Abstract
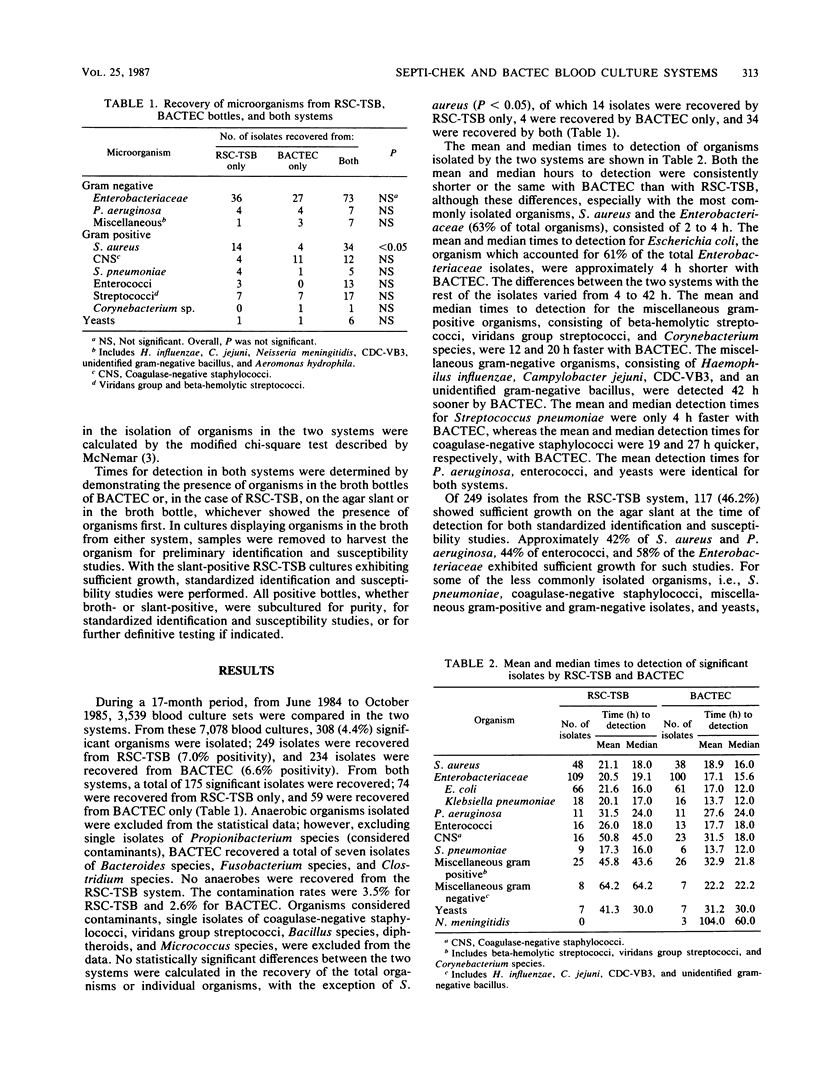
The positivity rate and time to recovery of pathogens were compared in Roche Septi-Chek (RSC-TSB) and BACTEC radiometric systems on 3,539 paired blood cultures. Both systems were steadily agitated, with frequent subculturing or processing of the RSC-TSB agar slides and BACTEC bottles, respectively, during the first 24 h of incubation. The RSC-TSB system recovered 249 pathogens (7.0% positivity rate), compared with 234 (6.6% positivity rate) isolates recovered from BACTEC. For the most common isolates, Staphylococcus aureus and the Enterobacteriaceae, the median time to detection was 15.8 h for BACTEC and 18.6 h for the RSC-TSB system. No statistically significant difference was observed in recovery of organisms from the two systems, except for S. aureus (P less than 0.05). In the RSC-TSB system, 42% of S. aureus, 58% of the Enterobacteriaceae, and 45% of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates had sufficient growth on the agar slant to allow performance of rapid standardized identification and susceptibility studies. In comparison with other studies using static incubation, it appears that agitation and frequent subculturing of the RSC-TSB system during the first 24 h of incubation decreased the time to detection for the majority of significant blood culture isolates.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryan L. E. Comparison of a slide blood culture system with a supplemented peptone broth culture method. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Oct;14(4):389–392. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.4.389-392.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry N. K., Grewell C. M., McLimans C. A., Washington J. A., 2nd Comparison of the Roche Septi-Chek blood culture bottle with a brain heart infusion biphasic medium bottle and with a tryptic soy broth bottle. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):315–317. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.315-317.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry N. K., Grewell C. M., Van Grevenhof P. E., Ilstrup D. M., Washington J. A., 2nd Comparison of lysis-centrifugation with a biphasic blood culture medium for the recovery of aerobic and facultatively anaerobic bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):413–416. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.413-416.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Sibley T. K., Westfall L. M., Hoppe-Bauer J. E., Keating M. A., Murray P. R. Clinical laboratory comparison of a slide blood culture system with a conventional broth system. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):525–530. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.525-530.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. A., Roberts F. J., Ngui-Yen J. Comparison of a radiometric and a broth-slide system for aerobic blood culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):217–218. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.217-218.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. P., Reller L. B., Mirrett S., Stratton C. W., Reimer L. G., Wang W. L. Controlled evaluation of the agar-slide and radiometric blood culture systems for the detection of bacteremia and fungemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):221–225. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.221-225.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


