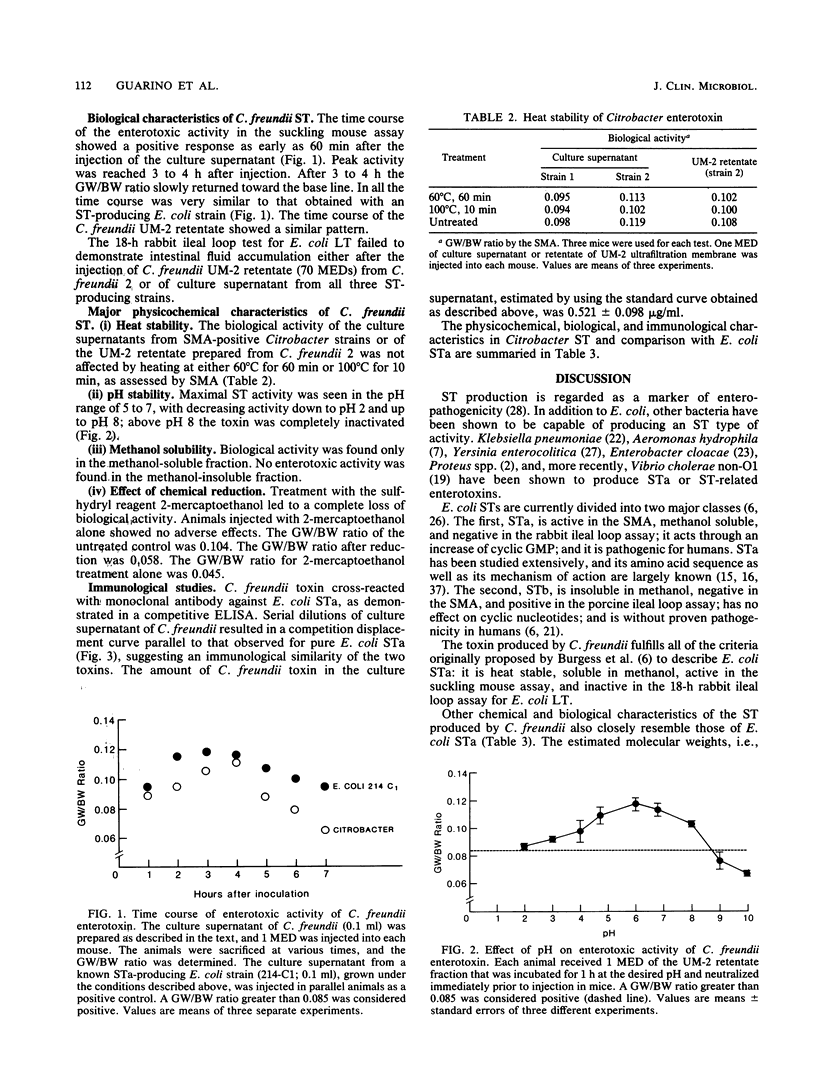
Abstract
Citrobacter species are often present in the stools of children and are generally considered a normal component of the intestinal microflora. Previous reports suggested that they might act as enteric pathogens. Aiming at defining the role of Citrobacter species in inducing diarrhea, we looked for their presence in the stools of 328 children with diarrhea and in 108 controls. Citrobacter strains were isolated from 46 patients (14%) and 7 controls (6.5%) (P less than 0.05). All isolates were tested for heat-stable (ST) and heat-labile (LT) enterotoxin. No LT-producing organisms were found. Three C. freundii strains, all isolated from children with diarrhea, elaborated an enterotoxin detected by the suckling mouse assay. A crude extract was prepared by acetone precipitation and a sequential ultrafiltration technique. The enterotoxin was heat stable, and its estimated molecular weight was between 2,000 and 10,000. Citrobacter enterotoxin was soluble in methanol and stable at acid and neutral pHs but not above pH 8, and its activity was destroyed by treatment with 2-mercaptoethanol. Citrobacter enterotoxin was inactive in the 18-h rabbit ileal loop test. All these characteristics closely resemble STa produced by Escherichia coli. The time course of Citrobacter enterotoxin-induced intestinal secretion in suckling mice was similar to that of E. coli STa. The enterotoxin produced by C. freundii cross-reacted with monoclonal antibodies raised against E. coli STa. These results suggest that C. freundii is capable of inducing diarrhea through the production of an E. coli-like STa, and its presence in the stools of patients with diarrhea should be considered as that of a possible etiologic agent.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAYLET R. J., LINHARD J. [Paracoli bethesda (Citrobacter) and Escherichia freundii in disease in Dakar]. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1959 Nov-Dec;52:723–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes L. A., Cherry W. B. A Group of Paracolon Organisms Having Apparent Pathogenicity. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1946 May;36(5):481–483. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandwein H., Deutsch A., Thompson M., Giannella R. Production of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):242–246. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.242-246.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. N., Bywater R. J., Cowley C. M., Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M. Biological evaluation of a methanol-soluble, heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin in infant mice, pigs, rabbits, and calves. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.526-531.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Gracey M., Robinson J., Peck D., Beaman J., Bundell C. The microbiology of childhood gastroenteritis: Aeromonas species and other infective agents. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):68–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butzler J. P., Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis. Clin Gastroenterol. 1979 Sep;8(3):737–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäck E., Möllby R., Kaijser B., Stintzing G., Wadström T., Habte D. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria of infantile diarrhea: surface antigens, hemagglutinins, colonization factor antigen, and loss of enterotoxigenicity. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):318–327. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capano G., Guandalini S., Guarino A., Caprioli A., Falbo V., Giraldi V., Ruggeri F. M., Vairano P., Vegnente A., Vairo U. Enteric infections, cow's milk intolerance and parenteral infections in 118 consecutive cases of acute diarrhoea in children. Eur J Pediatr. 1984 Sep;142(4):281–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00540253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Frantz J. C., Robertson D. C. Chemical properties of heat-stable enterotoxins produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of different host origins. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):539–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.539-548.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley M. V., Shotts E. B., Jr Medium for isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Aug;10(2):180–183. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.2.180-183.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Pierce N. F. Differences in the response of rabbit small intestine to heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):873–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.873-880.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin: biochemical and physiological effects on the intestine. Prog Food Nutr Sci. 1983;7(3-4):157–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Suckling mouse model for detection of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin: characteristics of the model. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.95-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R. N., Guerrant R. L. E. coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;13(3):507–531. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Dickens M. D., Wenzel R. P., Kapikian A. Z. Toxigenic bacterial diarrhea: nursery outbreak involving multiple bacterial strains. J Pediatr. 1976 Dec;89(6):885–891. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80591-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYANO M., DORFMAN R. I., YAMADA E. Y. The conversion of desoxycorticosterone to glycogenic material by adrenal homogenates. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):175–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Arita M., Takeda T., Yoh M., Miwatani T. Non-O1 Vibrio cholerae produces two newly identified toxins related to Vibrio parahaemolyticus haemolysin and Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Lancet. 1985 Jul 20;2(8447):163–164. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90277-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Arita M., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Further evaluation of the Biken test (modified Elek test) for detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli producing heat-labile enterotoxin and application of the test to sampling of heat-stable enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):60–62. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.60-62.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Taga S., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Modified Elek test for detection of heat-labile enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.1-5.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy D. J., Greenberg R. N., Dunn J. A., Abernathy R., Ryerse J. S., Guerrant R. L. Effects of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin STb on intestines of mice, rats, rabbits, and piglets. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):639–643. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.639-643.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Enterotoxigenic intestinal bacteria in tropical sprue. III. Preliminary characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae enterotoxin. J Infect Dis. 1975 Aug;132(2):200–203. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.2.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Partial purification and properties of Enterobacter cloacae heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1307–1314. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1307-1314.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Short H. B., Engert R. F., Jean L., Weaver G. A. Contamination of the small intestine by enterotoxigenic coliform bacteria among the rural population of Haiti. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jun;70(6):1035–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullan N. A., Burgess M. N., Newsome P. M. Characterization of a partially purified methanol-soluble heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin in infant mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):779–784. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.779-784.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Mors V. Production of enterotoxin by Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):908–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.908-911.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., Wachsmuth I. K., Buxton A. E., Evans D. G., DuPont H. L., Mason E., Barrett F. F. Infantile diarrhea produced by heat-stable enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 14;295(16):849–853. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610142951601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoub B. D., Greeff A. S., Lecatsas G., Prozesky O. W., Hay I. T., Prinsloo J. G., Ballard R. C. A microbiological investigation of acute summer gastroenteritis in black South African infants. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Jun;78(3):377–385. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400056278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples S. J., Asher S. E., Giannella R. A. Purification and characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a strain of E. coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4716–4721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stintzing G., Bäck E., Tufvesson B., Johnsson T., Wadström T., Habte D. Seasonal fluctuations in the occurrence of enterotoxigenic bacteria and rotavirus in paediatric diarrhoea in Addis Ababa. Bull World Health Organ. 1981;59(1):67–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stintzing G., Möllby R., Habte D. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and other enteropathogens in paediatric diarrhoea in Addis Ababa. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1982 Mar;71(2):279–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1982.tb09415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao T., Tominaga N., Yoshimura S., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Inoue T., Miyama A. Isolation, primary structure and synthesis of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Yersinia enterocolitica. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 1;152(1):199–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Yano T., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):978–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.978-985.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. R., Brandwein H., LaBine-Racke M., Giannella R. A. Simple and reliable enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal antibodies for detection of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxins. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):59–64. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.59-64.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. R., Giannella R. A. Revised amino acid sequence for a heat-stable enterotoxin produced by an Escherichia coli strain (18D) that is pathogenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):834–836. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.834-836.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Aust-Kettis A., Habte D., Holmgren J., Meeuwisse G., Möllby R., Söderlind O. Enterotoxin-producing bacteria and parasites in stools of Ethiopian children with diarrhoeal disease. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Nov;51(11):865–870. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.11.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


