Abstract
Background
The single‐leg squat on a 25° decline board has been described as a clinical assessment tool and as a rehabilitation exercise for patients with patellar tendinopathy. Several assumptions have been made about its working mechanism on patellar load and patellofemoral forces, but these are not substantiated by biomechanical evaluations.
Aim
To investigate knee moment and patellofemoral contact force as a function of decline angle in the single‐leg squat.
Methods
Five subjects performed single‐leg eccentric squats at decline angles of 0°, 5°, 10°, 15°, 20° and 25° (with/without a backpack of 10 kg), and 30° on a board that was placed over a forceplate. Kinematic and forceplate data were recorded by the Optotrak system. Joint moments of ankle, knee and hip were calculated by two‐dimensional inverse dynamics.
Results
Knee moment increased by 40% at decline angles of 15° and higher, whereas hip and ankle moment decreased. Maximum knee and ankle angles increased with steeper decline. With a 10 kg backpack at 25° decline, the knee moment was 23% higher than unloaded. Both patellar tendon and patellofemoral forces increased with higher decline angles, but beyond 60°, the patellofemoral force rose steeper than the tendon force.
Conclusions
All single‐leg squats at decline angles >15° result in 40% increase in maximum patellar tendon force. In knee flexions >60°, patellofemoral forces increase more than patellar tendon forces. Higher tendon load can be achieved by the use of a backpack with extra weight.
Patellar tendinopathy is a common overuse injury, especially in jumping athletes.1 Management of patellar tendinopathy is hampered by lack of valid and reliable diagnostic and reassessment tools. Exercise‐based conservative treatment, including specific eccentric‐strengthening exercises, is considered to be useful in a rehabilitation programme in patients with patellar tendinopathy.2,3,4
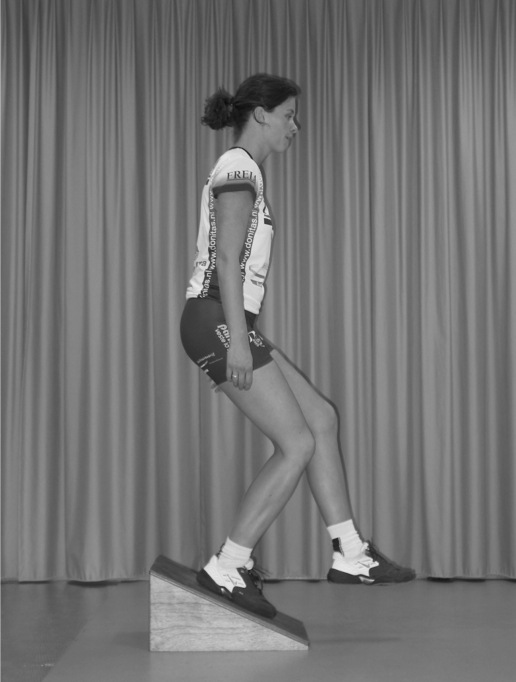
The single‐leg squat performed on a decline board (fig 1) has been described as a method to maximally load the knee extensors in an eccentric manner. This functional test is considered as a useful clinical assessment tool for patients with patellar tendinopathy.5,6 Furthermore, it is used as an easy and effective rehabilitation exercise for patients with patellar tendinopathy.7,8,9 Both Purdam et al8 and Young et al9 hypothesised that the superior effectiveness of the eccentric decline squat, compared to a normal eccentric squat on a flat floor, may be the result of the fact that standing in the decline position reduces the contribution of the calf to the squat. In this way, knee extensors and the patellar tendon are maximally loaded. Indeed, in a recent study, Kongsgaard et al10 demonstrated that the use of a 25° decline board increases the load and the strain of the patellar tendon during a single‐leg squat. However, this could not be explained by a decreased calf muscle activity, assessed by surface electromyography (EMG). Joint stop angles of ankle and hip changed significantly. They assumed that the less‐flexed ankle and hip joints during the decline squat displaces the body's centre of mass further behind the knee joint axis, thereby increasing the knee extensor moment and thereby the load on the patellar tendon. Moreover, it is also unclear why a decline angle of 25° is considered to be the most effective.
Figure 1 Eccentric decline squat (informed consent was obtained for publication of this figure).
Based on the results of previous biomechanical studies,11,12 Purdam et al6 recommended not to flex the knee over 50–60° during the decline squat in order to maximise the patellar tendon force while balancing against excessive patellofemoral compression, which occurs at 70° of knee flexion and beyond.6
To our knowledge, no studies about the decline squat have been published that validate these assumptions and recommendations. Therefore, we conducted a study on the biomechanics of the single‐leg decline squat. The objective of this study was to investigate knee moment and patellofemoral contact force as a function of decline angle.
Methods
Subjects
Two male and three female subjects participated in this study. Their ages were between 19 and 24 years (mean 22), their height ranged from 1.68 to 2 m (mean 1.8), and weight from 58 to 84 kg (mean 72). They were all moderately physically active in sports (2–5 h/week), healthy and had no actual or previous problems with the knee, ankle or hip joint. All subjects gave their informed consent for the procedure of the study. Participation was voluntary and in agreement with the local medical ethics committee guidelines.
Procedure
Two decline boards with the angle adjustable at 0–40° were constructed. The board for the dominant leg was placed on the force plate (Bertec 4060‐08, Columbus, Ohio, USA). Kinematics in sagittal view were recorded by an Optotrak (Northern Digital, Waterloo, Canada) optoelectronic system. Light‐emitting diodes were attached at the ankle (lateral malleolus), knee (lateral femoral condyle), hip (trochanter major) and shoulder (acromion). Kinematic and force plate data were recorded at 100 Hz by the Optotrak system. Joint moments of ankle, knee and hip were calculated by two‐dimensional inverse dynamics13 in Excel.
After a 5 min warm‐up on a cycle ergometer (Lode Excalibur, Groningen, The Netherlands) at 75 W, the subject performed two pretest single‐leg squats on the decline board to get used to the procedure and to check whether the force plate and positioning system worked correctly. Each subject performed two single‐leg decline squats at 0°, 5°, 10°, 15°, 20°, 25° and 30°. Declines of ⩾35° proved impracticable because the subject slid downwards and could not stand upright. All subjects performed the decline squat standing on their dominant leg and flexing their knee, starting from complete extension to maximal flexion. The contralateral leg was kept forward during the downward movement. Subjects came back to starting position by placing the contralateral leg on the second decline board and extending this leg. They were instructed to keep their trunk in an upright position and to avoid lateral weight shift.
With the board at a decline angle of 25°, some additional exercises and measurements were carried out: (a) the subject was loaded with an extra weight of 10 kg in a backpack, (b) raising up to starting position with the dominant leg, and (c) keeping the contralateral leg backward instead of forward.
Data handling
To account for differences in weight and stature of the subjects, biomechanical variables were normalised as:
normalised force
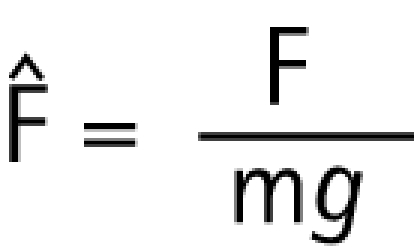 |
and normalised moment
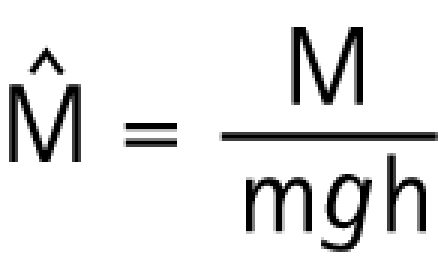 |
where m is body mass, g is the acceleration of gravity and h is leg length from the trochanter to the floor.14 All moments are presented with extension as positive.
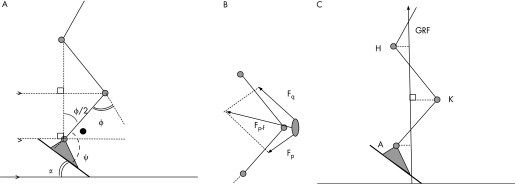
Knee flexion angle φ is defined as 0° at straight knee and ankle plantar flexion angle ψ as 90° at upright standing. When the subject stands with the hip vertically above the ankle and when the upper and lower parts of the leg are about equally long, it holds for the ankle angle (fig 2A):
Figure 2 (A) Diagram to show the relationship between decline α, knee joint angle φ and ankle angle ψ. Note that ψ−α = 90°−φ/2 (the angle with the dot). (B) Vector diagram to show the relationship between patellar tendon force Fp, quadriceps force Fq and patellofemoral contact force Fp‐f. The ratio between Fp and Fq, and the angle between them, were obtained from the model of Buff et al.11 (C) In a static approximation, the moments of hip (H), knee (K) and ankle (A) equal the ground reaction force (GRF) multiplied by the perpendicular distance from the joint to the GRF (dashed lines).
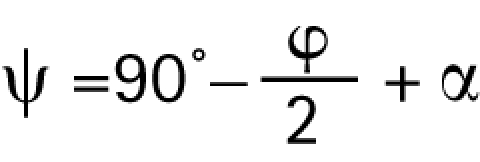 |
where α is the decline angle. (If the hip is not above the ankle—that is, when normalised hip and ankle moments are different—this relation is approximate.)
As all knee extensors act by way of the patellar tendon, (normalised) patellar tendon force equals:
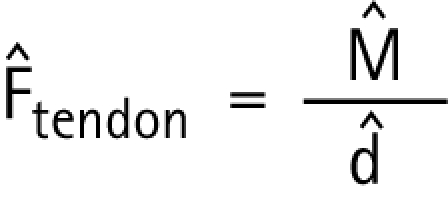 |
where d̂ = d/h is the normalised moment arm of the patellar tendon. For d̂, experimental data of Krevolin et al15 were used, which could be fitted by:
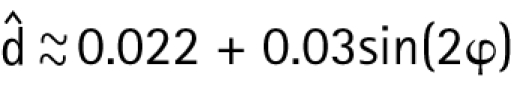 |
Assuming that there is no cocontraction by the knee flexor muscles, the patellofemoral contact force Fp‐f can be estimated by means of the model of Buff et al,11 which gives the ratio between the quadriceps force Fq and the patellar tendon force Fp, and the angle between them. The patellofemoral force can then be found from the vector diagram (fig 2B).
Statistical analysis
All data were analysed using Excel 2003 (Microsoft, USA). Comparisons were performed with use of the unpaired t test. The level of significance was set at 5%.
Results
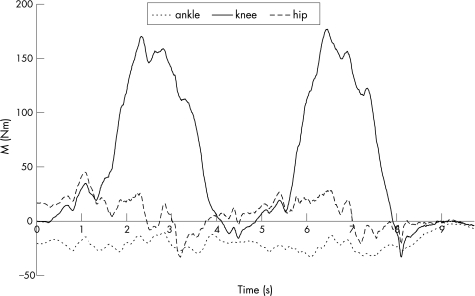
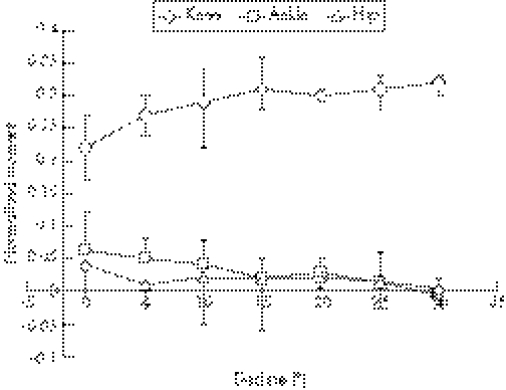
Figure 3 shows a recording of knee, hip and ankle moment. Hip and ankle moment were low during the movement, whereas the knee moment increased strongly with knee flexion during the squats. It was verified that the squatting movement was performed so slowly that contributions to the moments due to accelerations of the limb were always negligible (<4 Nm for the knee, and <8 Nm for the hip). In addition, the ground reaction force (GRF) vector ran perfectly vertical. Figure 4 shows the average of the maximum normalised moments, at maximal knee flexion. Knee moment increases, and hip and ankle moments decrease by up to about 15° of the decline board. The differences in knee moment at 0° and 15–30° were statistically significant (p = 0.035).
Figure 3 Sample recording of knee, hip and ankle moment (M) as a function of time in two squats.
Figure 4 Normalised moments at maximum knee flexion as a function of decline (bars indicate the range of the measured values).
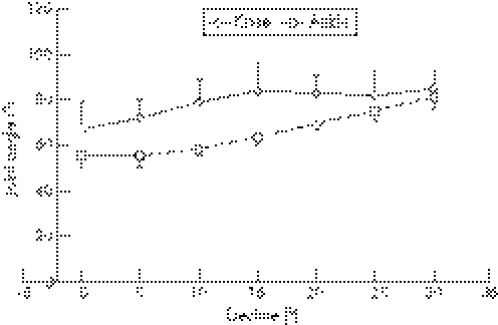
Maximum knee angle (fig 5) increased from 67° without decline, up to about 83° at declines of ⩾15°. Maximum ankle angle increased from 56° ( = 34° dorsiflexion) to 81° at the steepest decline.
Figure 5 Maximum knee flexion angle and minimum ankle plantar flexion angle versus decline (bars indicate the range of the measured values).
The additional exercises did not give significant differences, except for the situation in which the subject was loaded with a 10 kg backpack. In that case, the mean knee moment was 23% (SD 10%, p = 0.02) higher than unloaded, and the maximum knee angle was 5° smaller (p = 0.04).
Discussion
Knee moment/patellar tendon force
This study clearly demonstrates that performing a single‐leg decline squat on a decline board of ⩾15° results in a 40% higher knee moment, and thus patellar tendon force, compared to the same exercise on a flat floor. The hip moment is low at all decline angles and the ankle moment decreases with decline (fig 4).
From the mechanical viewpoint, these findings can be interpreted as follows. As the GRF vector ran vertical, and inertial components to the moments were negligible, joint moments are closely equal to the magnitude of the GRF multiplied by the horizontal distance from the joint to the GRF vector (fig 2C). With greater decline angles, the GRF is moved further from the knee joint, thus increasing the knee extensor moment. In addition, the knee can be flexed more in a decline position (fig 5).
In our opinion, the higher knee moment and better knee flexion on a steeper decline can be explained by properties of the ankle. At 0° or 5° decline, the ankle is in extreme dorsiflexion, around 56°. In this position, the passive ankle moment is considerable, in fact of the order of the measured values.16 This high ankle moment implies a more anterior position of the GRF, and therefore the knee moment will be lower as a consequence of the extreme dorsiflexion. In addition, this is uncomfortable to the subject, who can experience a tight feeling in the calf. The second reason is that the ankle, knee and decline angles are related according to equation 3. When, therefore, ankle dorsiflexion is restricted, the knee cannot be flexed maximally without a decline.
Although Kongsgaard et al10 also found that patellar load increased during a decline squat, they discussed that this could not be explained by a decrease in the ankle moment, as they had found equal EMG values for gastrocnemius and soleus with and without a decline. In our opinion, this argument is not convincing because research shows that a passive ankle moment exists at relevant dorsiflexion angles.16 In addition, the active force–length relation of the muscle changes with ankle angle, and hence also the ratio between EMG and ankle moment.16,17,18
The additional exercises with different postures of the contralateral leg showed no advantages. Only the addition of a 10 kg backpack showed a 23% increase in knee moment. This is in fact more than expected: 10 kg is 14% of the average body weight of 72 kg. This is because the load is located posterior to the unloaded body centre of mass, and thus has a larger moment arm relative to the knee.
What is already known on this topic
The single‐leg decline squat is used as a clinical assessment tool and as a rehabilitation exercise for patients with patellar tendinopathy.
What this study adds
This biomechanical analysis provides validation for the use of the single‐leg decline squat.
Decline angles between 15° and 30° can be used to increase the patellar tendon force.
Knee flexion >60° should be avoided to prevent excessive patellofemoral load.
Patellofemoral contact force
The aim of the single‐leg decline squat is to achieve a maximal patellar tendon force. A point of concern is that the patellofemoral contact force should not become excessive, as this may lead to the patellofemoral pain syndrome.19 When ankle and hip moment are assumed to be zero, it holds for the normalised knee moment.
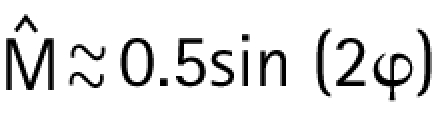 |
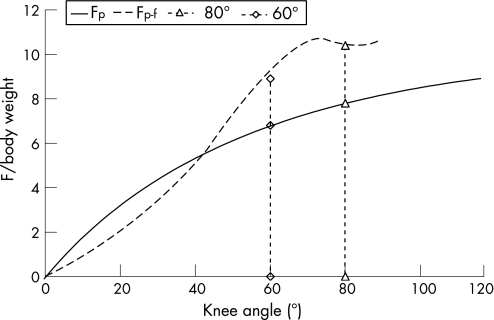
The theoretical tendon and patellofemoral forces can be calculated with the estimated moment arm (equation 5) and the model of Buff et al11 (fig 6). Both increase with higher decline angles, but beyond 60°, the patellofemoral force rises steeper than the tendon force. At 60°, the patellofemoral contact force is already nine‐times the body weight, a further increase seems undesirable. Knee flexion >60° should thus better be avoided. When a higher tendon force is required, it may be better to give an additional backpack load.
Figure 6 Calculated force (F) in the tendon (Fp; solid line) and patellofemoral contact force (Fp‐f; dashed line) as a function of knee angle.
Practical consequences
Our experiments demonstrate that performing single‐leg squats at decline angles >15° all result in a significant increase in the maximum patellar tendon force. Any decline board between 15° and 30° can thus be used, whichever feels most comfortable to the patient. To prevent patellofemoral pain syndrome, we recommend avoiding knee flexions >60°. In case a higher tendon load is required, we recommend the use of a backpack with extra weight.
Acknowledgements
We thank A Kingma, M Slotman and M Uitman for executing the experiments.
Abbreviations
EMG - electromyography
GRF - ground reaction force
Footnotes
Competing interests: None.
Informed consent was obtained for publication of the patients' details described in this report and for publiction of figure 1.
References
- 1.Lian O B, Engebretsen L, Bahr R. Prevalence of jumper's knee among elite athletes from different sports: a cross‐sectional study. Am J Sports Med 200533561–567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cannell L J, Taunton J E, Clement D B.et al A randomised clinical trial of the efficacy of drop squats or leg extension/leg curl exercises to treat clinically diagnosed jumper's knee in athletes: pilot study. Br J Sports Med 20013560–64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jensen K, Di Fabio R P. Evaluation of eccentric exercise in treatment of patellar tendinitis. Phys Ther 198969211–216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stanish W D, Rubinovich R M, Curwin S. Eccentric exercise in chronic tendinitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 198620865–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cook J L, Khan K M, Maffulli N.et al Overuse tendinosis, not tendinitis: part 2 applying the new approach to patellar tendinopathy. Physician Sportsmed 20002831–46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Purdam C R, Cook J L, Hopper D M.et al Discriminative ability of functional loading tests for adolescent jumper's knee. Phys Ther Sport 200343–9. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jonsson P, Alfredson H. Superior results with eccentric compared to concentric quadriceps training in patients with jumper's knee: a prospective randomised study. Br J Sports Med 200539847–850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Purdam C R, Jonsson P, Alfredson H.et al A pilot study of the eccentric decline squat in the management of painful chronic patellar tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med 200438395–397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Young M A, Cook J L, Purdam C R.et al Eccentric decline squat protocol offers superior results at 12 months compared with traditional eccentric protocol for patellar tendinopathy in volleyball players. Br J Sports Med 200539102–105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kongsgaard M, Aagaard P, Roikjaer S.et al Decline eccentric squats increases patellar tendon loading compared to standard eccentric squats. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 200621748–754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Buff H U, Jones L C, Hungerford D S. Experimental determination of forces transmitted through the patello‐femoral joint. J Biomech 19882117–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Huberti H H, Hayes W C, Stone J L.et al Force ratios in the quadriceps tendon and ligamentum patellae. J Orthop Res 1984249–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hof A L. An explicit expression for the moment in multi‐body systems. J Biomechanics 1992251209–1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hof A L. Scaling gait data to body size. Gait Posture 19964222–223. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Krevolin J, Pandy M, Pearce J. Moment arm of the patellar tendon in the human knee 107. J Biomech 200437785–788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hof A L, Berg Jwvd EMG to force processing II: estimation of parameters of the Hill muscle model for the human triceps surae by means of a calf ergometer. J Biomech 198114759–770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nourbakhsh M R, Kukulka C G. Relationship between muscle length and moment arm on EMG activity of human triceps surae muscle. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 200414263–273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sanderson D J, Martin P E, Honeyman G.et al Gastrocnemius and soleus muscle length, velocity, and EMG responses to changes in pedalling cadence. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 200616642–649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Macdonald D A, Hutton J F, Kelly I G. Maximal isometric patellofemoral contact force in patients with anterior knee pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br 198971296–299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]