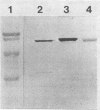
Abstract
The genes encoding the 56-kDa polypeptides were amplified by polymerase chain reaction from the genomic DNAs of three serotypes of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi, Gilliam, Karp, and Boryong. The amplified products were cloned into expression vector pIH821, and the recombinant antigens were expressed in Escherichia coli as fusion proteins with maltose-binding protein. The recombinant 56-kDa polypeptides were purified by affinity chromatography for the sensitization of sheep erythrocytes. The recombinant 56-kDa polypeptides were evaluated with 89 serum specimens from health blood donors, 94 serum specimens from scrub typhus patients, and 31 serum specimens from patients with other febrile diseases by a passive hemagglutination assay (PHA). Among the scrub typhus patients diagnosed by indirect immunofluorescent-antibody testing, the antibodies to R. tsutsugamushi were detected in 93 patients (99%). One serum specimen from a healthy person showed a false-positive reaction by this method. The recombinant PHA showed no cross-reactions with sera obtained from other febrile patients with diseases such as murine typhus, hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome, and leptospirosis. In conclusion, this recombinant PHA could be substituted for the conventional indirect immunofluorescent-antibody test and the immunoperoxidase test.
Full text
PDF

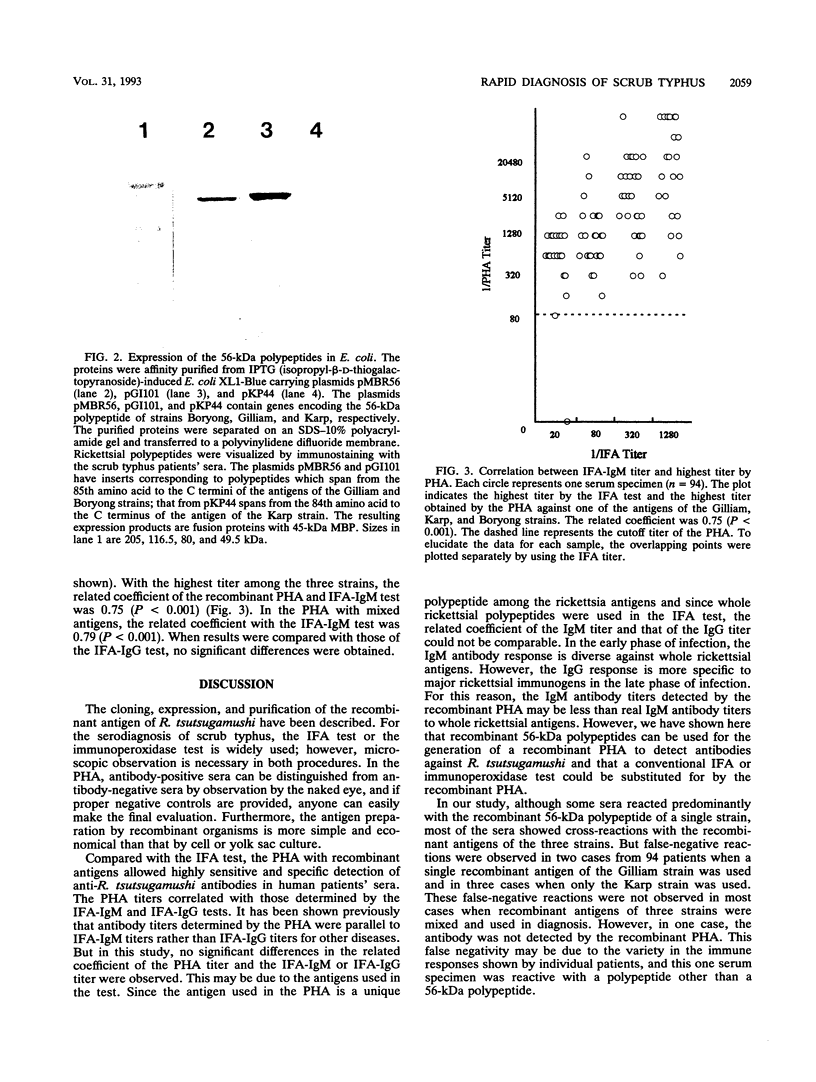

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOZEMAN F. M., ELISBERG B. L. Serological diagnosis of scrub typhus by indirect immunofluorescence. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Mar;112:568–573. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botros B. A., Soliman A. K., Darwish M., el Said S., Morrill J. C., Ksiazek T. G. Seroprevalence of murine typhus and fièvre boutonneuse in certain human populations in Egypt. J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Dec;92(6):373–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. W., Shirai A., Rogers C., Groves M. G. Diagnostic criteria for scrub typhus: probability values for immunofluorescent antibody and Proteus OXK agglutinin titers. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Sep;32(5):1101–1107. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang W. H., Kang J. S., Lee W. K., Choi M. S., Lee J. H. Serological classification by monoclonal antibodies of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi isolated in Korea. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Apr;28(4):685–688. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.4.685-688.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisemann C. S., Osterman J. V. Identification of strain-specific and group-reactive antigenic determinants on the Karp, Gilliam and Kato strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Nov;34(6):1173–1178. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuya Y., Yamamoto S., Otu M., Yoshida Y., Ohashi N., Murata M., Kawabata N., Tamura A., Kawamura A., Jr Use of monoclonal antibodies against Rickettsia tsutsugamushi Kawasaki for serodiagnosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Feb;29(2):340–345. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.2.340-345.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson B. Identification and partial characterization of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi major protein immunogens. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):603–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.603-609.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. J., Wong P. W., Gan E., Lewis G. E., Jr Comparative evaluation of the indirect immunoperoxidase test for the serodiagnosis of rickettsial disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Mar;38(2):400–406. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.38.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim I. S., Seong S. Y., Woo S. G., Choi M. S., Chang W. H. High-level expression of a 56-kilodalton protein gene (bor56) of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi Boryong and its application to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Mar;31(3):598–605. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.3.598-605.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maina C. V., Riggs P. D., Grandea A. G., 3rd, Slatko B. E., Moran L. S., Tagliamonte J. A., McReynolds L. A., Guan C. D. An Escherichia coli vector to express and purify foreign proteins by fusion to and separation from maltose-binding protein. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata M., Yoshida Y., Osono M., Ohashi N., Oyanagi M., Urakami H., Tamura A., Nogami S., Tanaka H., Kawamura A., Jr Production and characterization of monoclonal strain-specific antibodies against prototype strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(7):599–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb02987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks E. V., Rice R. M., Kelly D. J., Stover C. K. Antigenic and genetic relatedness of eight Rickettsia tsutsugamushi antigens. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3116–3122. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3116-3122.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi N., Nashimoto H., Ikeda H., Tamura A. Cloning and sequencing of the gene (tsg56) encoding a type-specific antigen from Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Gene. 1990 Jul 2;91(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90171-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi N., Tamura A., Ohta M., Hayashi K. Purification and partial characterization of a type-specific antigen of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1427–1431. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1427-1431.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi N., Tamura A., Suto T. Immunoblotting analysis of anti-rickettsial antibodies produced in patients of Tsutsugamushi disease. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(11):1085–1092. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stover C. K., Marana D. P., Carter J. M., Roe B. A., Mardis E., Oaks E. V. The 56-kilodalton major protein antigen of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi: molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the sta56 gene and precise identification of a strain-specific epitope. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2076–2084. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2076-2084.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Ohashi N., Urakami H., Takahashi K., Oyanagi M. Analysis of polypeptide composition and antigenic components of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):671–675. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.671-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Urakami H., Tsuruhara T. Purification of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi by Percoll density gradient centrifugation. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(4):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1982.tb00181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urakami H., Yamamoto S., Tsuruhara T., Ohashi N., Tamura A. Serodiagnosis of scrub typhus with antigens immobilized on nitrocellulose sheet. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1841–1846. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1841-1846.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Minamishima Y. Serodiagnosis of tsutsugamushi fever (scrub typhus) by the indirect immunoperoxidase technique. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1128–1132. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1128-1132.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Guan C., Li P., Riggs P. D., Inouye H. Vectors that facilitate the expression and purification of foreign peptides in Escherichia coli by fusion to maltose-binding protein. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]