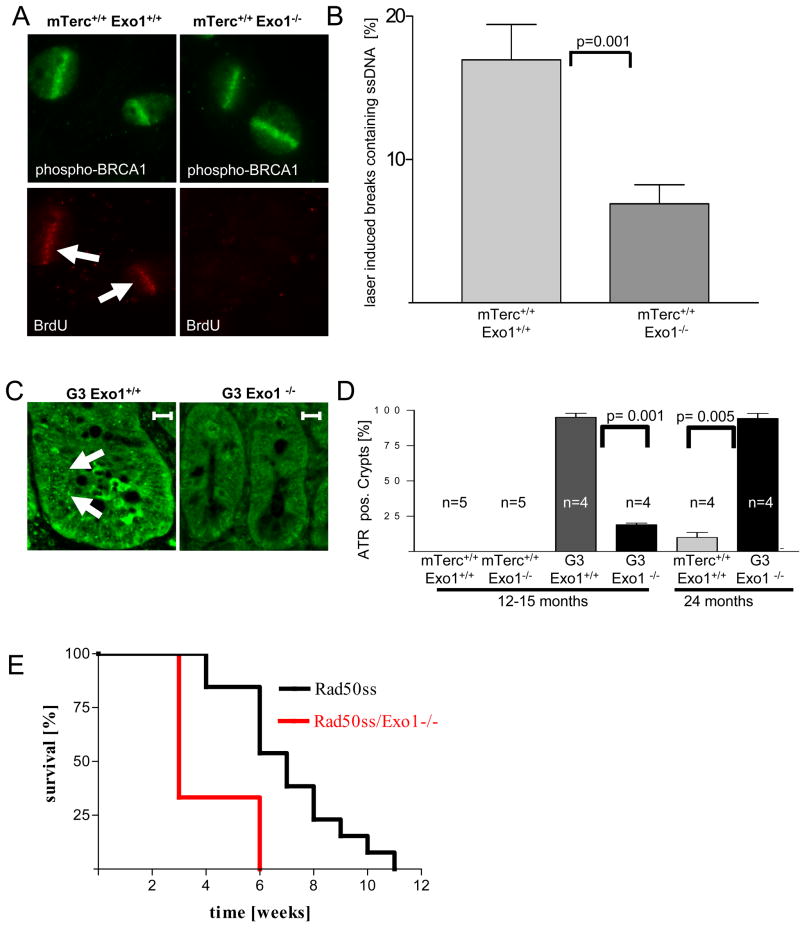
Figure 7. Exo1 deletion impairs formation of ssDNA at laser induced DNA breaks in MEFs and the formation of ATR-foci in telomere dysfunctional mice.
A) Representative photograph showing co-localization of ssDNA (stained by non-denaturing BrdU staining) and laser induced DNA breaks (stained by a phospho-BRCA1-antibody) in mTerc+/+, Exo1+/+ MEFs, but absence of such co-localization in mTerc+/+, Exo1−/− MEFs. B) Histogram showing the percentage of laser-induced DNA breaks (phospho-BRCA1) staining positive for ssDNA (non-denaturing BrdU) in MEFs of the indicated genotypes. C) Representative photograph showing γH2AX-formation and recruitment of RPA to laser induced DNA breaks in mTerc+/+, Exo1+/+ MEFs. Note that γH2AX-formation is independent of the Exo1-genotype but recruitment of RPA is reduced in mTerc+/+, Exo1−/− MEFs. D) Histogram showing the percentage of laser-induced DNA breaks staining positive for RPA in MEFs of the indicated genotypes. E) Representative photographs showing ATR-foci in nuclei of cells in basal crypts of 12–15 month old mice of the indicated genotypes (magnification bar 50 μm). F) Histogram showing the percentage of ATR positive basal crypts in 12–15 and 24 month old mice of the indicated genotypes (n= 4–5 mice/group).