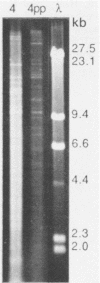
Abstract
The epidemiology of equine herpesvirus 2 was examined by using restriction endonuclease DNA fingerprints to distinguish viruses isolated from two groups of horses. The first group consisted of three yearlings isolated from other horses but in contact with each other for 418 days, whereas the second comprised seven mares and their foals, which were sampled at monthly intervals from parturition until the foals were about 180 days old. There was a complex pattern of transmission, with 15 different viruses isolated from both groups. Four distinguishable viruses were isolated from the three yearlings by day 16 of quarantine, and by day 141 an additional two viruses were isolated. Up to five different viruses were isolated from one yearling. Although four repeat isolations of one virus from the nasal cavity of one yearling over 54 days indicated that equine herpesvirus 2 established persistent infection with constant shedding, most repeat isolations yielded distinguishable viruses. Identical viruses were isolated from the nasal cavity and leukocytes of one yearling and the nasal cavity and vagina of another, indicating that a particular equine herpesvirus 2 strain was not site specific. Although seven different viruses were isolated from the three yearlings throughout the quarantine period, two appeared to establish latent infections; one virus was not isolated until 141 days after quarantine, whereas the second was first isolated 16 days after quarantine and then for the second time, from the same horse, 402 days later. Multiple concurrent local infections were demonstrated by the isolation of two or more viruses from the same nasal swab.
Full text
PDF
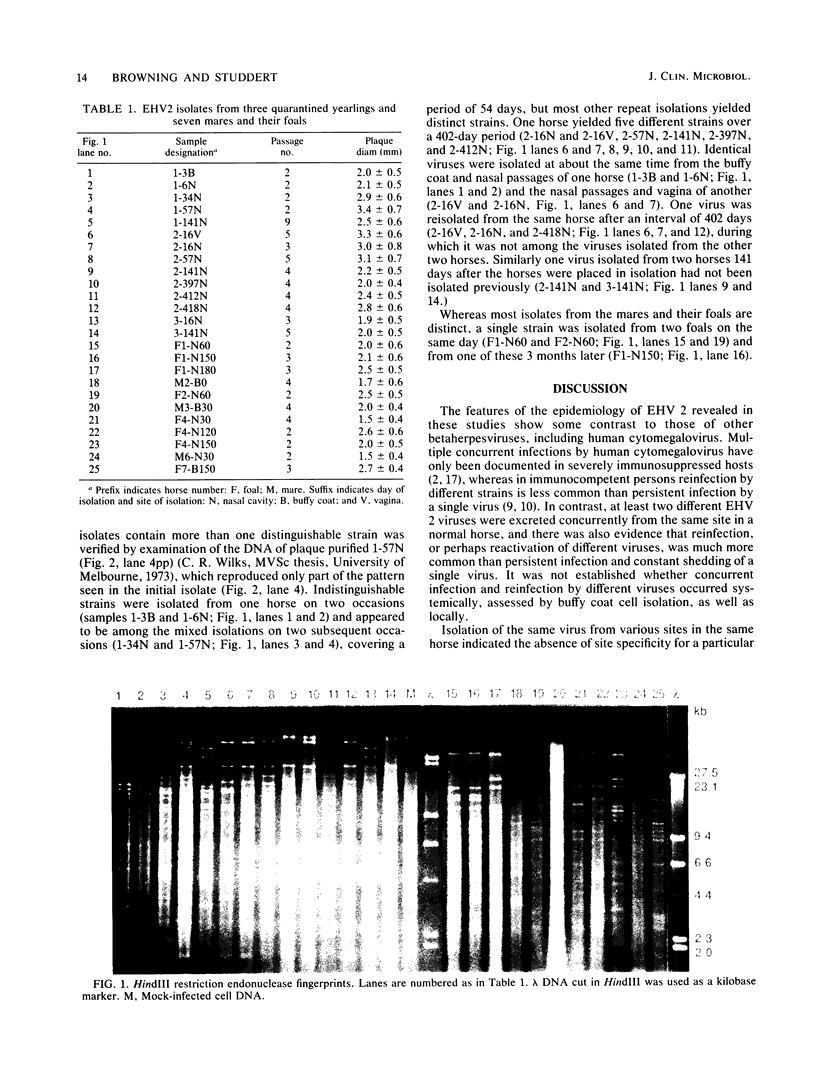


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blakeslee J. R., Jr, Olsen R. G., McAllister E. S., Fassbender J., Dennis R. Evidence of respiratory tract infection induced by equine herpesvirus, type 2, in the horse. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Dec;21(12):1940–1946. doi: 10.1139/m75-281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew W. L., Sweet E. S., Miner R. C., Mocarski E. S. Multiple infections by cytomegalovirus in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: documentation by Southern blot hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):952–953. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta S. K., Campbell D. L. Pathogenicity of equine herpesvirus: in vivo persistence in equine tissue macrophages of herpesviuus type 2 detected in monolayer macrophage cell culture. Am J Vet Res. 1978 Sep;39(9):1422–1427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta S. K., Myrup A. C. Infectious center assay of intracellular virus and infective virus titer for equine mononuclear cells infected in vivo and in vitro with equine herpesviruses. Can J Comp Med. 1983 Jan;47(1):64–69. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson L. J., Coggins L. Equine herpesvirus type 2: cell-virus relationship during persistent cell-associated viremia. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Jan;46(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson L. J., Studdert M. J. Equine herpesviruses. Experimental infection of a foetus with type 2. Aust Vet J. 1977 Aug;53(8):360–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1977.tb07951.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. J., Bagust T. J., Pascoe R. R., Spradbrow P. B. Studies on equine herpesviruses. 5. Isolation and characterisation of slowly cytopathic equine herpesviruses in Queensland. Aust Vet J. 1974 Nov;50(11):483–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1974.tb14052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiung G. D., Fischman H. R., Fong C. K., Green R. H. Characterization of a cytomegalo-like virus isolated from spontaneously degenerated equine kidney cell culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jan;130(1):80–84. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Alford C. A., Reynolds D. W., Stagno S., Pass R. F. Molecular epidemiology of cytomegalovirus infections in women and their infants. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 23;303(17):958–962. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010233031702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Huong S. M., Tegtmeier G. E., Alford C. Cytomegalovirus: genetic variation of viral genomes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:332–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemeny L., Pearson J. E. Isolation of herpesvirus from equine leukocytes: comparison with equine rhinopneumonitis virus. Can J Comp Med. 1970 Jan;34(1):59–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer G., Goodheart C. R., Studdert M. J. Equine herpesviruses: antigenic relationships and deoxyribonucleic acid densities. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):621–627. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.621-627.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder P. L., Scott G. R. The prevalence of equid herpes virus 2 infections. Vet Rec. 1975 May 3;96(18):404–405. doi: 10.1136/vr.96.18.404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. A., Hirata K. K., Newman T. R. Identification of multiple cytomegalovirus strains in homosexual men with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):953–956. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studdert M. J., Blackney M. H. Equine herpesviruses: on the differentiation of respiratory from foetal strains of type 1. Aust Vet J. 1979 Oct;55(10):488–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1979.tb00377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studdert M. J. Comparative aspects of equine herpesviruses. Cornell Vet. 1974 Jan;64(1):94–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studdert M. J. Restriction endonuclease DNA fingerprinting of respiratory, foetal and perinatal foal isolates of equine herpesvirus type 1. Arch Virol. 1983;77(2-4):249–258. doi: 10.1007/BF01309272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller T. H. The cytomegaloviruses: ubiquitous agents with protean clinical manifestations. I. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 22;285(4):203–214. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107222850406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J. H., Henry B. E., O'Callaghan D. J. Equine cytomegalovirus: cultural characteristics and properties of viral DNA. Virology. 1981 Feb;109(1):106–119. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90475-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks C. R., Studdert M. J. Equine herpesviruses. 5. Epizootiology of slowly cytopathic viruses in foals. Aust Vet J. 1974 Oct;50(10):438–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1974.tb06866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]