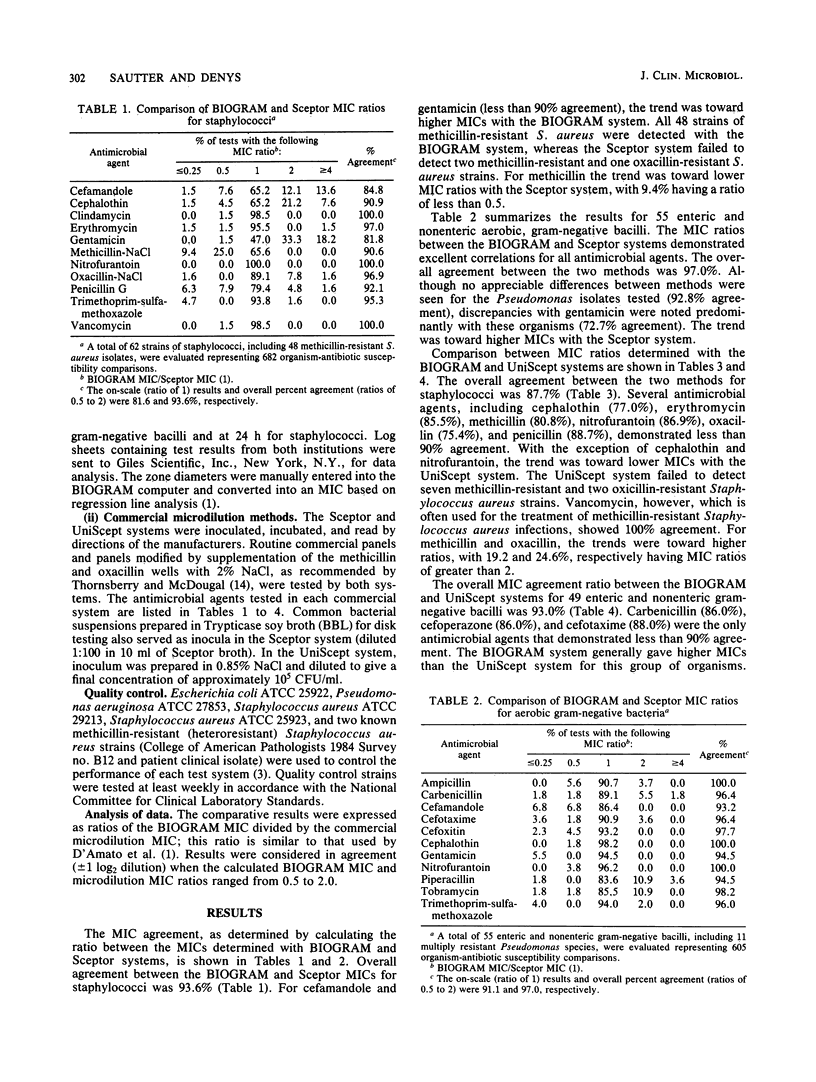
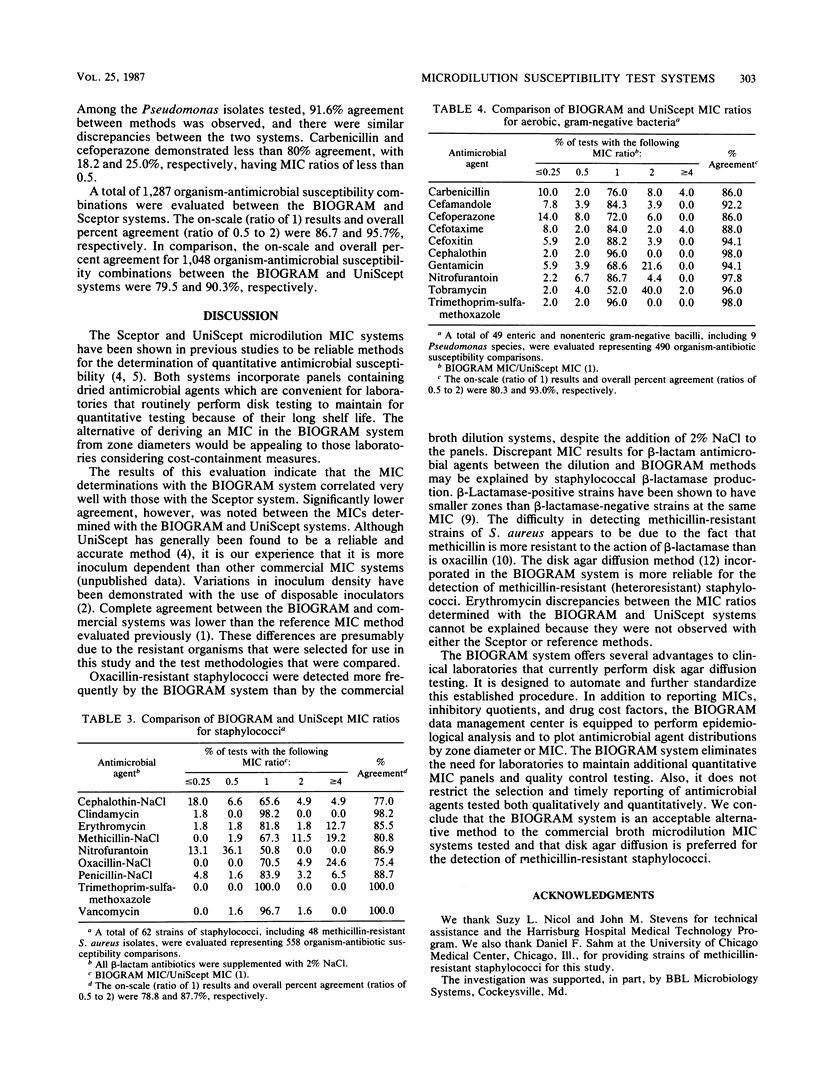
Abstract
The BIOGRAM (Difco Laboratories, Detroit, Mich.) system, which is designed to calculate MICs from disk diffusion zone diameters, was compared with two commercial microdilution antimicrobial susceptibility systems. A total of 111 clinical isolates were evaluated with each test system. Six additional isolates were tested in a comparison between BIOGRAM and Sceptor (Johnston Laboratories, Inc. Towson, Md.) systems. BIOGRAM demonstrated an overall correlation with the Sceptor microdilution method of 95.7% for 1,287 organism-antimicrobial susceptibility combinations. The BIOGRAM and UniScept (Analytab Products, Inc., Plainview, N.Y.) systems were in agreement in 90.3% of 1,048 organism-antimicrobial susceptibility combinations tested. All methicillin-resistant staphylococci were detected by the standard disk agar diffusion method used with the BIOGRAM system. The BIOGRAM system provides an acceptable alternative to these commercial systems for the determination of quantitative susceptibility.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- D'Amato R. F., Hochstein L., Vernaleo J. R., Cleri D. J., Wallman A. A., Gradus M. S., Thornsberry C. Evaluation of the BIOGRAM antimicrobial susceptibility test system. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):793–798. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.793-798.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavan T. L., Jones R. N., Barry A. L. Evaluation of the Sensititre system for quantitative antimicrobial drug susceptibility testing: a collaborative study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):464–469. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen S. L., Freedy P. K. Variation in the abilities of automated, commercial, and reference methods to detect methicillin-resistant (heteroresistant) Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):494–499. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.494-499.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg H. D., D'Amato R. F., McKinley G. A., Hochstein L., Sampson-Scherer J. Collaborative evaluation of the UniScept quantitative antimicrobial susceptibility test. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):733–735. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.733-735.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST): a review of changing trends, quality control guidelines, test accuracy, and recommendation for the testing of beta-lactam drugs. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;1(1):1–24. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(83)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M., Chambers S. Responsibility of the infectious disease community for optimal use of antibiotics: views of the membership of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jul-Aug;7(4):547–559. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsen J. M., Koepcke M. J., Quie P. G. Evaluation of the Bauer-Kirby-Sherris-Turck single-disc diffusion method of antibiotic susceptibility testing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1969;9:445–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal L. K., Thornsberry C. New recommendations for disk diffusion antimicrobial susceptibility tests for methicillin-resistant (heteroresistant) staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;19(4):482–488. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.4.482-488.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal L. K., Thornsberry C. The role of beta-lactamase in staphylococcal resistance to penicillinase-resistant penicillins and cephalosporins. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):832–839. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.832-839.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Zeitinger J. R., Krogstad D. J. Reliability of disc diffusion susceptibility testing. Infect Control. 1982 May-Jun;3(3):230–237. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700056150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., McDougal L. K. Successful use of broth microdilution in susceptibility tests for methicillin-resistant (heteroresistant) staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1084–1091. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1084-1091.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


