Abstract
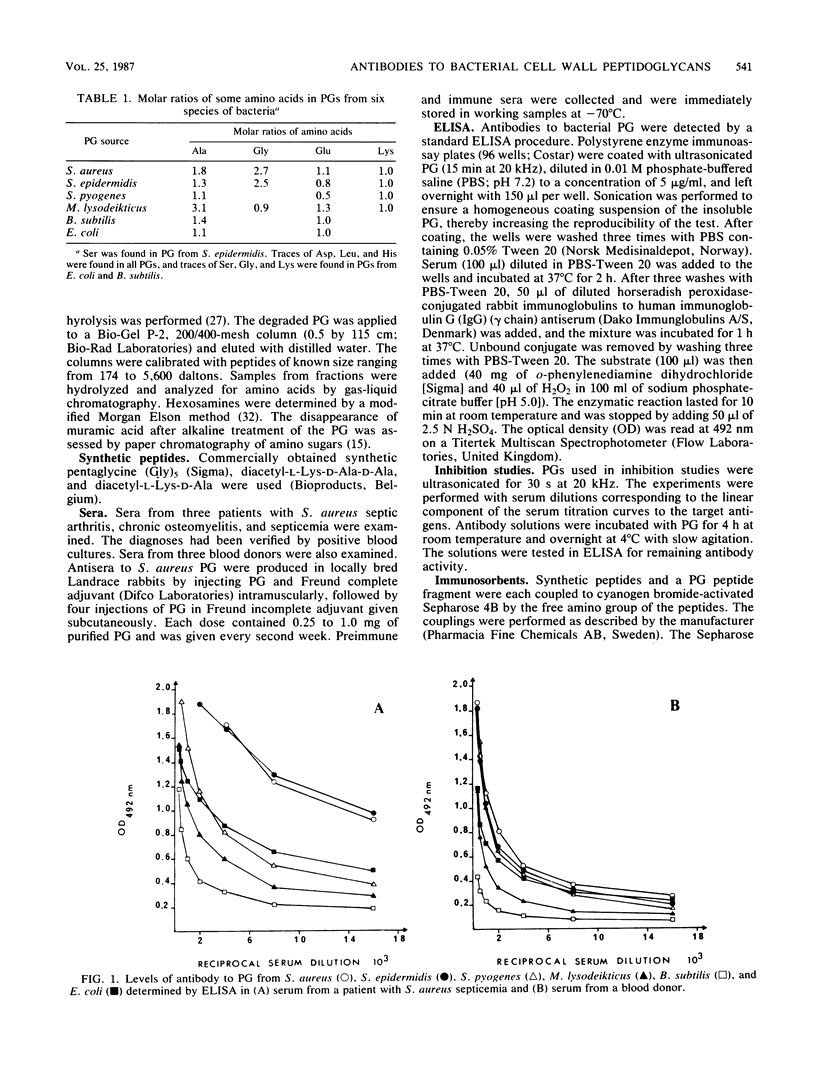
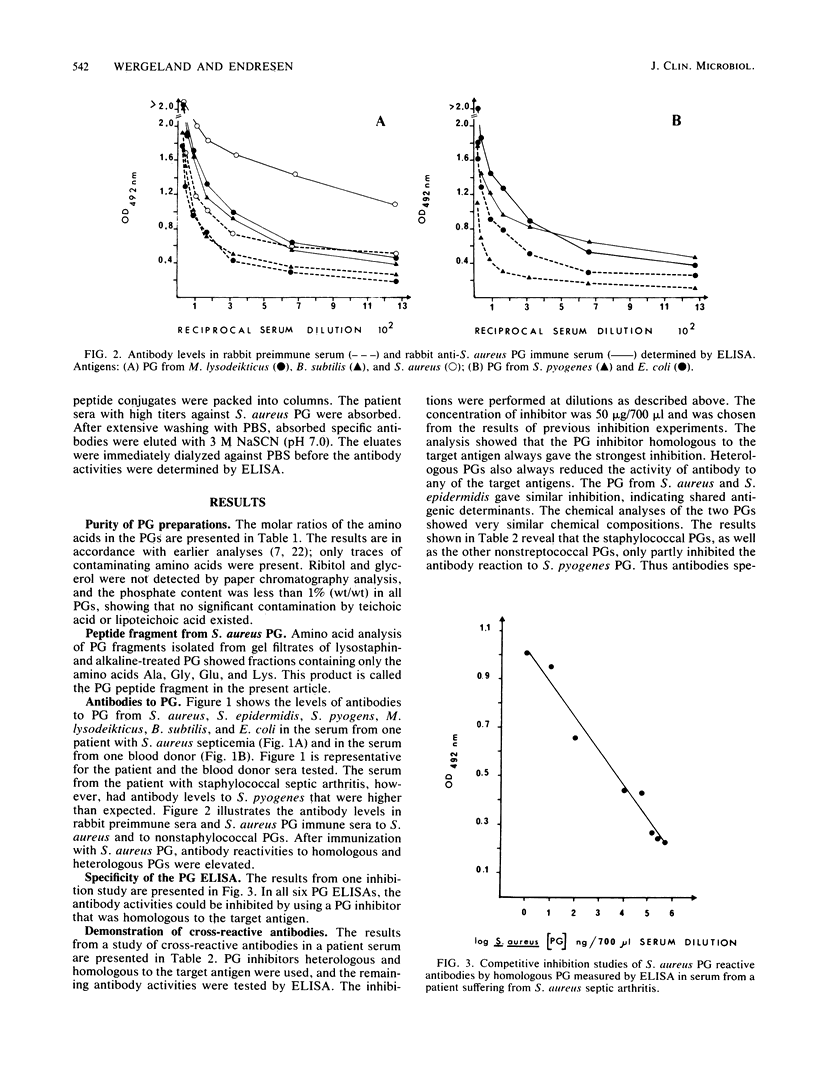
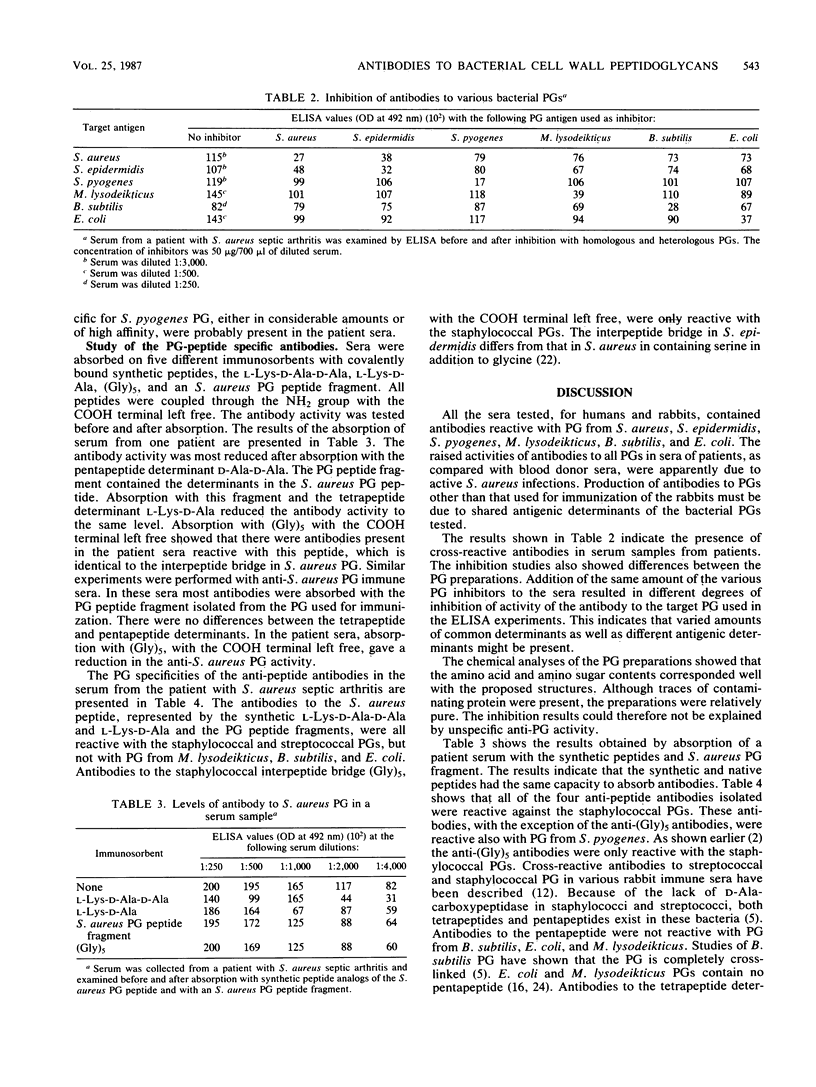
Sera from patients with verified systemic staphylococcal infection contained antibodies reactive with peptidoglycan (PG) from Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pyogenes, Micrococcus lysodeikticus, Bacillus subtilis, and Escherichia coli. The presence of anti-PG cross-reactive antibodies was verified in patient sera by inhibition studies with the various bacterial PGs. Antibodies to nonstaphylococcal PGs were also elevated in sera from rabbits immunized with S. aureus PG. Antibodies to S. aureus PG were removed with the synthetic peptide analogs of S. aureus PG, the L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala, L-Lys-D-Ala, and (Gly)5 determinants, as well as with an S. aureus PG peptide fragment containing the determinants D-Ala-D-Ala and L-Lys-D-Ala. Isolated antibodies to the PG peptides, both synthetic and native, were reactive with S. aureus and S. epidermidis PGs. The antibodies to the D-Ala-D-Ala and the L-Lys-D-Ala determinants were also reactive with S. pyogenes PG, but not with PGs from M. lysodeikticus, B. subtilis, and E. coli.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christensson B., Espersen F., Hedström S. A., Kronvall G. Serological assays against Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan, crude staphylococcal antigen and staphylolysin in the diagnosis of serious S. aureus infections. Scand J Infect Dis. 1985;17(1):47–53. doi: 10.3109/00365548509070419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensson B., Espersen F., Hedström S. A., Kronvall G. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of immunoglobulin G antibodies to Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan in patients with staphylococcal infections. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Dec;91(6):401–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franken N., Seidl P. H., Kuchenbauer T., Kolb H. J., Schleifer K. H., Weiss L., Tympner K. D. Specific immunoglobulin A antibodies to a peptide subunit sequence of bacterial cell wall peptidoglycan. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):182–187. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.182-187.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grov A. Studies on antigen preparations from Staphylococcus aureus. 8. The substance of crude protein A sensitizing tanned erythrocytes. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;76(4):629–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgeland S. M., Grov A. Immunochemical characterization of staphylococcal and microbial mucopeptides. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(6):819–826. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgeland S., Grov A., Schleifer K. H. The immunochemistry of Staphylococcus aureus mucopeptide. I. Antigenic specificity of the peptide subunits. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Aug;81(4):413–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymer B. Biological properties of the peptidoglycan. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):245–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Braun D. G., Lackland H., Krause R. M. Immunochemical studies on the cross-reactivity between streptococcal and staphylococcal mucopeptide. J Exp Med. 1968 Aug 1;128(2):325–340. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Lackland H., Krause M. An immunochemical analysis of bacterial mucopeptides. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):797–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Lackland H., Krause R. M. Antigenic properties of the hexosamine polymer of streptococcal mucopeptide. J Immunol. 1967 Dec;99(6):1178–1182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Maurer P. H., Walsh P., Krause R. M. The role of D-alanine in the antigenic specificity of bacterial mucopeptides. J Immunol. 1970 Jan;104(1):230–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Immunological properties of teichoic acids. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):215–257. doi: 10.1128/br.37.2.215-257.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa J., Tamaki S., Tomioka S., Matsuhashi M. Functional biosynthesis of cell wall peptidoglycan by polymorphic bifunctional polypeptides. Penicillin-binding protein 1Bs of Escherichia coli with activities of transglycosylase and transpeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13937–13946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen-Huy H., Nauciel C., Wermuth C. G. Immunochemical study of the peptidoglycan of gram-negative bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 15;66(1):79–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., HANCOCK R. A fractionation procedure for studies of the synthesis of cell-wall mucopeptide and of other polymers in cells of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Feb;22:249–258. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-1-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranu R. S. Studies on the immunochemistry of Staphylococcus aureus cell wall: antigenicity of pentaglycine bridges. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1975;161(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02120770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolicka M., Park J. T. Antimucopeptide antibodies and their specificity. J Immunol. 1969 Aug;103(2):196–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Krause R. M. The immunochemistry of peptidoglycan. I. The immunodominant site of the peptide subunit and the contribution of each of the amino acids to the binding properties of the peptides. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):986–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Krause R. M. The immunochemistry of peptidoglycan. Separation and characterization of antibodies to the glycan and to the peptide subunit. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Apr 30;19(4):471–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidl P. H., Schleifer K. H. Specific antibodies to the N-termini of the interpeptide bridges of peptidoglycan. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Aug 1;118(2):185–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00415728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solsvik E., Grov A., Endresen C. Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan studied by electron microscopy of immunoperoxidase-treated sections of cell walls. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1984 Feb;92(1):7–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb02787.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peters R., Rozenberg-Arska M., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Antibodies to cell wall peptidoglycan of Staphylococcus aureus in patients with serious staphylococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jul;144(1):1–9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., van Dijk W. C., Peters R., van Erne M. E., Daha M. R., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Opsonic recognition of staphylococci mediated by cell wall peptidoglycan: antibody-independent activation of human complement and opsonic activity of peptidoglycan antibodies. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1167–1173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., FRANK H., LEUTGEB W. Autolytic enzymes as a source of error in the preparation and study of gram-negative cell walls. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jan;30:127–130. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wergeland H., Endresen C., Natås O. B., Aasjord P., Oeding P. Antibodies to Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid in sera from blood donors and patients with staphylococcal infections. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1984 Oct;92(5):265–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb02832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikler M. Isolation and characterization of homogenous rabbit antibodies to Micrococcus lysodeikticus with specificity to the peptidoglycan and to the glucose-N-acetylaminomannuronic acid polymer. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):193–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


