Abstract
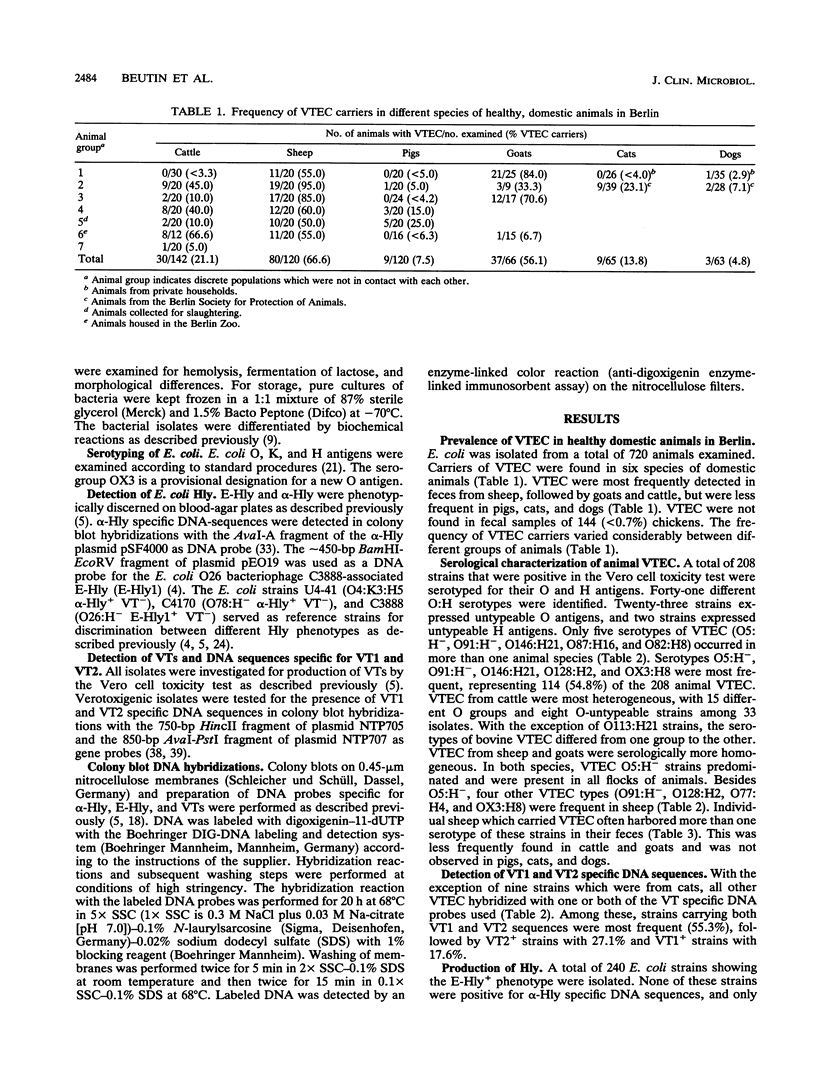
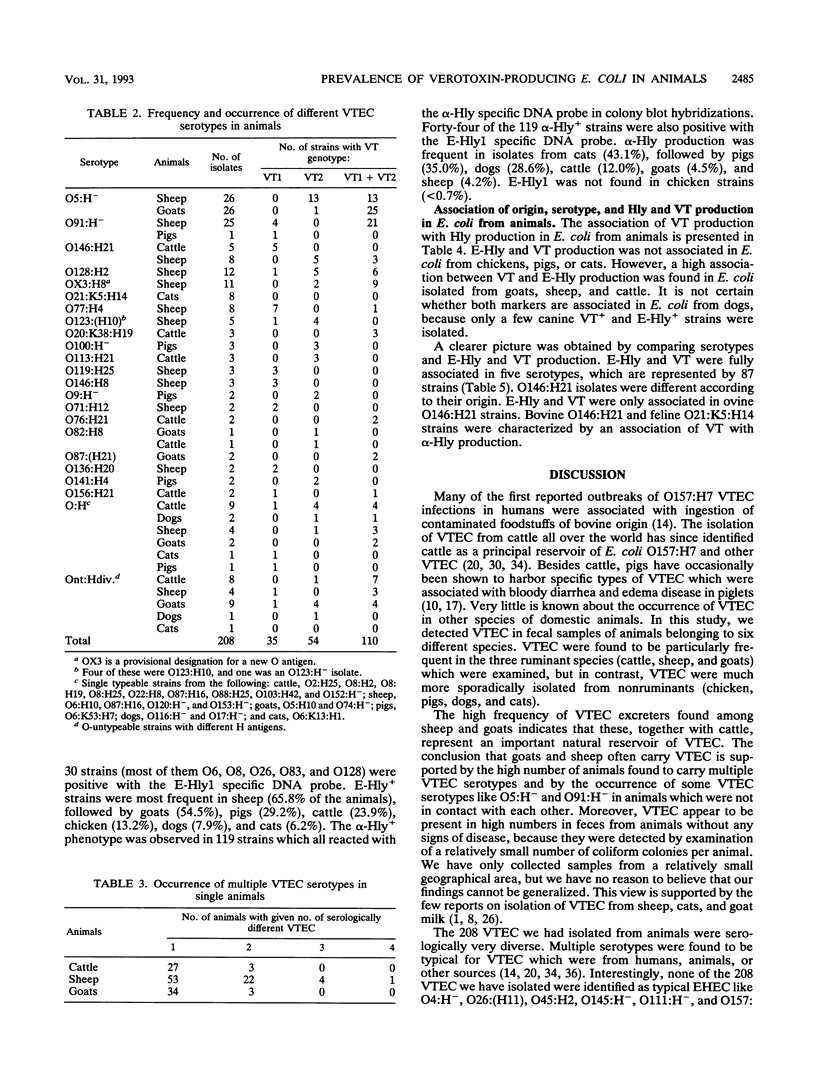
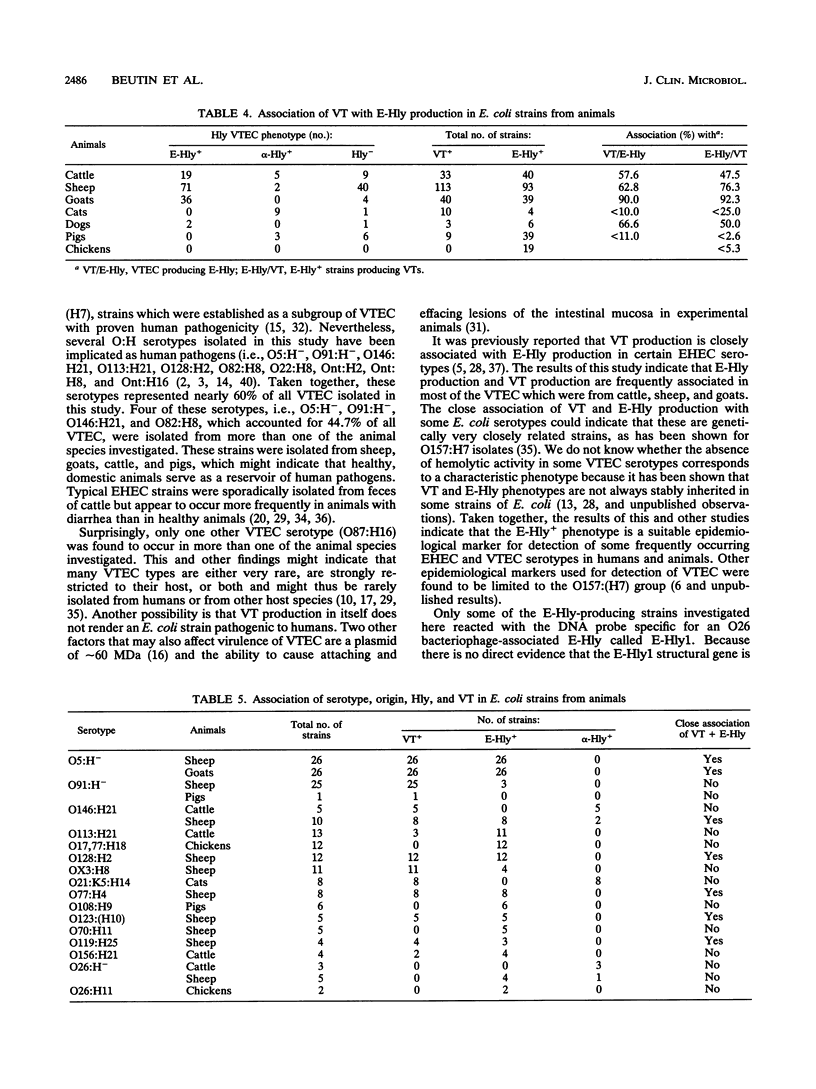
Fecal samples from 720 healthy, domestic animals representing seven different species (cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, chickens, dogs, and cats) were investigated for verotoxin (VT [Shiga-like toxin])-producing Escherichia coli (VTEC). VTEC were isolated from 208 animals (28.9%), most frequently from sheep (66.6% VTEC carriers), goats (56.1%), and cattle (21.1%). VTEC were isolated less frequently from pigs (7.5%), cats (13.8%), and dogs (4.8%) and were not found in chickens (< 0.7%). Forty-one different O:H serotypes and 23 untypeable O-groups were isolated. Five serotypes (O5:H-, O91:H-, O146:H21, O87:H16, and O82:H8) occurred in more than one animal species. Serotypes O5:H-, O91:H-, O146:H21, O128:H2, and OX3:H8 represented 54.8% of the VTEC strains. Nearly 60% of all VTEC O:H serotypes isolated in this study have been implicated as human pathogens, indicating that healthy, domestic animals may serve as a reservoir of human pathogens. All VTEC, except nine feline strains, hybridized with one or both of the VT1 and VT2 specific DNA probes. VT production and enterohemolysin (E-Hly+) production were associated in E. coli from goats, sheep, and cattle but not in E. coli from chickens, pigs, dogs, and cats. A close association of VT with E-Hly+ was found in O5:H-, O146:H21, O128:H2, O77:H4, O119:H25, and O123:(H10) strains. Thirty of 240 (12.5%) E-Hly+ strains hybridized with an E-Hly+ specific DNA probe, indicating heterogeneity of regulatory or structural E-Hly+ genes in strains of E. coli.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abaas S., Franklin A., Kühn I., Orskov F., Orskov I. Cytotoxin activity on Vero cells among Escherichia coli strains associated with diarrhea in cats. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Aug;50(8):1294–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T. J., Kaper J. B., Jerse A. E., Wachsmuth I. K. Virulence factors in Shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from humans and cattle. J Infect Dis. 1992 May;165(5):979–980. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.5.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettelheim K. A., Brown J. E., Lolekha S., Echeverria P. Serotypes of Escherichia coli that hybridized with DNA probes for genes encoding Shiga-like toxin I, Shiga-like toxin II, and serogroup O157 enterhemorrhagic E. coli fimbriae isolated from adults with diarrhea in Thailand. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):293–295. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.293-295.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutin L., Bode L., Ozel M., Stephan R. Enterohemolysin production is associated with a temperate bacteriophage in Escherichia coli serogroup O26 strains. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6469–6475. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6469-6475.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutin L., Montenegro M. A., Orskov I., Orskov F., Prada J., Zimmermann S., Stephan R. Close association of verotoxin (Shiga-like toxin) production with enterohemolysin production in strains of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2559–2564. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2559-2564.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockemühl J., Aleksić S., Karch H. Serological and biochemical properties of Shiga-like toxin (verocytotoxin)-producing strains of Escherichia coli, other than O-group 157, from patients in Germany. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1992 Jan;276(2):189–195. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn C. R. Hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome caused by Escherichia coli in people consuming undercooked beef and unpasteurized milk. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1988 Dec 1;193(11):1360–1361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn C. R., Scotland S. M., Smith H. R., Willshaw G. A., Rowe B. Properties of Vero cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli of human and animal origin belonging to serotypes other than O157:H7. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Aug;103(1):83–95. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800030387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon V. P., Gyles C. L., Friendship R. W. Characteristics of verotoxigenic Escherichia coli from pigs. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;52(3):331–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon V. P., Teerling C., Masri S. A., Gyles C. L. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of another variant of the Escherichia coli Shiga-like toxin II family. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1125–1135. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-6-1125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Meyer T. Evaluation of oligonucleotide probes for identification of shiga-like-toxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1180–1186. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1180-1186.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Meyer T., Rüssmann H., Heesemann J. Frequent loss of Shiga-like toxin genes in clinical isolates of Escherichia coli upon subcultivation. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3464–3467. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3464-3467.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A. Infection by verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):15–38. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Xu J. G., Kaper J. B., Lior H., Prado V., Tall B., Nataro J., Karch H., Wachsmuth K. A DNA probe to identify enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli of O157:H7 and other serotypes that cause hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):175–182. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linggood M. A., Thompson J. M. Verotoxin production among porcine strains of Escherichia coli and its association with oedema disease. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Dec;24(4):359–362. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-4-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montenegro M. A., Bülte M., Trumpf T., Aleksić S., Reuter G., Bulling E., Helmuth R. Detection and characterization of fecal verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli from healthy cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1417–1421. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1417-1421.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I., Villar J. A. Cattle as reservoir of verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lancet. 1987 Aug 1;2(8553):276–276. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90860-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierard D., Huyghens L., Lauwers S., Lior H. Diarrhoea associated with Escherichia coli producing porcine oedema disease verotoxin. Lancet. 1991 Sep 21;338(8769):762–762. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91487-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prada J., Zimmermann S., Stephan R., Beutin L. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms associated with alpha-hemolysin determinants are correlating with the expression of alpha-hemolysin in strains of Escherichia coli. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1992 Jan;276(2):152–164. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon R. L., Farrell I. D., Hutchison J. G., Coleman D. J., Gross R. J., Fry N. K., Rowe B., Palmer S. R. A christening party outbreak of haemorrhagic colitis and haemolytic uraemic syndrome associated with Escherichia coli O 157.H7. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Oct;103(2):249–254. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800030600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samadpour M., Liston J., Ongerth J. E., Tarr P. I. Evaluation of DNA probes for detection of Shiga-like-toxin-producing Escherichia coli in food and calf fecal samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1212–1215. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1212-1215.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt C. K., McKee M. L., O'Brien A. D. Two copies of Shiga-like toxin II-related genes common in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli strains are responsible for the antigenic heterogeneity of the O157:H- strain E32511. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1065–1073. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1065-1073.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotland S. M., Willshaw G. A., Smith H. R., Rowe B. Properties of strains of Escherichia coli O26:H11 in relation to their enteropathogenic or enterohemorrhagic classification. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1069–1074. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. R., Scotland S. M., Willshaw G. A., Wray C., McLaren I. M., Cheasty T., Rowe B. Vero cytotoxin production and presence of VT genes in Escherichia coli strains of animal origin. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Mar;134(3):829–834. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-3-829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suthienkul O., Brown J. E., Seriwatana J., Tienthongdee S., Sastravaha S., Echeverria P. Shiga-like-toxin-producing Escherichia coli in retail meats and cattle in Thailand. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):1135–1139. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.1135-1139.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Karch H., Wachsmuth K. I., Robins-Browne R. M., O'Brien A. D., Lior H., Cohen M. L., Smithers J., Levine M. M. Role of a 60-megadalton plasmid and Shiga-like toxins in the pathogenesis of infection caused by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 in gnotobiotic piglets. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3117–3125. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3117-3125.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Wachsmuth K. I., Smithers J., Jackson C. Studies in gnotobiotic piglets on non-O157:H7 Escherichia coli serotypes isolated from patients with hemorrhagic colitis. Gastroenterology. 1988 Mar;94(3):590–597. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Hull R., Falkow S. Molecular cloning and physical characterization of a chromosomal hemolysin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):178–186. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.178-186.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. G., Shipman L. D., Greene K. D., Sowers E. G., Green J. H., Cameron D. N., Downes F. P., Martin M. L., Griffin P. M., Ostroff S. M. Isolation of Escherichia coli serotype O157:H7 and other Shiga-like-toxin-producing E. coli from dairy cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):985–989. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.985-989.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam T. S., Wachsmuth I. K., Wilson R. A. Genetic evidence of clonal descent of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;157(6):1124–1133. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.6.1124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieler L. H., Bauerfeind R., Baljer G. Characterization of Shiga-like toxin producing Escherichia coli (SLTEC) isolated from calves with and without diarrhoea. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1992 Jan;276(2):243–253. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willshaw G. A., Scotland S. M., Smith H. R., Rowe B. Properties of Vero cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli of human origin of O serogroups other than O157. J Infect Dis. 1992 Oct;166(4):797–802. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.4.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willshaw G. A., Smith H. R., Scotland S. M., Field A. M., Rowe B. Heterogeneity of Escherichia coli phages encoding Vero cytotoxins: comparison of cloned sequences determining VT1 and VT2 and development of specific gene probes. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 May;133(5):1309–1317. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-5-1309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willshaw G. A., Smith H. R., Scotland S. M., Rowe B. Cloning of genes determining the production of vero cytotoxin by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Nov;131(11):3047–3053. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-11-3047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


