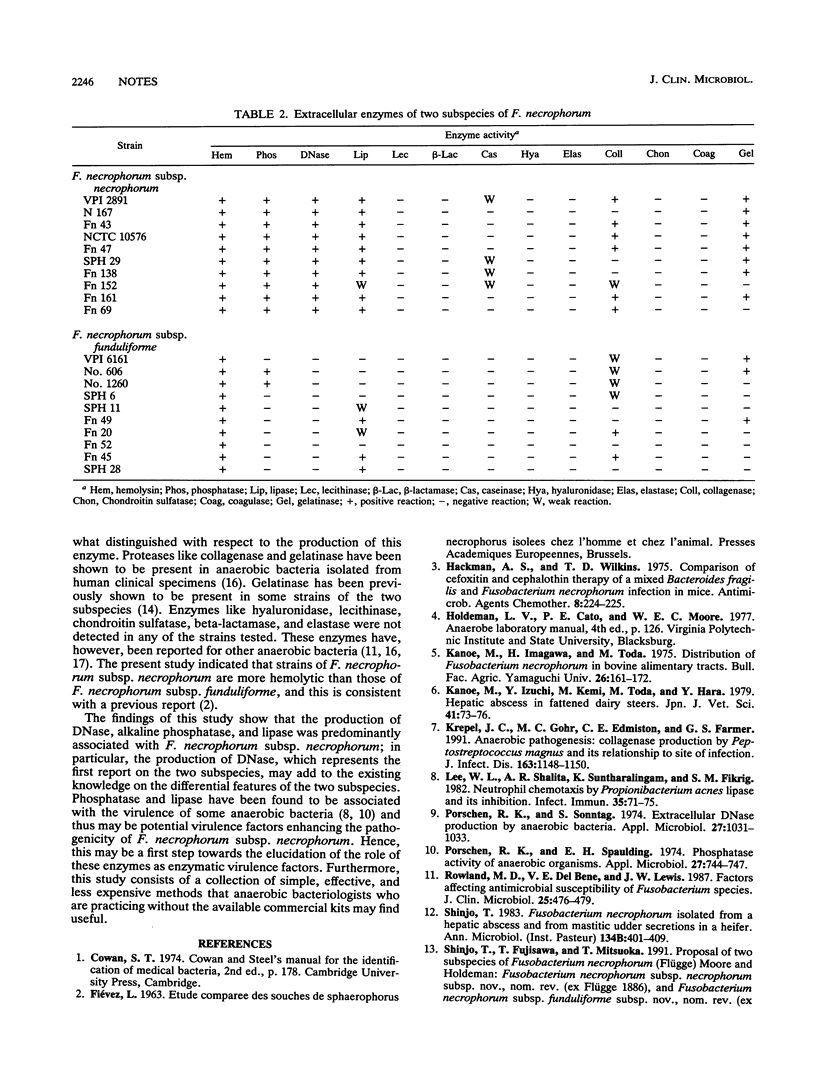
Abstract
A total of 10 strains each of Fusobacterium necrophorum subsp. necrophorum and Fusobacterium necrophorum subsp. funduliforme were tested for the production of 13 extracellular enzymes. DNase, alkaline phosphatase, and lipase were predominantly associated with all the strains of F. necrophorum subsp. necrophorum, with DNase not detected in any of the strains of F. necrophorum subsp. funduliforme. In addition, the strains of F. necrophorum subsp. necrophorum were generally more hemolytic than those of F. necrophorum subsp. funduliforme. Lecithinase, beta-lactamase, elastase, hyaluronidase, chondroitin sulfatase, and coagulase were not detected in any of the strains. DNase may be used to differentiate between the two subspecies.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hackman A. S., Wilkins T. D. Comparison of cefoxitin and cephalothin therapy of a mixed Bacteroides fragilis and Fusobacterius necrophorum infection in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Aug;8(2):224–225. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.2.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanoe M., Izuchi Y., Kemi M., Toda M., Hara Y. Hepatic abscess in fattened dairy steers. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1979 Feb;41(1):73–76. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.41.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krepel C. J., Gohr C. M., Edmiston C. E., Jr, Farmer S. G. Anaerobic pathogenesis: collagenase production by Peptostreptococcus magnus and its relationship to site of infection. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1148–1150. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. L., Shalita A. R., Suntharalingam K., Fikrig S. M. Neutrophil chemotaxis by Propionibacterium acnes lipase and its inhibition. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):71–78. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.71-78.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porschen R. K., Sonntag S. Extracellular deoxyribonuclease production by anaerobic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jun;27(6):1031–1033. doi: 10.1128/am.27.6.1031-1033.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porschen R. K., Spaulding E. H. Phosphatase activity of anaerobic organisms. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Apr;27(4):744–747. doi: 10.1128/am.27.4.744-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland M. D., Del Bene V. E., Lewis J. W. Factors affecting antimicrobial susceptibility of Fusobacterium species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):476–479. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.476-479.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinjo T. Fusobacterium necrophorum isolated from a hepatic abscess and from mastitic udder secretions in a heifer. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 Nov-Dec;134B(3):401–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinjo T., Miyazato S., Kaneuchi C., Mitsuoka T. Physiological and biochemical characteristics of Fusobacterium necrophorum biovar A and biovar B strains and their deoxyribonucleic acid homology. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1981 Apr;43(2):233–241. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.43.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F., Willett N. P. Rapid plate method for screening hyaluronidase and chondroitin sulfatase-producing microorganisms. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1434–1436. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1434-1436.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen E. K., Hentges D. J. Hydrolytic enzymes of anaerobic bacteria isolated from human infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(2):153–156. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.2.153-156.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J. The role of elastase in the differentiation of Bacteroides nodosus infections in sheep and cattle. Res Vet Sci. 1979 Jul;27(1):99–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


