Abstract
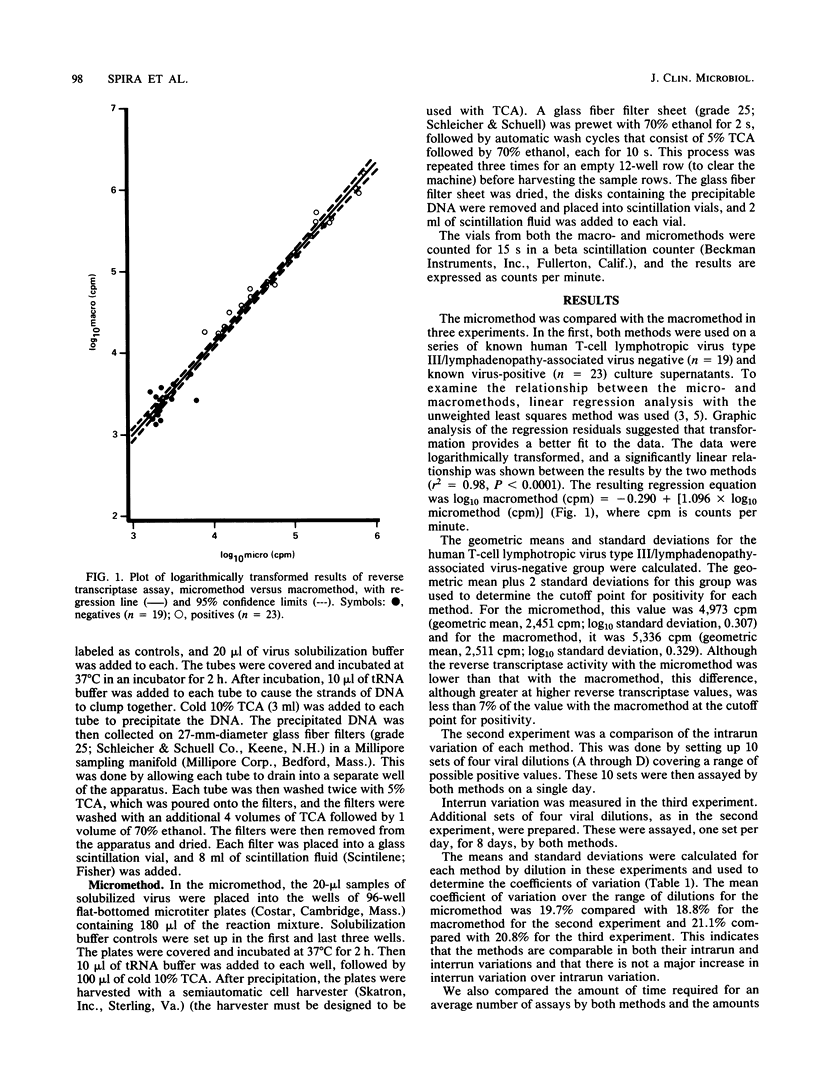
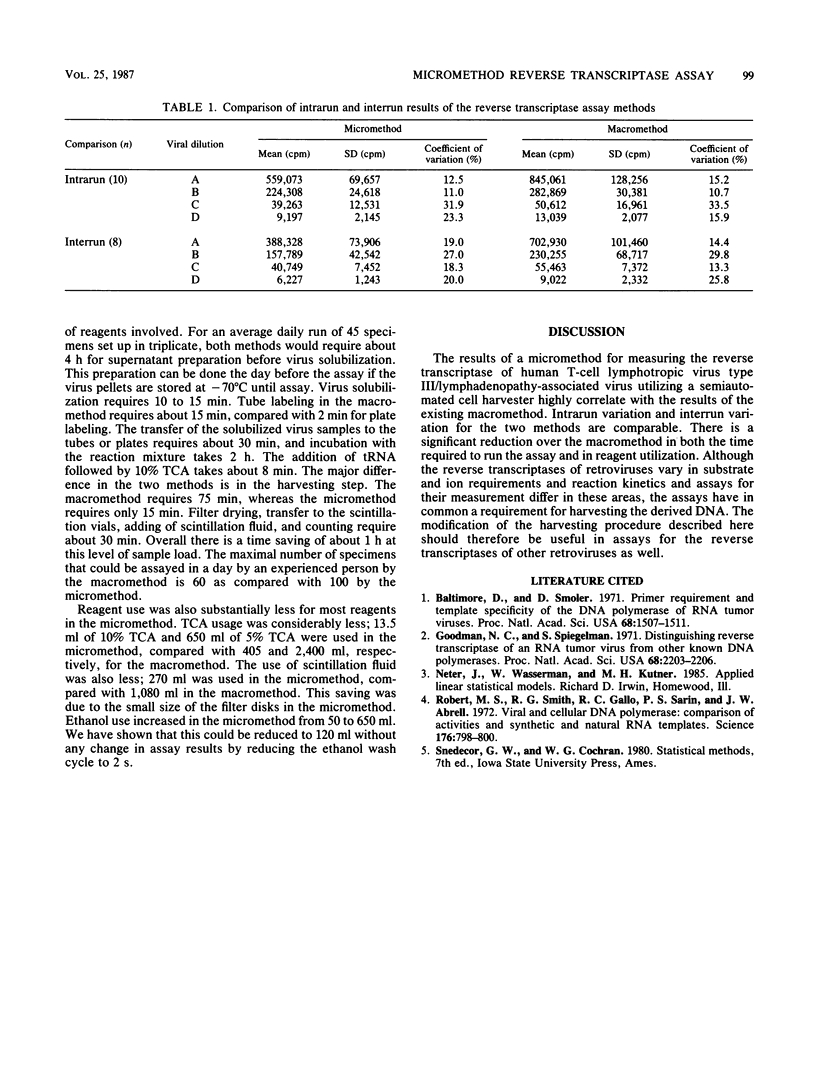
A micromethod for assaying the reverse transcriptase enzyme of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus in cocultures of clinical specimens for viral isolation was developed and compared with the macromethod in use. Ultracentrifuged, pelleted, and solubilized viral culture supernatants were transferred into either tubes (macromethod) or microtiter plates (micromethod) and incubated with tritiated enzyme substrate. Trichloroacetic acid-precipitated DNA was collected on individual filter papers with a Millipore filtration manifold (macromethod) or on filter sheets using a semiautomated cell harvester (micromethod). Filters were then placed in scintillation fluid and counted on a beta scintillation counter. Results of the micromethod significantly correlated to those of the macromethod, with a linear relationship between the two. The cutoffs for positivity based on the mean + 2 standard deviations for a set of known negative specimens (n = 19) was 4,973 cpm for the micromethod compared with 5,336 for the macromethod. The intrarun and interrun variations were comparable for both methods. There was a 67% increase in the maximal daily number of specimens which could be run (100 versus 60) as well as a reduction in reagent use. In summary, the micromethod utilizing a semiautomated cell harvester is comparable to the existing macromethod in accuracy and is an improvement due to savings in time and reagents.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D., Smoler D. Primer requirement and template specificity of the DNA polymerase of RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1507–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman N. C., Spiegelman S. Distinguishing reverse transcriptase of an RNA tumor virus from other known DNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2203–2206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert M. S., Smith R. G., Gallo R. C., Sarin P. S., Abrell J. W. Viral and cellular DNA polymerase: comparison of activities with synthetic and natural RNA templates. Science. 1972 May 19;176(4036):798–800. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4036.798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


