Abstract
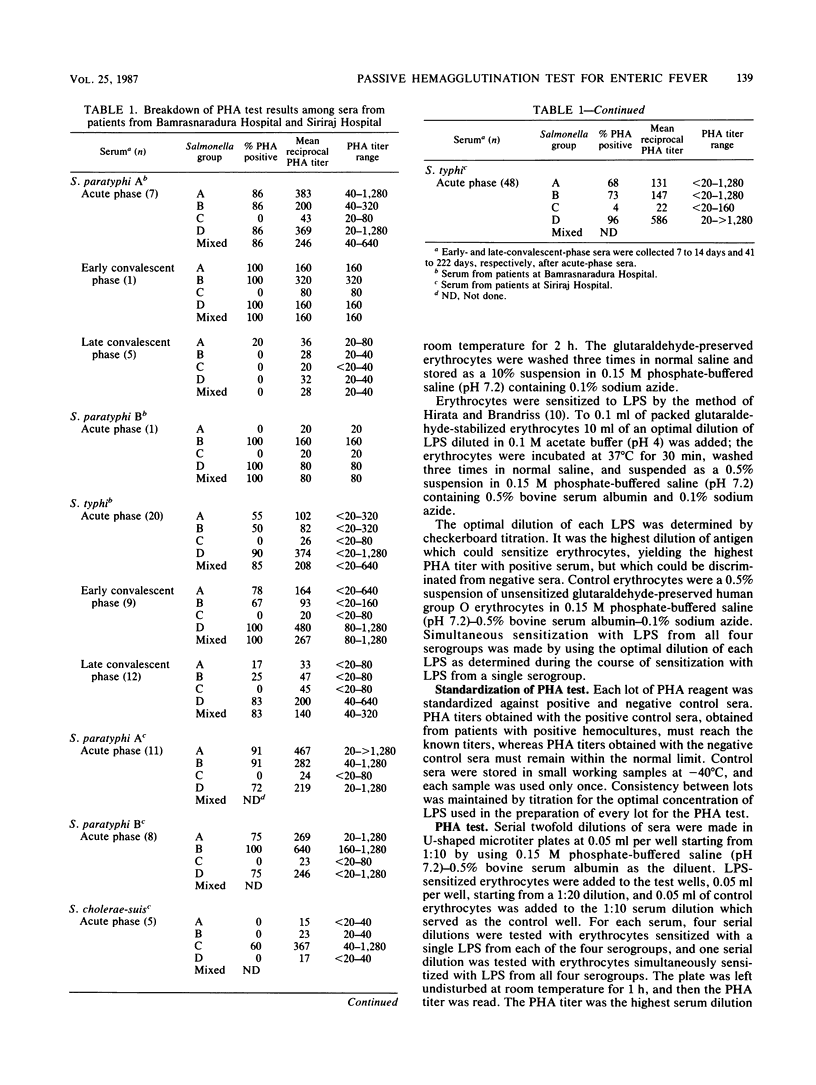
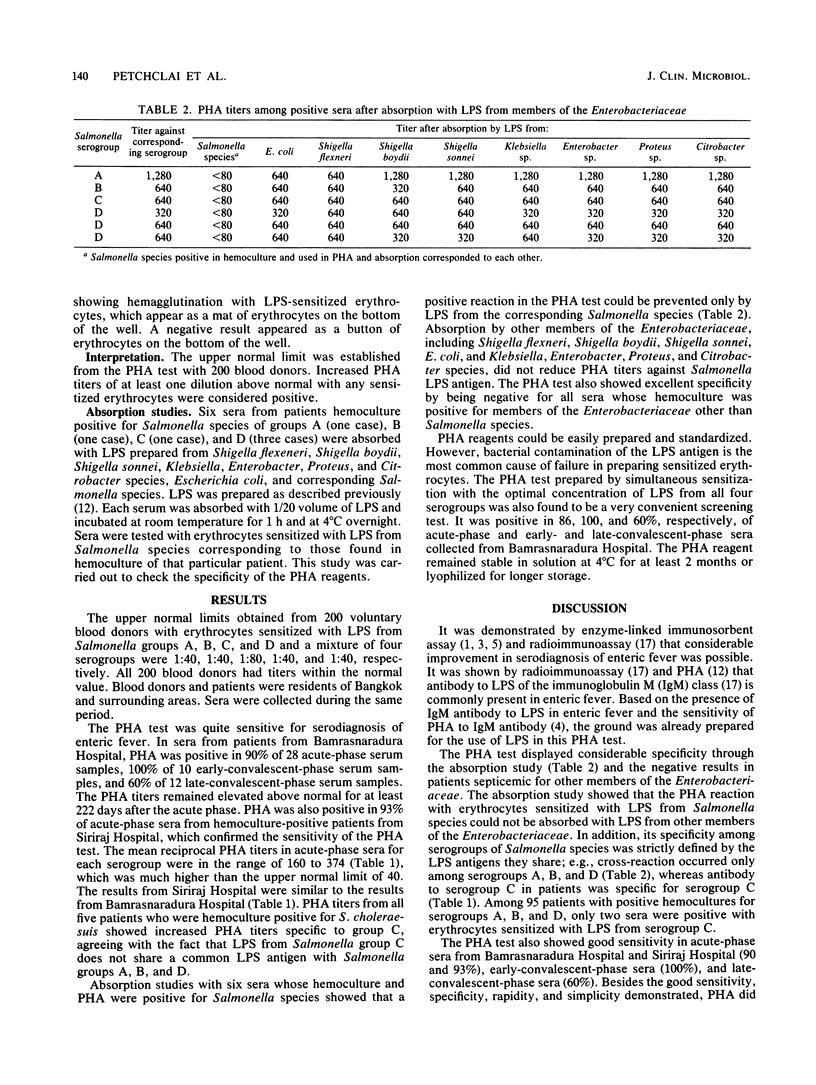
A passive hemagglutination (PHA) test for serodiagnosis of enteric fever was developed by sensitizing glutaraldehyde-preserved erythrocytes with lipopolysaccharide from Salmonella serogroups A, B, C, and D singly or simultaneously. The lipopolysaccharide-sensitized erythrocytes were tested with sera from 200 blood donors, 100 patients whose hemoculture was positive for Salmonella species, and 10 patients septicemic for other members of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The PHA test was positive in 90% of 28 acute-phase serum samples from patients with enteric fever from one hospital and in 93% of 72 acute-phase serum samples from another hospital. It was also positive in 100 and 60% of early- and late-convalescent-phase sera, respectively. The PHA test was negative in all patients septicemic for other members of the Enterobacteriaceae. Absorption of sera from patients with enteric fever with lipopolysaccharide from other members of the Enterobacteriaceae did not reduce PHA titers, indicating the specificity of the PHA test. Simultaneous sensitization with lipopolysaccharide from Salmonella serogroups A, B, C, and D was useful as a screening test in a limited trial with 28 acute-phase sera, 10 early-convalescent-phase sera, and 17 late-convalescent-phase sera. The PHA test is indeed a simple, sensitive, specific, and rapid test supplementing hemoculture in laboratory diagnosis of enteric fever.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett T. J., Blake P. A., Brown S. L., Hoffman K., Llort J. M., Feeley J. C. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of human antibodies to Salmonella typhi Vi antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):625–627. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.625-627.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsoum I. S., Awad A. Y. Microtiter plate agglutination test for Salmonella antibodies. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):425–426. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.425-426.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley W. J., Joseph S. W., Weiss E. Improved serodiagnosis of Salmonella enteric fevers by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):106–114. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.106-114.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedict A. A. Sensitivity of passive haemagglutination for assay of 7S and 19S antibodies in primary rabbit anti-bovine serum albumin sera. Nature. 1965 Jun 26;206(991):1368–1369. doi: 10.1038/2061368b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson H. E., Lindberg A. A., Hammarström S., Ljunggren A. Quantitation of Salmonella O-antibodies in human sera by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;48(4):485–494. doi: 10.1159/000231336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVillier A. B., Deupree R. H., Dickinson C., Beeler M. F. Comparative study of typhoid O antigens. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 Oct;44(4):410–412. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/44.4.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaultney J. B., Wende R. D., Williams R. P. Microagglutination procedures for febrile agglutination tests. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):635–640. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.635-640.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta A. K., Rao K. M. Simultaneous detection of Salmonella typhi antigen and antibody in serum by counter-immunoelectrophoresis for an early and rapid diagnosis of typhoid fever. J Immunol Methods. 1979;30(4):349–353. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata A. A., Brandriss M. W. Passive hemagglutination procedures for protein and polysaccharide antigens using erythrocytes stabilized by aldehydes. J Immunol. 1968 Mar;100(3):641–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Grados O., Gilman R. H., Woodward W. E., Solis-Plaza R., Waldman W. Diagnostic value of the Widal test in areas endemic for typhoid fever. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Jul;27(4):795–800. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neter E. Indirect bacterial hemagglutination, and its application to the study of bacterial antigens and serologic diagnosis. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1965;28(6):859–877. doi: 10.1159/000161853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan C. M., Feeley J. C., White P. C., Jr, Hambie E. A., Brown S. L., Wong K. H. Evaluation of a new assay for Vi antibody in chronic carriers of Salmonella typhi. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):22–26. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.22-26.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. W., Carpenter R. L., Simon W. H. Diagnostic specificity of Widal's reaction for typhoid fever. JAMA. 1970 Dec 21;214(12):2192–2193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder S. A. Interpretation of serologic tests for typhoid fever. JAMA. 1968 Oct 21;206(4):839–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Pollard R. A., Blake P. A. Typhoid in the United States and the risk to the international traveler. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):599–602. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang R. S., Chau P. Y., Lam S. K., La Brooy J. T., Rowley D. Antibody response to the lipopolysaccharide and protein antigens of Salmonella typhi during typhoid infection. I. Measurement of serum antibodies by radioimmunoassay. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Dec;46(3):508–514. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


