Abstract
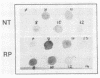
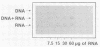
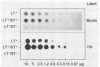
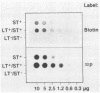
A dot blot hybridization test was developed for the detection of enterotoxigenic E. coli without the use of radioisotopes. Three biotin-labeled DNA (Bio-DNA) probes corresponding to structural genes specifying heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of porcine and human origin were prepared by random priming; label incorporation was significantly higher than that obtained from the use of nick translation. Bio-DNA probes were highly specific when reacted with protein- and RNA-free DNA preparations in a dot blot hybridization assay. The Bio-DNA probe, in which 40% of available thymidines were replaced by a biotin-labeled deoxyuridine, readily detected 160 pg of target DNA mixed with 6 micrograms of carrier DNA. The minimum amount of total DNA required for reliable identification of a single-copy enterotoxin gene of porcine origin within a 5,000-kilobase chromosome was found to be approximately 5 micrograms. Complete agreement among the results of Bio-DNA probe hybridization, [32P]DNA hybridization, and biological assay was demonstrated for 15 (100%) of the clinical isolates. This procedure provides a more suitable approach for the diagnosis of enterotoxigenic E. coli infections in clinical settings than the hybridization assay based on 32P-labeled DNA probes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bialkowska-Hobrzanska H., Gilchrist C. A., Denhardt D. T. Escherichia coli rep gene: identification of the promoter and N terminus of the rep protein. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1004-1010.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Martinez-Arias A., Shapira S. K., Chou J. Beta-galactosidase gene fusions for analyzing gene expression in escherichia coli and yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:293–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chollet A., Kawashima E. H. Biotin-labeled synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides: chemical synthesis and uses as hybridization probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1529–1541. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S. Conformity between heat-labile toxin genes from human and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):647–652. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.647-652.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., McInnes J. L., Skingle D. C., Symons R. H. Non-radioactive hybridization probes prepared by the chemical labelling of DNA and RNA with a novel reagent, photobiotin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):745–761. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyypiä T. Detection of adenovirus in nasopharyngeal specimens by radioactive and nonradioactive DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):730–733. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.730-733.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. R., Waldrop A. A., Ward D. C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6633–6637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R., Hirth P., DeWilde M., Harford N., Lecocq J. P. Cell-free synthesis of enterotoxin of E. coli from a cloned gene. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):473–474. doi: 10.1038/284473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas R., Silva R. M., Gomes T. A., Trabulsi L. R., Maas W. K. Detection of genes for heat-stable enterotoxin I in Escherichia coli strains isolated in Brazil. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):46–51. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.46-51.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Merson M. H., Sack D. A., Wells J. G., Martin W. T., Dewitt W. E., Feeley J. C., Sack R. B., Bessudo D. M. Laboratory investigation of diarrhea in travelers to Mexico: evaluation of methods for detecting enterotoxigenic Echerichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 May;3(5):486–495. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.5.486-495.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Echeverria P., Seriwatana J., Tirapat C., Chaicumpa W., Sakuldaipeara T., Falkow S. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by colony hybridization using three enterotoxin gene probes. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):863–869. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Hardy J. W., Hug M. I., Echeverria P., Falkow S. Isolation and nucleotide sequence determination of a gene encoding a heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1167–1174. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1167-1174.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Huq I., Alim A. R., So M., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):892–898. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Sack R. B. Test for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli using Y-1 adrenal cells in miniculture. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.334-336.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The relationship between two apparently different enterotoxins produced by enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli of porcine origin. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):387–401. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Dallas W. S., Falkow S. Characterization of an Escherichia coli plasmid encoding for synthesis of heat-labile toxin: molecular cloning of the toxin determinant. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):405–411. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.405-411.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., McCarthy B. J. Nucleotide sequence of the bacterial transposon Tn1681 encoding a heat-stable (ST) toxin and its identification in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4011–4015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub F., Thompson E. B. An improved method for preparing large arrays of bacterial colonies containing plasmids for hybridization: in situ purification and stable binding of DNA on paper filters. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):222–230. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Sequence of heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli pathogenic for humans. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):728–733. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.728-733.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang R., Lis J., Wu R. Elution of DNA from agarose gels after electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:176–182. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]