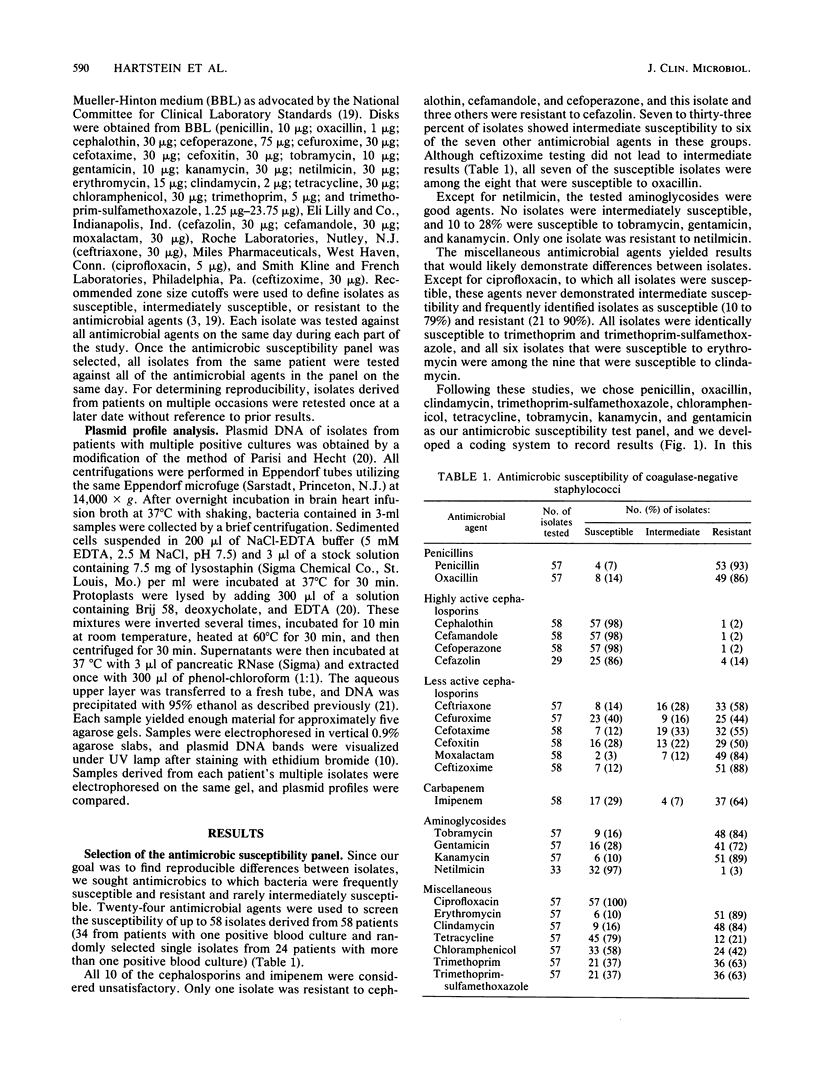
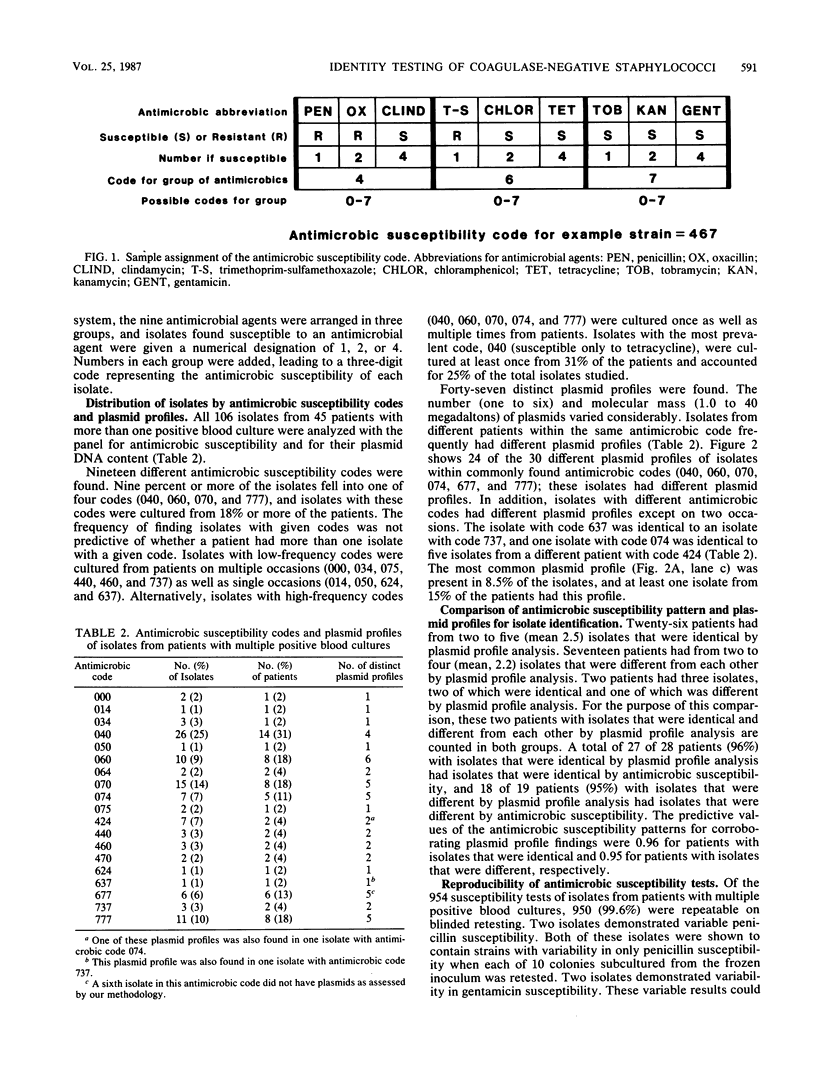
Abstract
We compared a disk diffusion antimicrobic susceptibility panel with plasmid DNA profiles as tests for identity of 106 isolates of coagulase-negative staphylococci cultured from the blood of 45 patients on multiple occasions. The antimicrobic panel included penicillin, oxacillin, clindamycin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, chloramphenicol, tetracycline, tobramycin, kanamycin, and gentamicin. Nineteen patterns of antimicrobic susceptibility were found. The most common pattern was present in 25% of the isolates, and at least one isolate from 31% of the patients had this pattern. Forty-seven distinct plasmid DNA profiles were found. The most common plasmid profile was present in 8.5% of the isolates, and at least one isolate from 15% of the patients had this profile. Twenty-eight patients had multiple isolates that were identical by plasmid profile analysis. Twenty-seven (96%) of these patients had isolates that were also identical by antimicrobic susceptibility. Nineteen patients had multiple isolates that were different by plasmid profile analysis. In 18 (95%) of these patients, the isolates were also different by antimicrobic susceptibility. Although plasmid DNA profile analysis is a more discriminating tool, these data confirm that a selected disk diffusion antimicrobic susceptibility panel may be used to screen multiple blood isolates of coagulase-negative staphylococci for identity or differences.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G. L., Karchmer A. W., Vishniavsky N., Johnston J. L. Plasmid-pattern analysis for the differentiation of infecting from noninfecting Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jun;149(6):913–920. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.6.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L., Vishniavsky N., Stiver H. G. Plasmid pattern analysis of Staphylococcal epidermidis isolates from patients with prosthetic valve endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):627–632. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.627-632.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Fass R. J., Anhalt J. P., Neu H. C., Thornsberry C., Tilton R. C., Painter B. G., Washington J. A., 2nd Ciprofloxacin disk susceptibility tests: interpretive zone size standards for 5-microgram disks. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):880–883. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.880-883.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battisti O., Mitchison R., Davies P. A. Changing blood culture isolates in a referral neonatal intensive care unit. Arch Dis Child. 1981 Oct;56(10):775–778. doi: 10.1136/adc.56.10.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgart S., Hall S. E., Campos J. M., Polin R. A. Sepsis with coagulase-negative staphylococci in critically ill newborns. Am J Dis Child. 1983 May;137(5):461–463. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1983.02140310043012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchard K. W., Minor L. B., Slotman G. J., Gann D. S. Staphylococcus epidermidis sepsis in surgical patients. Arch Surg. 1984 Jan;119(1):96–100. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1984.01390130078014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamovitz B., Bryant R. E., Gilbert D. N., Hartstein A. I. Prosthetic valve endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis. Development of rifampin resistance during vancomycin and rifampin therapy. JAMA. 1985 May 17;253(19):2867–2868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Bisno A. L., Parisi J. T., McLaughlin B., Hester M. G., Luther R. W. Nosocomial septicemia due to multiply antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jan;96(1):1–10. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Parisi J. T., Bisno A. L., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Characterization of clinically significant strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):258–269. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.258-269.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Schiewe M. H., Falkow S. Evidence for plasmid contribution to the virulence of fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):509–513. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.509-513.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman L. E., Brown A. E., Miller D. R., Armstrong D. Staphylococcus epidermidis septicemia in children with leukemia and lymphoma. Am J Dis Child. 1984 Aug;138(8):715–719. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1984.02140460007005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill V. J., Selepak S. T., Williams E. C. Species identification and antibiotic susceptibilities of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1314–1319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1314-1319.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson S. J., Parisi J. T. Bacteriophage typing of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):396–397. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.396-397.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchhoff L. V., Sheagren J. N. Epidemiology and clinical significance of blood cultures positive for coagulase-negative staphylococcus. Infect Control. 1985 Dec;6(12):479–486. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700063591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Schleifer K. H. Simplified scheme for routine identification of human Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.82-88.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor R. R., Beaty H. N. Evaluation of positive blood cultures. Guidelines for early differentiation of contaminated from valid positive cultures. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Jul;130(1):84–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi J. T., Lampson B. C., Hoover D. L., Khan J. A. Comparison of epidemiologic markers for Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):56–60. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.56-60.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price S. B., Flournoy D. J. Comparison of antimicrobial susceptibility patterns among coagulase-negative staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Mar;21(3):436–440. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. F., Marples R. R. Changing resistance to antimicrobial drugs, and resistance typing in clinically significant strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Nov;15(4):475–484. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-4-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattler F. R., Foderaro J. B., Aber R. C. Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteremia associated with vascular catheters: an important cause of febrile morbidity in hospitalized patients. Infect Control. 1984 Jun;5(6):279–283. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700060331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell C. M., Clarridge J. E., Young E. J., Guthrie R. K. Clinical significance of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):236–239. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.236-239.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skahan J. M., Parisi J. T. Development of a bacteriophage-typing set for Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jul;6(1):16–18. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.1.16-18.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. C., Schimpff S. C., Newman K. A., Wiernik P. H. Staphylococcus epidermidis: an increasing cause of infection in patients with granulocytopenia. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Oct;97(4):503–508. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-4-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. P., Reller L. B., Murphy J. R., Lichtenstein K. A. The clinical significance of positive blood cultures: a comprehensive analysis of 500 episodes of bacteremia and fungemia in adults. I. Laboratory and epidemiologic observations. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jan-Feb;5(1):35–53. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. R., Van Scoy R. E., Washington J. A., 2nd Incidence of bacteremia in adults without infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;2(2):94–95. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Dudnick D. V., Chapin M., Ho W. G., Gale R. P., Martin W. J. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal bacteremia in patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Jan;143(1):32–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



