Abstract
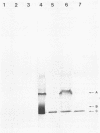
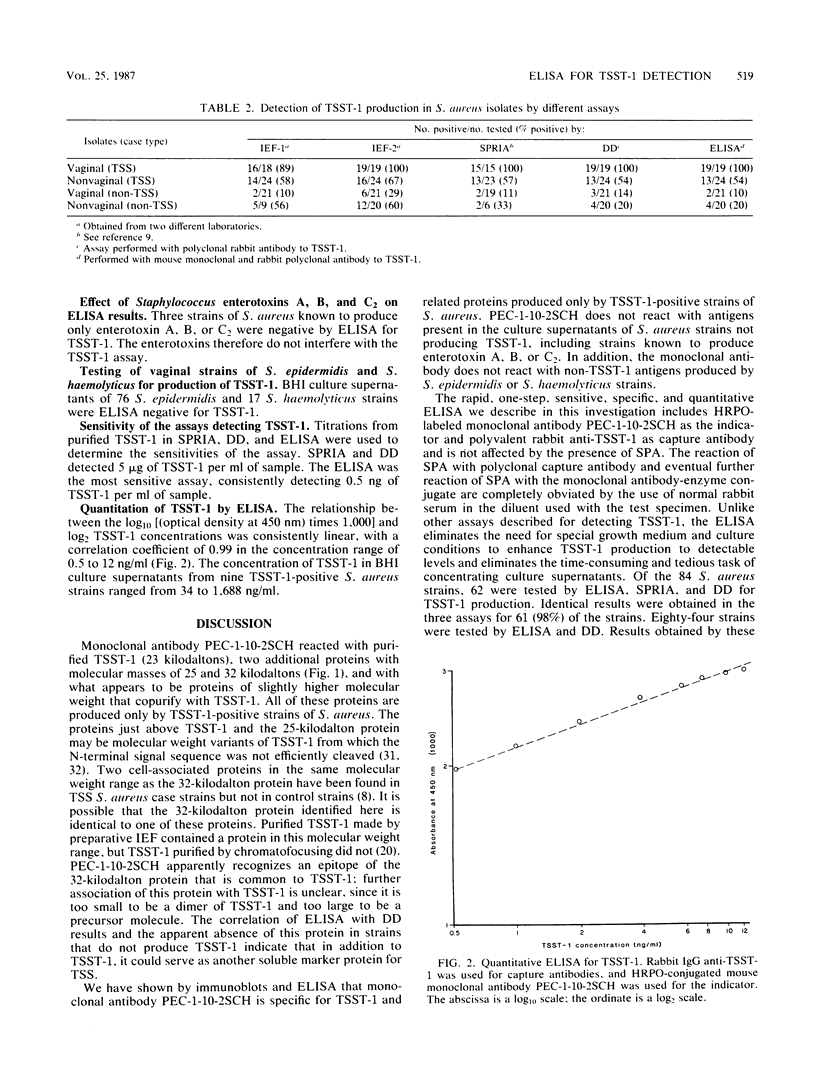
Twenty-six hybridoma cell lines that produced monoclonal antibodies to toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1) were generated by immunizing mice with a highly purified preparation of TSST-1 and fusing their splenic lymphocytes with SP2/0-Ag-14 cells. One monoclonal antibody of the immunoglobulin G1 isotype, designated as PEC-1 10-2SCH, was selected for extensive study. The specificity of this antibody was determined by testing spent culture fluid filtrates of TSST-1- and non-TSST-1-producing strains of Staphylococcus aureus by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot techniques. Monoclonal antibody PEC-1-10-2SCH was specific for TSST-1-producing strains of S. aureus, reacting with TSST-1 and two other proteins which appear to be unique to S. aureus strains that produce TSST-1. Monoclonal antibody PEC-1-10-2SCH was used in conjunction with polyclonal rabbit antibodies to TSST-1 in a rapid, one-step, sensitive, specific, and quantitative enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. This assay was shown to be more sensitive, faster, and simpler to perform than previously described isoelectric focusing, immunodiffusion, and solid-phase radioimmunoassays for TSST-1. Monoclonal antibody PEC-1-10-2SCH was not reactive with Staphylococcus protein A under the conditions of the test.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arko R. J., Rasheed J. K., Broome C. V., Chandler F. W., Paris A. L. A rabbit model of toxic shock syndrome: clinicopathological features. J Infect. 1984 May;8(3):205–211. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(84)93859-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Vaginal isolates of Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic shock syndrome. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):442–449. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.442-449.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Crass B. A., Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Davis J. P. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet. 1981 May 9;1(8228):1017–1021. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos E. S., van der Doelen A. A., van Rooy N., Schuurs A. H. 3,3',5,5' - Tetramethylbenzidine as an Ames test negative chromogen for horse-radish peroxidase in enzyme-immunoassay. J Immunoassay. 1981;2(3-4):187–204. doi: 10.1080/15321818108056977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claflin L., Williams K. Mouse myeloma--spleen cell hybrids: Enhanced hybridization frequencies and rapid screening procedures. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:107–109. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Falkow S. Protein antigens from Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with toxic-shock syndrome. Science. 1981 Feb 20;211(4484):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.7466361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Graves L. M., Hayes P. S., Gibson R. J., Rasheed J. K., Feeley J. C. Toxic shock syndrome: modification and comparison of methods for detecting marker proteins in Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):372–375. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.372-375.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. P., Chesney P. J., Wand P. J., LaVenture M. Toxic-shock syndrome: epidemiologic features, recurrence, risk factors, and prevention. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 18;303(25):1429–1435. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012183032501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbe P. L., Arko R. J., Reingold A. L., Graves L. M., Hayes P. S., Hightower A. W., Chandler F. W., Broome C. V. Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with nonmenstrual toxic shock syndrome. Evidence for additional toxins. JAMA. 1985 May 3;253(17):2538–2542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Use of staphylococcal protein A as an immunological reagent. J Immunol Methods. 1978;20:241–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi H., Fujikawa H., Usami H., Kawabata S., Morita T. Purification and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus FRI 1169 and 587 toxic shock syndrome exotoxins. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):175–181. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.175-181.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A. Epidermal toxin production by Staphylococcus aureus strains from patients with toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):972–974. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Schleifer K. H. Simplified scheme for routine identification of human Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.82-88.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Kawaoi A. Peroxidase-labeled antibody. A new method of conjugation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Mills J. T., Gillis Z. A., Pier G. B. Competitive, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):26–31. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.26-31.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed J. K., Arko R. J., Feeley J. C., Chandler F. W., Thornsberry C., Gibson R. J., Cohen M. L., Jeffries C. D., Broome C. V. Acquired ability of Staphylococcus aureus to produce toxic shock-associated protein and resulting illness in a rabbit model. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):598–604. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.598-604.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Pine L., Feeley J. C., Wells D. E. Presence of toxic shock toxin in toxic shock and other clinical strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):590–597. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.590-597.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L., Dan B. B., Shands K. N., Broome C. V. Toxic-shock syndrome not associated with menstruation. A review of 54 cases. Lancet. 1982 Jan 2;1(8262):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92552-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L., Hargrett N. T., Dan B. B., Shands K. N., Strickland B. Y., Broome C. V. Nonmenstrual toxic shock syndrome: a review of 130 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):871–874. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L., Hargrett N. T., Shands K. N., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Strickland B. Y., Broome C. V. Toxic shock syndrome surveillance in the United States, 1980 to 1981. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):875–880. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Shands K. N., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Nishimura R. D. Identification and characterization of an exotoxin from Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):509–516. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. F., Kling J. M., Kirkland J. J., Best G. K. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with toxic shock syndrome, using polyethylene infection chambers in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):383–387. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.383-387.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands K. N., Schmid G. P., Dan B. B., Blum D., Guidotti R. J., Hargrett N. T., Anderson R. L., Hill D. L., Broome C. V., Band J. D. Toxic-shock syndrome in menstruating women: association with tampon use and Staphylococcus aureus and clinical features in 52 cases. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 18;303(25):1436–1442. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012183032502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J., Fishaut M., Kapral F., Welch T. Toxic-shock syndrome associated with phage-group-I Staphylococci. Lancet. 1978 Nov 25;2(8100):1116–1118. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Hancock K., Maddison S. E., Beatty A. L., Moss D. M. Demonstration of species-specific and cross-reactive components of the adult microsomal antigens from Schistosoma mansoni and S. japonicum (MAMA and JAMA). J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2607–2613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Peralta J. M., Simons A. R. Enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot techniques (EITB) for studying the specificities of antigens and antibodies separated by gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:377–391. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweten R. K., Christianson K. K., Iandolo J. J. Transport and processing of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):524–528. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.524-528.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweten R. K., Iandolo J. J. Transport and processing of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):297–303. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.297-303.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergeront J. M., Evenson M. L., Crass B. A., Davis J. P., Bergdoll M. S., Wand P. J., Noble J. H., Petersen G. K. Recovery of staphylococcal enterotoxin F from the breast milk of a woman with toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):456–459. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weckbach L. S., Thompson M. R., Staneck J. L., Bonventre P. F. Rapid screening assay for toxic shock syndrome toxin production by Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):18–22. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.18-22.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]