Abstract
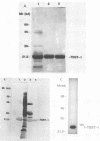
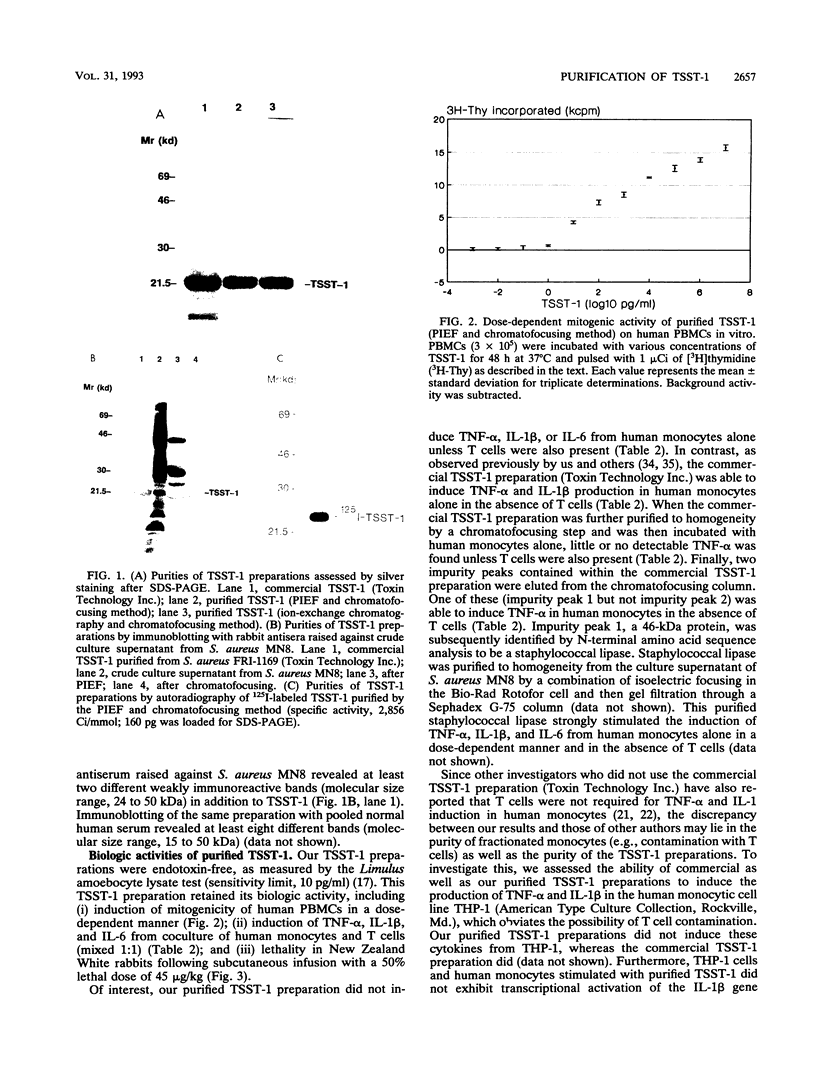
An improved method for producing highly purified toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1) by preparative isoelectric focusing in a Bio-Rad Rotofor cell and then chromatofocusing is described. Purification to homogeneity was confirmed by silver staining after sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE; 50 micrograms of protein was loaded), by immunoblotting with polyclonal rabbit antiserum raised against the crude culture supernatant used for purification, and by autoradiography after iodination and SDS-PAGE. Biologic activity was demonstrated by mitogenicity and cytokine induction (tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-alpha], interleukin 1-beta [IL-1 beta], and IL-6) of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and by lethality in New Zealand White rabbits following subcutaneous infusion. In contrast to commercial TSST-1 preparations, our TSST-1 preparation required the presence of both monocytes and T cells for the induction of TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta from human PBMCs. A 46-kDa contaminating protein in the commercial TSST-1 preparation, identified as staphylococcal lipase, was likely responsible for the induction of TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta from human monocytes in the absence of T cells, a biologic activity falsely attributed to purified TSST-1. Our improved purification procedure for TSST-1 provides a high yield and is both more rapid and less labor intensive than previously reported methods. Furthermore, our studies clearly demonstrate the need for stringent methods of purity assessment of TSST-1 preparations before ascribing to them their potent biologic activities.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarden L. A., De Groot E. R., Schaap O. L., Lansdorp P. M. Production of hybridoma growth factor by human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Oct;17(10):1411–1416. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Crass B. A., Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Davis J. P. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet. 1981 May 9;1(8228):1017–1021. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomster-Hautamaa D. A., Kreiswirth B. N., Novick R. P., Schlievert P. M. Resolution of highly purified toxic-shock syndrome toxin 1 into two distinct proteins by isoelectric focusing. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):54–59. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomster-Hautamaa D. A., Schlievert P. M. Preparation of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. Methods Enzymol. 1988;165:37–43. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)65009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvano S. E., Quimby F. W., Antonacci A. C., Reiser R. F., Bergdoll M. S., Dineen P. Analysis of the mitogenic effects of toxic shock toxin on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Oct;33(1):99–110. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ende I. A., Terplan G., Kickhöfen B., Hammer D. K. Chromatofocusing: a new method for purification of staphylococcal enterotoxins B and C1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Dec;46(6):1323–1330. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.6.1323-1330.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast D. J., Schlievert P. M., Nelson R. D. Nonpurulent response to toxic shock syndrome toxin 1-producing Staphylococcus aureus. Relationship to toxin-stimulated production of tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):949–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast D. J., Schlievert P. M., Nelson R. D. Toxic shock syndrome-associated staphylococcal and streptococcal pyrogenic toxins are potent inducers of tumor necrosis factor production. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):291–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.291-294.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H., Dohlsten M., Lindvall M., Sjögren H. O., Carlsson R. Binding of staphylococcal enterotoxin A to HLA-DR on B cell lines. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3151–3157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjörloff A., Fischer H., Hedlund G., Hansson J., Kenney J. S., Allison A. C., Sjögren H. O., Dohlsten M. Induction of interleukin-1 in human monocytes by the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin A requires the participation of T cells. Cell Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;137(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90056-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi H., Fujikawa H., Usami H., Kawabata S., Morita T. Purification and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus FRI 1169 and 587 toxic shock syndrome exotoxins. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):175–181. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.175-181.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikejima T., Okusawa S., van der Meer J. W., Dinarello C. A. Induction by toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1 of a circulating tumor necrosis factor-like substance in rabbits and of immunoreactive tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 from human mononuclear cells. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):1017–1025. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass E. H., Parsonnet J. On the pathogenesis of toxic shock syndrome. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Sep-Oct;9 (Suppl 5):S482–S489. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_5.s482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN J., BANG F. B. THE ROLE OF ENDOTOXIN IN THE EXTRACELLULAR COAGULATION OF LIMULUS BLOOD. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1964 Sep;115:265–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei Z., Reiser R. F., Bergdoll M. S. Chromatofocusing in the purification of staphylococcal enterotoxin D. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1236–1237. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1236-1237.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Van Keuren M. L. Gel protein stains: silver stain. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:441–447. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notermans S., Dufrenne J. B. A simple purification method for enterotoxin F produced by Staphylococcus aureus and some properties of the toxin. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1982 Dec;48(5):447–455. doi: 10.1007/BF00448416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Gillis Z. A., Pier G. B. Induction of interleukin-1 by strains of Staphylococcus aureus from patients with nonmenstrual toxic shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):55–63. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Gillis Z. A. Production of tumor necrosis factor by human monocytes in response to toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):1026–1033. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poindexter N. J., Schlievert P. M. Toxic-shock-syndrome toxin 1-induced proliferation of lymphocytes: comparison of the mitogenic response of human, murine, and rabbit lymphocytes. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):65–72. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed J. K., Arko R. J., Feeley J. C., Chandler F. W., Thornsberry C., Gibson R. J., Cohen M. L., Jeffries C. D., Broome C. V. Acquired ability of Staphylococcus aureus to produce toxic shock-associated protein and resulting illness in a rabbit model. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):598–604. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.598-604.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Arko R. J., Chandler F. W., Bridges N. B. Affinity purification of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 and its pathologic effects in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):431–439. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.431-439.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Khoe G. P., Bergdoll M. S. Purification and some physicochemical properties of toxic-shock toxin. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 2;22(16):3907–3912. doi: 10.1021/bi00285a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosten P. M., Bartlett K. H., Chow A. W. Detection and quantitation of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 in vitro and in vivo by noncompetitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):327–332. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.327-332.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosten P. M., Bartlett K. H., Chow A. W. Purification and purity assessment of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jan-Feb;11 (Suppl 1):S110–S116. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_1.s110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Shands K. N., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Nishimura R. D. Identification and characterization of an exotoxin from Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):509–516. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholl P., Diez A., Mourad W., Parsonnet J., Geha R. S., Chatila T. Toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 binds to major histocompatibility complex class II molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4210–4214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- See R. H., Krystal G., Chow A. W. Binding competition of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 and other staphylococcal exoproteins for receptors on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2392–2396. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2392-2396.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- See R. H., Kum W. W., Chang A. H., Goh S. H., Chow A. W. Induction of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 by purified staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 requires the presence of both monocytes and T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2612–2618. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2612-2618.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trede N. S., Geha R. S., Chatila T. Transcriptional activation of IL-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha genes by MHC class II ligands. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2310–2315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Azavedo J. C., Arbuthnott J. P. Toxicity of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):314–317. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.314-317.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]