Abstract
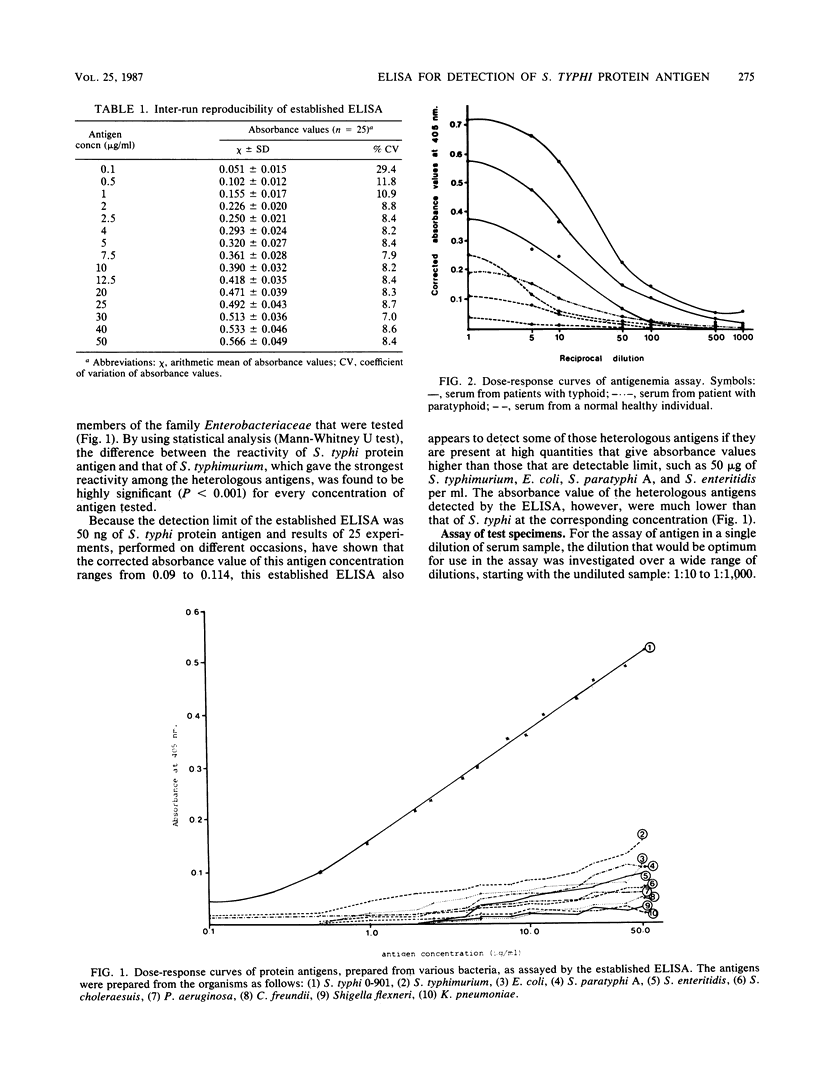
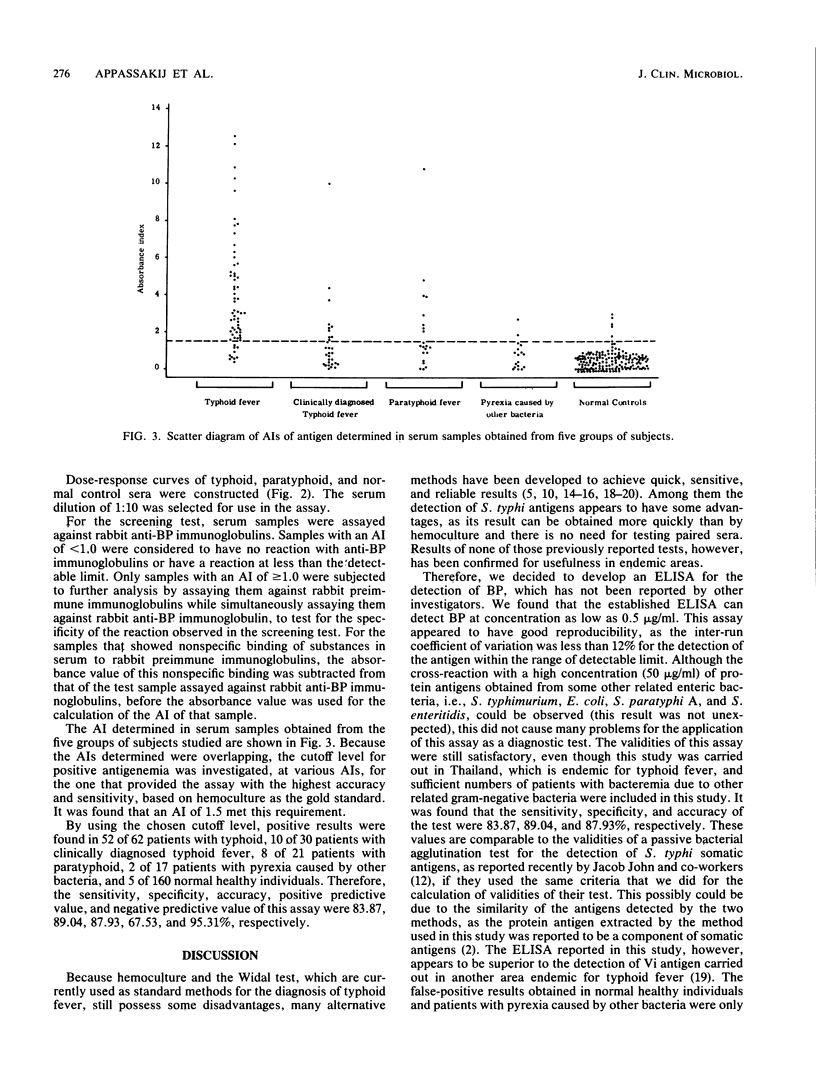
A double-antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was designed for the detection of Salmonella typhi protein antigen. The optimal concentration of antibody for coating the plate was found to be 50 micrograms/ml. The optimum conditions for antibody coating and antigen and conjugate incubation were 37 degrees C for 3 h, 37 degrees C for 2 h, and 4 degrees C overnight, respectively. The enzyme-substrate reaction was allowed to take place at 30 degrees C for 1 h. The established ELISA was found to be reproducible, with an inter-run coefficient of variation of less than 12% for the detection of an S. typhi protein antigen concentration of 0.5 to 50 micrograms/ml. The minimal detectable level of the antigen was 0.5 micrograms/ml. Cross-reactions were observed with the high level (50 micrograms/ml) of protein antigens obtained from Salmonella typhimurium, Escherichia coli, Salmonella paratyphi A, and Salmonella enteritidis. The ELISA established was used for the detection of S. typhi protein antigen in serum from 62 patients with typhoid, 30 patients with clinically diagnosed typhoid fever, 21 patients with paratyphoid, 17 patients with pyrexia caused by other bacteria, and 160 normal, healthy individuals. It was found that the sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of this assay were 83.87, 89.04, 87.93, 67.53, and 95.31%, respectively.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banchuin N., Vanadurongwan S., Sarasombath S., Sukosol T., Pimolpan V. ELISA for the measurement of intestinal antibody to Salmonella typhi protein antigen. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 1984 Jun;2(1):85–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber C., Eylan E. Cross-protection induced in mice by immunizations with proteins of related bacteria species. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1976 Jan;234(1):46–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber C., Eylan E. The serological specificities of Salmonella typhi antigens. Microbios. 1976;16(64):125–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber C., Vladoianu I. R., Dimache G. Contributions to the study of Salmonella. Immunological specificity of proteins separated from Salmonella typhi. Immunology. 1966 Oct;11(4):287–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T. J., Snyder J. D., Blake P. A., Feeley J. C. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Salmonella typhi Vi antigen in urine from typhoid patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):235–237. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.235-237.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau P. Y., Tsang R. S., Lam S. K., La Brooy J. T., Rowley D. Antibody response to the lipopolysaccharide and protein antigens of Salmonella typhi during typhoid infection. II. Measurement of intestinal antibodies by radioimmunoassay. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Dec;46(3):515–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E. Enzyme immunoassay ELISA and EMIT. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):419–439. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman R. H., Terminel M., Levine M. M., Hernandez-Mendoza P., Hornick R. B. Relative efficacy of blood, urine, rectal swab, bone-marrow, and rose-spot cultures for recovery of Salmonella typhi in typhoid fever. Lancet. 1975 May 31;1(7918):1211–1213. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92194-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta A. K., Rao K. M. Simultaneous detection of Salmonella typhi antigen and antibody in serum by counter-immunoelectrophoresis for an early and rapid diagnosis of typhoid fever. J Immunol Methods. 1979;30(4):349–353. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John T. J., Sivadasan K., Kurien B. Evaluation of passive bacterial agglutination for the diagnosis of typhoid fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):751–753. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.751-753.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Grados O., Gilman R. H., Woodward W. E., Solis-Plaza R., Waldman W. Diagnostic value of the Widal test in areas endemic for typhoid fever. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Jul;27(4):795–800. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardiello S., Pizzella T., Russo M., Galanti B. Serodiagnosis of typhoid fever by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay determination of anti-Salmonella typhi lipopolysaccharide antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):718–721. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.718-721.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockhill R. C., Rumans L. W., Lesmana M., Dennis D. T. Detection of Salmonella typhi D, Vi, and d antigens, by slide coagglutination, in urine from patients with typhoid fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Mar;11(3):213–216. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.3.213-216.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangpetchsong V., Tharavanij S. Diagnosis of typhoid fever by indirect hemagglutination with lyophilized cells. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1983 Sep;14(3):374–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senewiratne B., Senewiratne K. Reassessment of the Widal test in the diagnosis of typhoid. Gastroenterology. 1977 Aug;73(2):233–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundararaj T., Ilango B., Subramanian S. A study on the usefulness of counter immuno-electrophoresis for the detection of Salmonella typhi antigen in the sera of suspected cases of enteric fever. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(2):194–197. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90067-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Harris J. R., Barrett T. J., Hargrett N. T., Prentzel I., Valdivieso C., Palomino C., Levine M. M., Blake P. A. Detection of urinary Vi antigen as a diagnostic test for typhoid fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):872–876. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.872-876.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang R. S., Chau P. Y., Lam S. K., La Brooy J. T., Rowley D. Antibody response to the lipopolysaccharide and protein antigens of Salmonella typhi during typhoid infection. I. Measurement of serum antibodies by radioimmunoassay. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Dec;46(3):508–514. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang R. S., Chau P. Y. Serological diagnosis of typhoid fever by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 May 9;282(6275):1505–1507. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6275.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


