Abstract
We analyzed Escherichia coli O157:H7 isolates from stool samples of five patients who had bloody diarrhea and were infected during a large food-borne outbreak of hemorrhagic colitis in Washington state. The isolates were assessed for Shiga-like toxin profile, adherence and plasmid traits, mouse virulence, capsule, and enterohemolysin production. The profiles of the five isolates were indistinguishable from each other and similar to that of E. coli O157:H7 strain EDL933, an organism responsible for a similar hamburger-associated food poisoning episode in 1982.
Full text
PDF
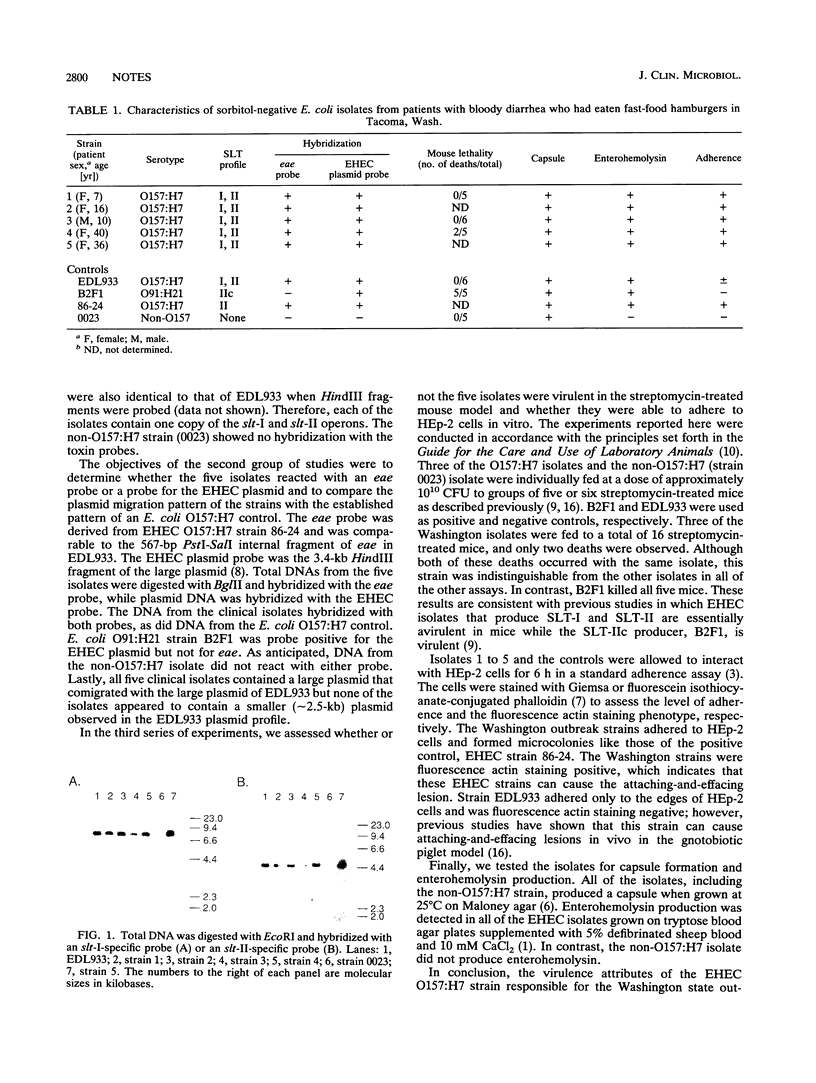

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutin L., Montenegro M. A., Orskov I., Orskov F., Prada J., Zimmermann S., Stephan R. Close association of verotoxin (Shiga-like toxin) production with enterohemolysin production in strains of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2559–2564. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2559-2564.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin P. M., Ostroff S. M., Tauxe R. V., Greene K. D., Wells J. G., Lewis J. H., Blake P. A. Illnesses associated with Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections. A broad clinical spectrum. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Nov 1;109(9):705–712. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-9-705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M., Lior H., Bezanson G. S. Cytotoxic Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with haemorrhagic colitis in Canada. Lancet. 1983 Jan 1;1(8314-5):76–76. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91616-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junkins A. D., Doyle M. P. Demonstration of exopolysaccharide production by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Curr Microbiol. 1992 Jul;25(1):9–17. doi: 10.1007/BF01570076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldwin T., Williams P. H., McNeish A. S. Actin accumulation at sites of bacterial adhesion to tissue culture cells: basis of a new diagnostic test for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1290-1298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Xu J. G., Kaper J. B., Lior H., Prado V., Tall B., Nataro J., Karch H., Wachsmuth K. A DNA probe to identify enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli of O157:H7 and other serotypes that cause hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):175–182. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren S. W., Melton A. R., O'Brien A. D. Virulence of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O91:H21 clinical isolates in an orally infected mouse model. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3832–3842. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3832-3842.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. O., Lively T. A., Chen M. E., Rothman S. W., Formal S. B. Escherichia coli O157:H7 strains associated with haemorrhagic colitis in the United States produce a Shigella dysenteriae 1 (SHIGA) like cytotoxin. Lancet. 1983 Mar 26;1(8326 Pt 1):702–702. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91987-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff S. M., Tarr P. I., Neill M. A., Lewis J. H., Hargrett-Bean N., Kobayashi J. M. Toxin genotypes and plasmid profiles as determinants of systemic sequelae in Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):994–998. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt C. K., McKee M. L., O'Brien A. D. Two copies of Shiga-like toxin II-related genes common in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli strains are responsible for the antigenic heterogeneity of the O157:H- strain E32511. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1065–1073. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1065-1073.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh V. L., Burris J. A., Owens J. W., Gordon V. M., Wadolkowski E. A., O'Brien A. D., Samuel J. E. Comparison of the relative toxicities of Shiga-like toxins type I and type II for mice. Infect Immun. 1993 Aug;61(8):3392–3402. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.8.3392-3402.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Karch H., Wachsmuth K. I., Robins-Browne R. M., O'Brien A. D., Lior H., Cohen M. L., Smithers J., Levine M. M. Role of a 60-megadalton plasmid and Shiga-like toxins in the pathogenesis of infection caused by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 in gnotobiotic piglets. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3117–3125. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3117-3125.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadolkowski E. A., Sung L. M., Burris J. A., Samuel J. E., O'Brien A. D. Acute renal tubular necrosis and death of mice orally infected with Escherichia coli strains that produce Shiga-like toxin type II. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3959–3965. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3959-3965.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Sokolow R., Morris G. K. Laboratory investigation of hemorrhagic colitis outbreaks associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):512–520. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.512-520.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Kaper J. B. Cloning and characterization of the eae gene of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(3):411–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



