Abstract
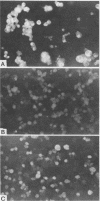
There was 100% agreement between the results of indirect immunofluorescence (IF) and Western blot testing when these methods were used to detect antibodies to the human immunodeficiency virus in sera from 25 patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS), 20 patients with AIDS-related complex, 186 subjects at high risk for AIDS, and 40 healthy heterosexuals. However, there was only an 88.7% correlation between IF and Western blot results for 728 sera from blood and plasma donor centers that were selected on the basis of screening enzyme immunoassay reactivity. IF tests yielded nine false-negatives and were equivocal, yielding a nonspecific pattern of reactivity for both infected and uninfected cells for 73 of these specimens. The IF and Western blot methods were equal in performance for the detection of anti-human immunodeficiency virus antibodies in the high-risk and unselected low-risk groups, proving to be a practical approach for testing specimens from these subjects. However, the Western blot was the most acceptable method for the validation of specimens from groups at low risk for AIDS that were selected based on enzyme immunoassay reactivity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg R. S., Sandstrom E. G., Paradis T. J., Neumeyer D. N., Sarngadharan M. G., Hartshorn K. L., Byington R. E., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T. Detection of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III-related antigens and anti-human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III antibodies by anticomplementary immunofluorescence. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1072–1077. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1072-1077.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson J. R., Bryant M. L., Hinrichs S. H., Yamamoto J. K., Levy N. B., Yee J., Higgins J., Levine A. M., Holland P., Gardner M. B. AIDS serology testing in low- and high-risk groups. JAMA. 1985 Jun 21;253(23):3405–3408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban J. I., Shih J. W., Tai C. C., Bodner A. J., Kay J. W., Alter H. J. Importance of western blot analysis in predicting infectivity of anti-HTLV-III/LAV positive blood. Lancet. 1985 Nov 16;2(8464):1083–1086. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90683-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo D., Diggs J. L., Shell G. R., Dailey P. J., Hoffman M. N., Riggs J. L. Comparison of detection of antibody to the acquired immune deficiency syndrome virus by enzyme immunoassay, immunofluorescence, and Western blot methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1049–1051. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1049-1051.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminsky L. S., McHugh T., Stites D., Volberding P., Henle G., Henle W., Levy J. A. High prevalence of antibodies to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)-associated retrovirus (ARV) in AIDS and related conditions but not in other disease states. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5535–5539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühnl P., Seidl S., Holzberger G. HLA DR4 antibodies cause positive HTLV-III antibody ELISA results. Lancet. 1985 May 25;1(8439):1222–1223. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92910-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saag M. S., Britz J. Asymptomatic blood donor with a false positive HTLV-III Western blot. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jan 9;314(2):118–118. doi: 10.1056/nejm198601093140212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandstrom E. G., Schooley R. T., Ho D. D., Byington R., Sarngadharan M. G., MacLane M. E., Essex M., Gallo R. C., Hirsch M. S. Detection of human anti-HTLV-III antibodies by indirect immunofluorescence using fixed cells. Transfusion. 1985 Jul-Aug;25(4):308–312. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1985.25485273806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorr J. B., Berkowitz A., Cumming P. D., Katz A. J., Sandler S. G. Prevalence of HTLV-III antibody in American blood donors. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 8;313(6):384–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508083130610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]