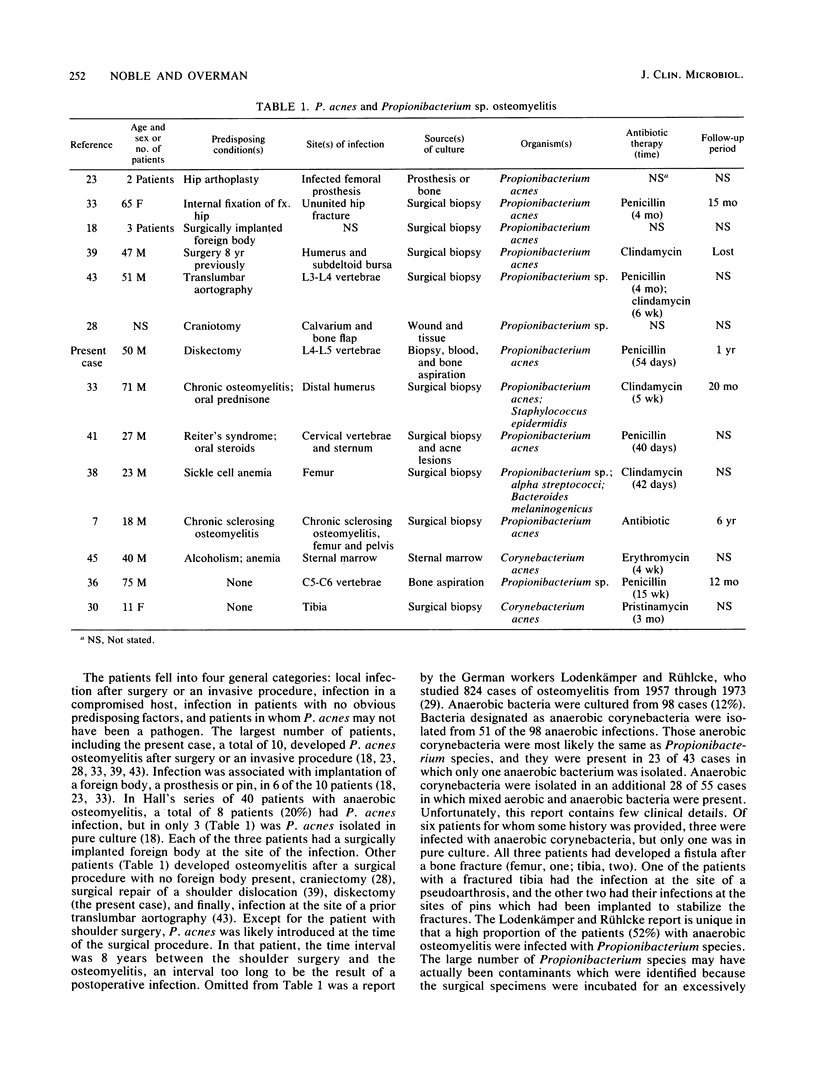
Abstract
Propionibacterium acnes, a part of the skin flora, caused vertebral osteomyelitis in a man who had recently undergone a microdiskectomy. The identifying characteristics and antibiotic susceptibility pattern are presented for this unusual human pathogen. The relationship of P. acnes to bone infection is summarized for the first time. A typical patient with P. acnes osteomyelitis is an adult male who has had prior surgery. Most patients respond favorably to prolonged antibiotic therapy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartholomew L. E., Nelson F. R. Corynebacterium acnes in rheumatoid arthritis. I. Isolation and antibody studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Jan;31(1):22–27. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler B. A., Crowder J. G., Smith J. W., White A. Propionibacterium acnes: pathogen in central nervous system shunt infection. Report of three cases including immune complex glomerulonephritis. Am J Med. 1976 Dec;61(6):935–938. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90418-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer N. S., MacCarty C. S., Wellman W. E. Brain abscess: a review of recent experience. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Apr;82(4):571–576. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-4-571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlage R. S., Ellner P. D. Comparison of the PRAS II, AN-Ident, and RapID-ANA systems for identification of anaerobic bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):32–35. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.32-35.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collert S., Isacson J. Chronic sclerosing osteomyelitis (Garré). Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982 Apr;(164):136–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cros D., Gamby T., Serratrice G. Acne rheumatism. Report of a case. J Rheumatol. 1981 Mar-Apr;8(2):336–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. I. Intracranial epidural suppuration: the occult empyema. Neurosurgery. 1982 Sep;11(3):390–394. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198209000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drulak M. W., Chow A. W. Comparative in vitro activity of ceftizoxime, cefoperazone, and cefoxitin against anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Nov;20(5):683–685. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.5.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkle L. M., Brotherton T. J., Feigin R. D. Anaerobic infections in children: a prospective study. Pediatrics. 1976 Mar;57(3):311–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edson R. S., Rosenblatt J. E., Lee D. T., McVey E. A., 3rd Recent experience with antimicrobial susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria: increasing resistance to penicillin. Mayo Clin Proc. 1982 Dec;57(12):737–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett E. D., Eickhoff T. C., Simon R. H. Cerebrospinal fluid shunt infections with anaerobic diphtheroids (Propionibacterium species). J Neurosurg. 1976 May;44(5):580–584. doi: 10.3171/jns.1976.44.5.0580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., Bartlett J. G. Anaerobic pleuropulmonary infections. Clinical considerations. Cleve Clin Q. 1975 Spring;42(1):101–111. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.42.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. H. Corynebacterium: an oral-systemic pathogen: report of cases. J Oral Surg. 1971 May;29(5):349–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E. J., Citron D. M., Finegold S. M. Role of anaerobic bacteria in bite-wound infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;6 (Suppl 1):S177–S183. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_1.s177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINEMAN H. S., BRAUDE A. I. ANAEROBIC INFECTION OF THE BRAIN. OBSERVATIONS ON EIGHTEEN CONSECUTIVE CASES OF BRAIN ABSCESS. Am J Med. 1963 Nov;35:682–697. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. B., Fitzgerald R. H., Jr, Rosenblatt J. E. Anaerobic osteomyelitis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983 Jan;65(1):30–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter L. Y., Hensinger R. N. Destructive arthritis associated with acne fulminans: a case report. Ann Rheum Dis. 1980 Aug;39(4):403–405. doi: 10.1136/ard.39.4.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsson S. Diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis of the mandible. Int J Oral Surg. 1984 Oct;13(5):363–385. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9785(84)80062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. D., Kaye D. Serious infections caused by diphtheroids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1970 Oct 30;174(2):568–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1970.tb45582.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamme C., Lidgren L., Lindberg L., Mårdh P. A. Anaerobic bacteria in late infections after total hip arthroplasty. Scand J Infect Dis. 1974;6(2):161–165. doi: 10.3109/inf.1974.6.issue-2.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K., Weinstein L. Diphtheroid infections of man. Ann Intern Med. 1969 May;70(5):919–929. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-5-919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. M., Miller M. H., Steigbigel N. H. Subdural empyema: analysis of 17 recent cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1975 Nov;54(6):485–498. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197511000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzynski T. A., Yrios J. W., Helstad A. G., Field C. R. Aerobically incubated thioglycolate broth disk method for antibiotic susceptibility testing of anaerobes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):727–732. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane JMLeyden J. J., Spiegel R. J. Acne arthralgia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976 Jul;58(5):673–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. P., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Bone infections involving anaerobic bacteria. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 Jul;57(4):279–305. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197807000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis J. J., Berard J., Cottin X., Maisonneuve J., Guillermet F. N., Larbre F. Ostéite à Corynebacterium acnes. Une observation chez l'enfant. Pediatrie. 1983 Jul-Aug;38(5):325–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrey B. F., Fitzgerald R. H., Kelly P. J., Dobyns J. H., Washington J. A., 2nd Diphtheroid osteomyelitis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977 Jun;59(4):527–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Weber C. J., Niles A. C. Comparative evaluation of three identification systems for anaerobes. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):52–55. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.52-55.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nault P., Lassonde M., St-Antoine P. Acne fulminans with osteolytic lesions. Arch Dermatol. 1985 May;121(5):662–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. H., Mitchell R. G. Diphtheroid infection of the cervical spine. Acta Orthop Scand. 1975 Apr;46(1):67–70. doi: 10.3109/17453677508989193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. P., Anderson I., Rosenthal F. D. Bone lesions in systemic acne (acne fulminans). Br J Dermatol. 1979 Jun;100(6):703–705. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1979.tb08076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton H. M., Conlan J. K., Long R. F., Waller J. T. Unusual presentation of anaerobic osteomyelitis. Am J Med. 1983 Oct;75(4):724–726. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90465-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. J., Melo J. C. Anaerobic osteomyelitis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 Jan;57(1):83–103. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197801000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serushan M., Spencer D. L., Yeh W. L., Kaminski M., Skosey J. L. Osteomyelitis of cervical spine from Propionibacterium acnes. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Mar;25(3):346–348. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton M. J. Pyogenic osteomyelitis of the vertebral body. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 1984 Jun;83(10):724–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirumoorthi M. C., Keen B. M., Dajani A. S. Anaerobic infections in children: a prospective survey. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Mar;3(3):318–323. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.3.318-323.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitzkin L. Latent corynebacterium acnes infection of bone marrow. N Engl J Med. 1969 Dec 18;281(25):1404–1405. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196912182812507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. R., Martin W. J., Wilkowske C. J., Washington J. A., 2nd Anaerobic bacteremia. Mayo Clin Proc. 1972 Sep;47(9):639–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa T. T., Chow A. W., Guze L. B. Role of anaerobic bacteria in subdural empyema. Report of four cases and review of 327 cases from the English literature. Am J Med. 1975 Jan;58(1):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90539-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



