Abstract
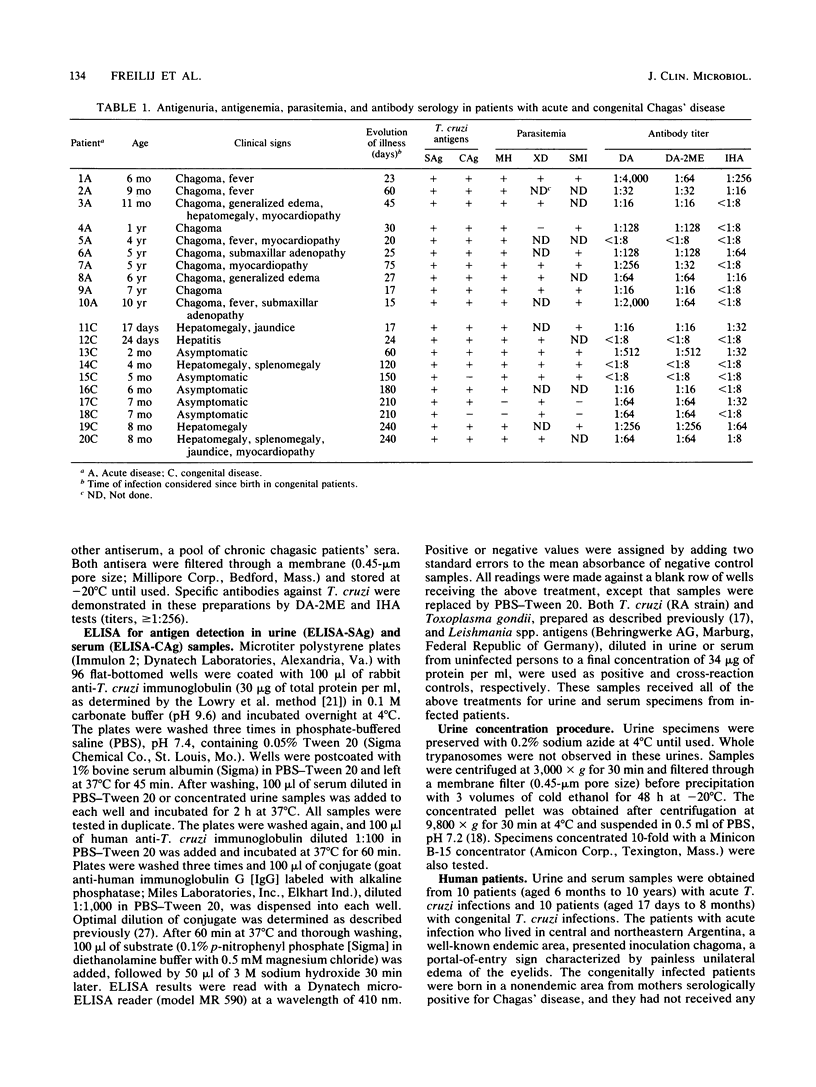
Detection and partial characterization of Trypanosoma cruzi soluble antigens (SAg) in urine, as well as demonstration of parasite circulating antigens (CAg) in serum from pediatric patients with acute (10 patients) and congenital (10 patients) Chagas' disease, are reported. Classical techniques for parasite detection and antibody serology were also conducted in both groups. Samples collected before the onset of parasiticidal drug treatment were tested by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for SAg and CAg demonstration. The control population consisted of 6 children with acute toxoplasmosis, 6 with cutaneous leishmaniasis, and 20 healthy individuals. Patients with acute cases were 100% positive for both SAg and CAg, whereas patients with congenital disease were 80% CAg positive and 100% SAg positive. Controls yielded negative results in all cases. Partial characterization of SAg from two patients with acute disease was performed by iodination, affinity chromatography, immunoprecipitation, and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Two different antigenic glycoproteins (80 kilodaltons, pI 6 to 6.5 and 55 kilodaltons, pI 6.5 to 7) were identified by these methods. Traditional serology and classical parasitologic tests failed, each in a different way, to provide an accurate diagnosis in the total of our patients. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for SAg detection proved to be the most effective procedure for achieving early and precise proof of infection in acute and congenital cases of Chagas' disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews N. W., Katzin A. M., Colli W. Mapping of surface glycoproteins of Trypanosoma cruzi by two-dimensional electrophoresis. A correlation with the cell invasion capacity. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 2;140(3):599–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araujo F. G., Chiari E., Dias J. C. Demonstration of Trypanosoma cruzi antigen in serum from patients with Chagas' disease. Lancet. 1981 Jan 31;1(8214):246–249. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araujo F. G. Detection of circulating antigens of Trypanosoma cruzi by enzyme immunoassay. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1982 Feb;76(1):25–36. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1982.11687501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltz T., Giroud C., Baltz D., Duvillier G., Degand P., Demaille J., Pautrizel R. The variable surface glycoproteins of Trypanosoma equiperdum are phosphorylated. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1393–1398. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bongertz V., Hungerer K. D., Galvão-Castro B. Trypanosoma cruzi: circulating antigens. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1981 Jan-Mar;76(1):71–82. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02761981000100008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossio P. M., Diez C., Szarfman A., Kreutzer E., Candiolo B., Arana R. M. Chagasic cardiopathy. Demonstration of a serum gamma globulin factor which reacts with endocardium and vascular structures. Circulation. 1974 Jan;49(1):13–21. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.49.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feilij H., Muller L., Gonzalez Cappa S. M. Direct micromethod for diagnosis of acute and congenital Chagas' disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):327–330. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.327-330.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González Cappa S. M., Bijovsky A. T., Freilij H., Muller L., Katzin A. M. Aislamiento de una cepa de trypanosoma cruzi a predominio de formas delgadas en la Argentina. Medicina (B Aires) 1981;41(1):119–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert G. A., Pelham P. L., Pittman B. Determination of the optimal ammonium sulfate concentration for the fractionation of rabbit, sheep, horse, and goat antisera. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jan;25(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/am.25.1.26-36.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzin A. M., Colli W. Lectin receptors in Trypanosoma cruzi. An N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-containing surface glycoprotein specific for the trypomastigote stage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 19;727(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanar D. E., Manning J. E. Major surface proteins and antigens on the different in vivo and in vitro forms of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Apr;11:119–131. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS N. R. Experimental studies on the quantitative transmission of Trypanosoma cruzi: considerations regarding the standardization of materials. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1960 Apr;54:60–70. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1960.11685957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., De Savigny D. Diagnostic serology of tropical parasitic diseases. J Immunol Methods. 1981;46(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Siqueira A. F., Filho F. F., Ribeiro R. D. Aspectos imunitários iniciais observados em ratos infectados por Trypanosoma cruzi. II. A circulaço de antígenos solúveis e as modificaçes do complemento sérico dos animais em dias sucessivos da infecço. Rev Bras Pesqui Med Biol. 1979 Apr;12(1):75–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]