1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga M., Yanagihara Y., Sohnaka M. The 23S/5S ribosomal RNA genes (rrl/rrf) are separate from the 16S ribosomal RNA gene (rrs) in Borrelia burgdorferi, the aetiological agent of Lyme disease. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 May;138(5):871–877. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-5-871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata M., Baba S., Iguchi K., Yamaguti N., Russell H. Lyme disease in Japan and its possible incriminated tick vector, Ixodes persulcatus. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):854–854. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo N., Arashima Y., Yoshida M., Kawabata M., Nishinarita S., Hayama T., Sawada S., Horie T., Nakao M., Miyamoto K. Questionnaire surveys of cases of tick bite and Lyme borreliosis in hunters in Hokkaido with reference to detection of anti-Borrelia burgdorferi antibody. Intern Med. 1992 Oct;31(10):1163–1168. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.31.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Garon C. F. Development of polymerase chain reaction primer sets for diagnosis of Lyme disease and for species-specific identification of Lyme disease isolates by 16S rRNA signature nucleotide analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2830–2834. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2830-2834.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto K., Nakao M., Sato N., Mori M. Isolation of Lyme disease spirochetes from an ixodid tick in Hokkaido, Japan. Acta Trop. 1991 Apr;49(1):65–68. doi: 10.1016/0001-706x(91)90031-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto K., Nakao M., Uchikawa K., Fujita H. Prevalence of Lyme borreliosis spirochetes in ixodid ticks of Japan, with special reference to a new potential vector, Ixodes ovatus (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1992 Mar;29(2):216–220. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/29.2.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao M., Miyamoto K., Kawagishi N., Hashimoto Y., Iizuka H. Comparison of Borrelia burgdorferi isolated from humans and ixodid ticks in Hokkaido, Japan. Microbiol Immunol. 1992;36(11):1189–1193. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1992.tb02121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao M., Miyamoto K., Uchikawa K., Fujita H. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi isolated from Ixodes persulcatus and Ixodes ovatus ticks in Japan. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Oct;47(4):505–511. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.47.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. J., Gazumyan A., Schwartz I. rRNA gene organization in the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3757–3765. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3757-3765.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Hardin J. A., Ruddy S., Askenase W., Andiman W. A. Erythema chronicum migrans and Lyme arthritis. The enlarging clinical spectrum. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):685–698. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., LiPuma J. J., Edlind T. D. A broad-spectrum probe for molecular epidemiology of bacteria: ribosomal RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Helmes C., Schaible U. E., Lobet Y., Moter S. E., Kramer M. D., Simon M. M. Evaluation of genetic divergence among Borrelia burgdorferi isolates by use of OspA, fla, HSP60, and HSP70 gene probes. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4856–4866. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4856-4866.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Göbel U. B., Graf B., Jauris S., Soutschek E., Schwab E., Zumstein G. An OspA serotyping system for Borrelia burgdorferi based on reactivity with monoclonal antibodies and OspA sequence analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):340–350. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.340-350.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]