Abstract
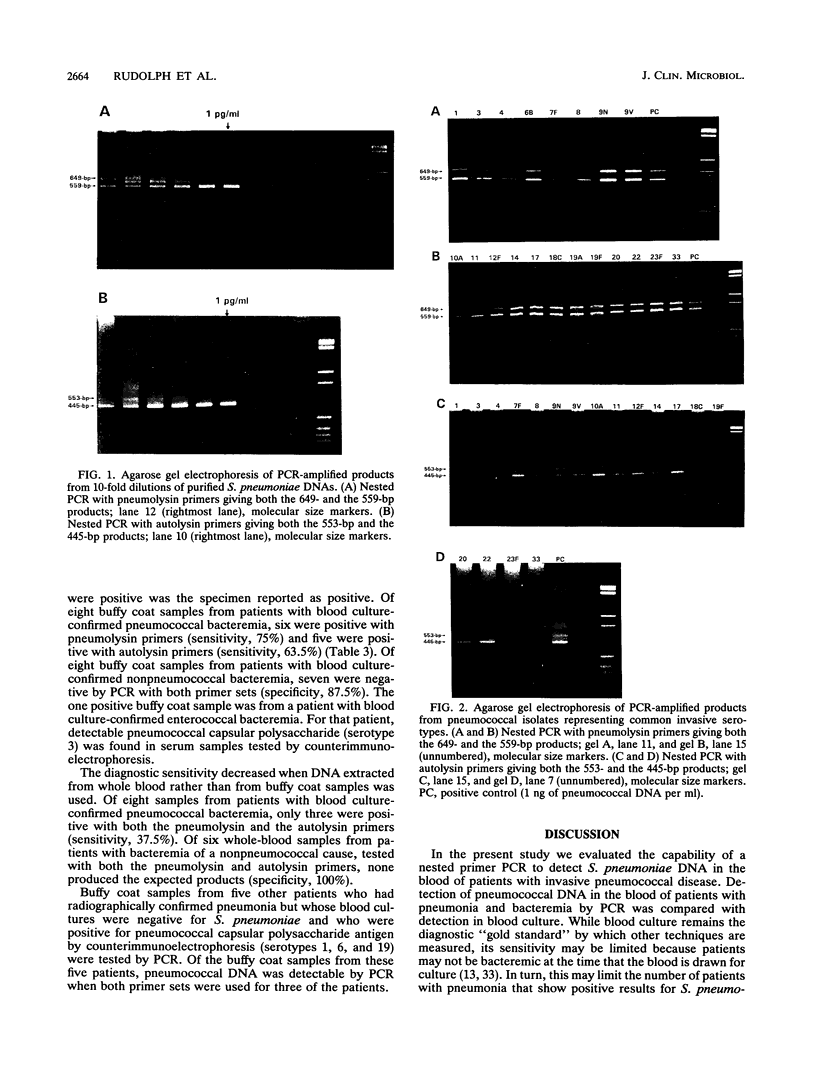
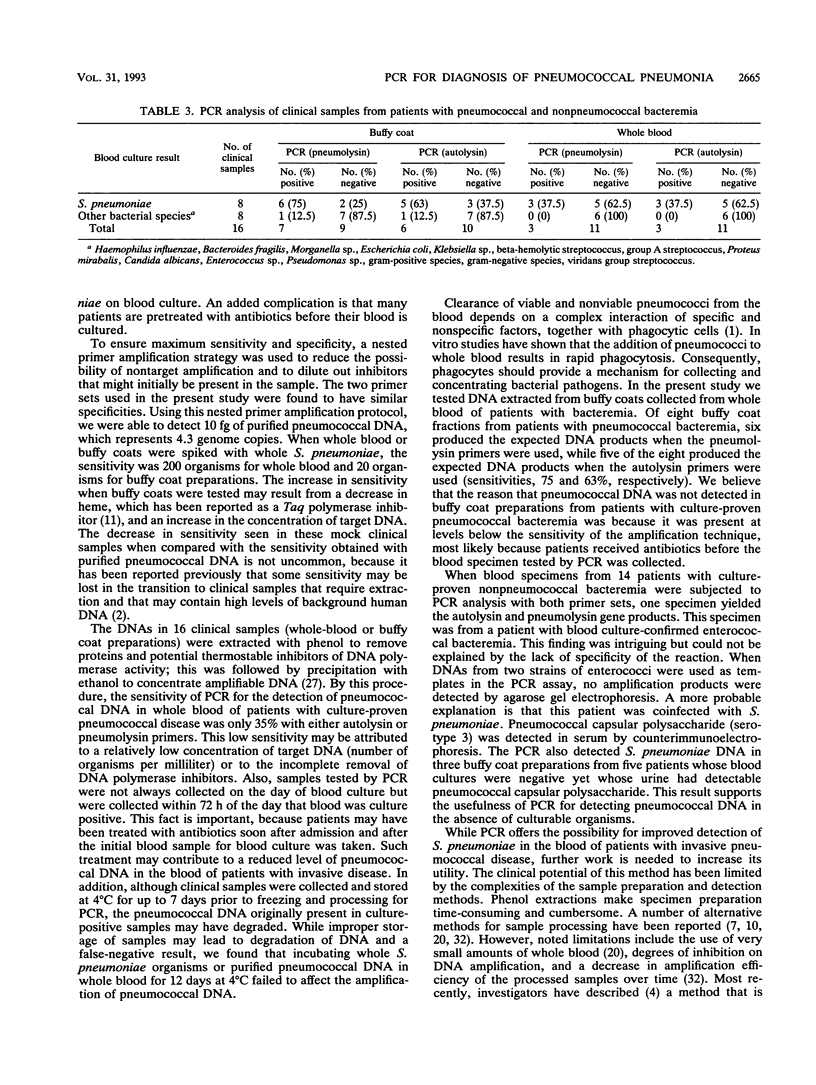
To test the ability of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to detect Streptococcus pneumoniae in blood, we generated two sets of nested primers. The first defined 559-bp and 649-bp regions of the pneumolysin gene, and the second defined 445-bp and 553-bp regions of the autolysin gene. These nucleotide segments were detected in DNAs from isolates of all 20 pneumococcal serotypes tested, but they were not detected when used to test DNAs from 41 isolates of nonpneumococcal bacteria and fungi. The sensitivity was evaluated by using purified pneumococcal DNA. We were able to detect 10 fg of S. pneumoniae DNA, or 4.3 genome equivalents. Blood samples were obtained from 16 patients with culture-proven pneumococcal bacteremia and were subjected to PCR analysis. Of eight buffy coat fractions tested, six showed reactivity in the PCR with the pneumolysin primers, and five of the eight produced the expected products when tested with the autolysin primers (sensitivities, 75 and 63%, respectively). Of the eight whole-blood specimens tested, only three produced the expected products with either set of primers. Additionally, we tested 14 samples from patients with bacteremia that were culture positive for nonpneumococcal bacterial species, and 13 were negative (specificity, 93%). This combination of sensitivity and specificity may make detection of S. pneumoniae in blood by PCR in comparison with that by blood culture a very promising alternative for a means of definitive diagnosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruyn G. A., Zegers B. J., van Furth R. Mechanisms of host defense against infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):251–262. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg J. L., Grover C. M., Pouletty P., Boothroyd J. C. Direct and sensitive detection of a pathogenic protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii, by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1787–1792. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1787-1792.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush C. E., Di Michele L. J., Peterson W. R., Sherman D. G., Godsey J. H. Solid-phase time-resolved fluorescence detection of human immunodeficiency virus polymerase chain reaction amplification products. Anal Biochem. 1992 Apr;202(1):146–151. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90219-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casareale D., Pottathil R., Diaco R. Improved blood sample processing for PCR. PCR Methods Appl. 1992 Nov;2(2):149–153. doi: 10.1101/gr.2.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerosaletti K. M., Roghmann M. C., Bentley D. W. Comparison of latex agglutination and counterimmunoelectrophoresis for the detection of pneumococcal antigen in elderly pneumonia patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):553–557. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.553-557.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K., Neimark H., Rumore P., Steinman C. R. Broad range DNA probes for detecting and amplifying eubacterial nucleic acids. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jan 1;48(1):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. Z., Evans G. A. A simple screening method for transgenic mice using the polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques. 1990 Jan;8(1):32–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M., Schraer C. D., Parkinson A. J., Campbell J. F., Facklam R. R., Wainwright R. B., Lanier A. P., Heyward W. L. Invasive pneumococcal disease in an Alaska native population, 1980 through 1986. JAMA. 1989 Feb 3;261(5):715–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García P., García J. L., García E., López R. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the pneumococcal autolysin gene from its own promoter in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1986;43(3):265–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton K., Sahli R., Bille J. Development of polymerase chain reaction assays for detection of Listeria monocytogenes in clinical cerebrospinal fluid samples. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):1931–1936. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.1931-1936.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalin M., Lindberg A. A. Diagnosis of pneumococcal pneumonia: a comparison between microscopic examination of expectorate, antigen detection and cultural procedures. Scand J Infect Dis. 1983;15(3):247–255. doi: 10.3109/inf.1983.15.issue-3.04. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G. H., Huang D. P., Manak M. M. Detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 DNA by polymerase chain reaction amplification and capture hybridization in microtiter wells. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):638–641. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.638-641.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenten J. H., Casadei J., Link J., Lupold S., Willey J., Powell M., Rees A., Massey R. Rapid electrochemiluminescence assays of polymerase chain reaction products. Clin Chem. 1991 Sep;37(9):1626–1632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S., Mack D. H., Mullis K. B., Poiesz B., Ehrlich G., Blair D., Friedman-Kien A., Sninsky J. J. Identification of human immunodeficiency virus sequences by using in vitro enzymatic amplification and oligomer cleavage detection. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1690–1694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1690-1694.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malloy D. C., Nauman R. K., Paxton H. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1089–1093. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1089-1093.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantero G., Zonaro A., Albertini A., Bertolo P., Primi D. DNA enzyme immunoassay: general method for detecting products of polymerase chain reaction. Clin Chem. 1991 Mar;37(3):422–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier B., Gaucher C., Feugeas O., Mazurier C. Direct PCR from whole blood, without DNA extraction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5908–5908. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musiani M., Zerbini M., Gibellini D., Gentilomi G., Venturoli S., Gallinella G., Ferri E., Girotti S. Chemiluminescence dot blot hybridization assay for detection of B19 parvovirus DNA in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):2047–2050. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.2047-2050.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noordhoek G. T., Wolters E. C., de Jonge M. E., van Embden J. D. Detection by polymerase chain reaction of Treponema pallidum DNA in cerebrospinal fluid from neurosyphilis patients before and after antibiotic treatment. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):1976–1984. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.1976-1984.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson A. J., Scott E. N., Muchmore H. G. Rapid micromethod for preparation of enzyme-antibody conjugates. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):737–739. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.737-739.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlino C. A. Laboratory diagnosis of pneumonia due to Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):139–144. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plikaytis B. B., Gelber R. H., Shinnick T. M. Rapid and sensitive detection of Mycobacterium leprae using a nested-primer gene amplification assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1913–1917. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1913-1917.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Okamoto N., Watanabe S., Kano T. Chemiluminescent microtiter method for detecting PCR amplified HIV-1 DNA. J Virol Methods. 1992 Jul;38(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(92)90174-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan P., Macfarlane J. T. Role of pneumococcal antigen in the diagnosis of pneumococcal pneumonia. Thorax. 1992 May;47(5):329–331. doi: 10.1136/thx.47.5.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield A. E., Pixley F. J., Banerji S., Sinclair K., Miller R. F., Moxon E. R., Hopkin J. M. Detection of Pneumocystis carinii with DNA amplification. Lancet. 1990 Aug 25;336(8713):451–453. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. A., Allen R. L., Falmagne P., Johnson M. K., Boulnois G. J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and complete nucleotide sequence of the gene for pneumolysin, the sulfhydryl-activated toxin of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1184–1189. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1184-1189.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitby M., Kristinsson K. G., Brown M. Assessment of rapid methods of pneumococcal antigen detection in routine sputum bacteriology. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Mar;38(3):341–344. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.3.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberg G. A rapid method for preparing DNA from blood, suited for PCR screening of transgenes in mice. PCR Methods Appl. 1991 Aug;1(1):72–74. doi: 10.1101/gr.1.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]