Abstract
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), restriction fragment length polymorphism of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes (RFLP-PCR), and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) were used to identify 25 isolates of spotted fever group rickettsia collected in the former USSR. Six Rickettsia akari isolates which were identical to the MK reference strain from the American Type Culture Collection were found. Also, 14 isolates were found to be Rickettsia sibirica and identical to reference strain 246. Two of three isolates previously considered as atypical, low-pathogenic strains of R. sibirica, were found to be strains of Rickettsia slovaca. The third, strain S, was similar in its RFLP-PCR profile to "R. africae" sp. nov. (proposed name for a rickettsia pathogenic for human beings in southern Africa) but in its SDS-PAGE and PFGE profiles was unique among spotted fever group rickettsiae. Strain M-1 was confirmed as a genetic variant of Rickettsia conorii. The Astrachan isolate, the causative agent of a tick-bite rickettsiosis at the North of the Caspian Sea, showed a previously described RFLP-PCR profile identical to that of the Israeli tick typhus rickettsia, but its SDS-PAGE and PFGE profiles different from those of the other strains tested.
Full text
PDF


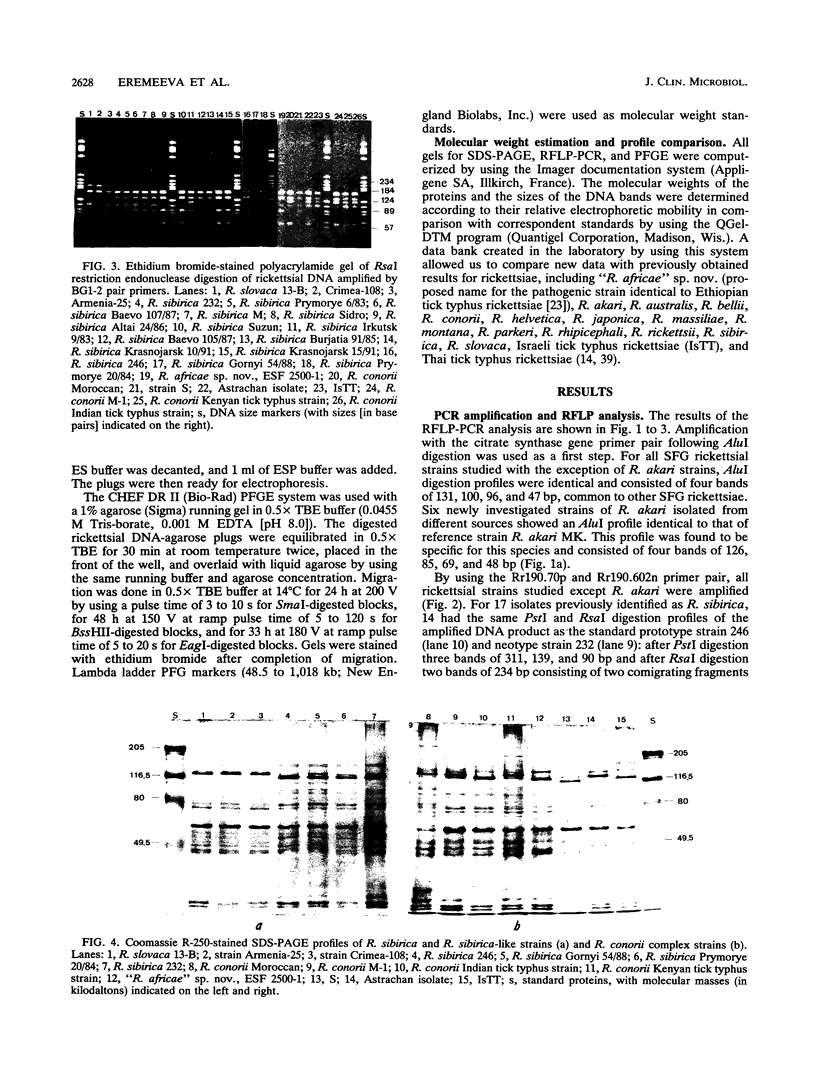





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anacker R. L., List R. H., Mann R. E., Wiedbrauk D. L. Antigenic heterogeneity in high- and low-virulence strains of Rickettsia rickettsii revealed by monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):653–660. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.653-660.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anacker R. L., Mann R. E., Gonzales C. Reactivity of monoclonal antibodies to Rickettsia rickettsii with spotted fever and typhus group rickettsiae. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):167–171. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.167-171.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. E., McDonald G. A., Jones D. C., Regnery R. L. A protective protein antigen of Rickettsia rickettsii has tandemly repeated, near-identical sequences. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2760–2769. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2760-2769.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL E. J., STOENNER H. G. Immunologic relationships among the spotted fever group of rickettsias determined by toxin neutralization tests in mice with convalescent animal serums. J Immunol. 1960 Feb;84:171–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beati L., Finidori J. P., Gilot B., Raoult D. Comparison of serologic typing, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis protein analysis, and genetic restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis for identification of rickettsiae: characterization of two new rickettsial strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):1922–1930. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.1922-1930.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beati L., Finidori J. P., Raoult D. First isolation of Rickettsia slovaca from Dermacentor marginatus in France. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1993 Feb;48(2):257–268. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1993.48.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drancourt M., Beati L., Tarasevich I., Raoult D. Astrakhan fever rickettsia is identical to Israel tick typhus rickettsia, a genotype of the Rickettsia conorii complex. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;165(6):1167–1168. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.6.1167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan M. Y., Yu X. J., Walker D. H. Antigenic analysis of Chinese strains of spotted fever group rickettsiae by protein immunoblotting. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Nov;39(5):497–501. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.39.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIMENEZ D. F. STAINING RICKETTSIAE IN YOLK-SAC CULTURES. Stain Technol. 1964 May;39:135–140. doi: 10.3109/10520296409061219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R. D., Jr, Hackstadt T. DNA polymorphism in the conserved 190 kDa antigen gene repeat region among spotted fever group Rickettsiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jul 26;1097(1):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(91)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R. D., Jr, Joste N., McDonald G. A. Cloning, expression and sequence analysis of the gene encoding the 120 kD surface-exposed protein of Rickettsia rickettsii. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1579–1586. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldwasser R. A., Steiman Y., Klingberg W., Swartz T. A., Klingberg M. A. The isolation of strains of rickettsiae of the spotted fever group in Israel and their differentiation from other members of the group by immunofluorescence methods. Scand J Infect Dis. 1974;6(1):53–62. doi: 10.3109/inf.1974.6.issue-1.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P., Matthewman L., Beati L., Raoult D., Mason P., Dreary M., Makombe R. African tick-bite fever: a new spotted fever group rickettsiosis under an old name. Lancet. 1992 Oct 17;340(8825):982–983. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92878-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladefoged S. A., Christiansen G. Physical and genetic mapping of the genomes of five Mycoplasma hominis strains by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2199–2207. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2199-2207.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manor E., Ighbarieh J., Sarov B., Kassis I., Regnery R. Human and tick spotted fever group Rickettsia isolates from Israel: a genotypic analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2653–2656. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2653-2656.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittermayer T., Brezina R., Urvölgyi J. First report of an infection with Rickettsia slovaca. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 1980;27(4):373–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. Determination of total protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:95–119. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R. N., Casper E. A., Burgdorfer W., Gerloff R. K., Hughes L. E., Bell E. J. Serologic typing of rickettsiae of the spotted fever group by microimmunofluorescence. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1961–1968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Public Health Weekly Reports for NOVEMBER 8, 1946. Public Health Rep. 1946 Nov 8;61(45):1605–1640. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnery R. L., Spruill C. L., Plikaytis B. D. Genotypic identification of rickettsiae and estimation of intraspecies sequence divergence for portions of two rickettsial genes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1576–1589. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1576-1589.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. G., Wisseman C. L., Jr Tick-borne rickettsiae of the spotted fever group in West Pakistan. II. Serological classification of isolates from West Pakistan and Thailand: evidence for two new species. Am J Epidemiol. 1973 Jan;97(1):55–64. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux V., Drancourt M., Raoult D. Determination of genome sizes of Rickettsia spp. within the spotted fever group, using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(22):7455–7457. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.22.7455-7457.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux V., Raoult D. Genotypic identification and phylogenetic analysis of the spotted fever group rickettsiae by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(15):4895–4904. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.15.4895-4904.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarasevich I. V., Makarova V. A., Fetisova N. F., Stepanov A. V., Miskarova E. D., Balayeva N., Raoult D. Astrakhan fever, a spotted-fever rickettsiosis. Lancet. 1991 Jan 19;337(8734):172–173. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90833-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarasević I. V., Plotnikova L. F., Fetisova N. F., Makarova V. A., Jablonskaja V. A., Rehácek J., Zupancicová M., Kovácova E., Urvölgyi J., Brezina R. Rickettsioses studies. 1. Natural foci of rickettsioses in the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53(1):25–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Uchiyama T., Kumano K., Walker D. H. Rickettsia japonica sp. nov., the etiological agent of spotted fever group rickettsiosis in Japan. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;42(2):303–305. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-2-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. G., Walker D. D., Li H., Lenz B., Jerrells T. R. Barbash strain spotted fever group rickettsia is a strain of Rickettsia conorii and differs from Rickettsia sibirica. Acta Virol. 1987 Nov;31(6):489–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. Adenosine Triphosphate and Other Requirements for the Utilization of Glucose by Agents of the Psittacosis-Trachoma Group. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):243–253. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.243-253.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Peacock M. G., McCaul T. F. Immunological and biological characterization of Coxiella burnetii, phases I and II, separated from host components. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):840–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.840-851.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. O., Williamson L. R., Winkler H. H., Krause D. C. Nucleotide sequence of the Rickettsia prowazekii citrate synthase gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3564–3572. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3564-3572.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu X., Jin Y., Fan M., Xu G., Liu Q., Raoult D. Genotypic and antigenic identification of two new strains of spotted fever group rickettsiae isolated from China. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jan;31(1):83–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.1.83-88.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]