Abstract
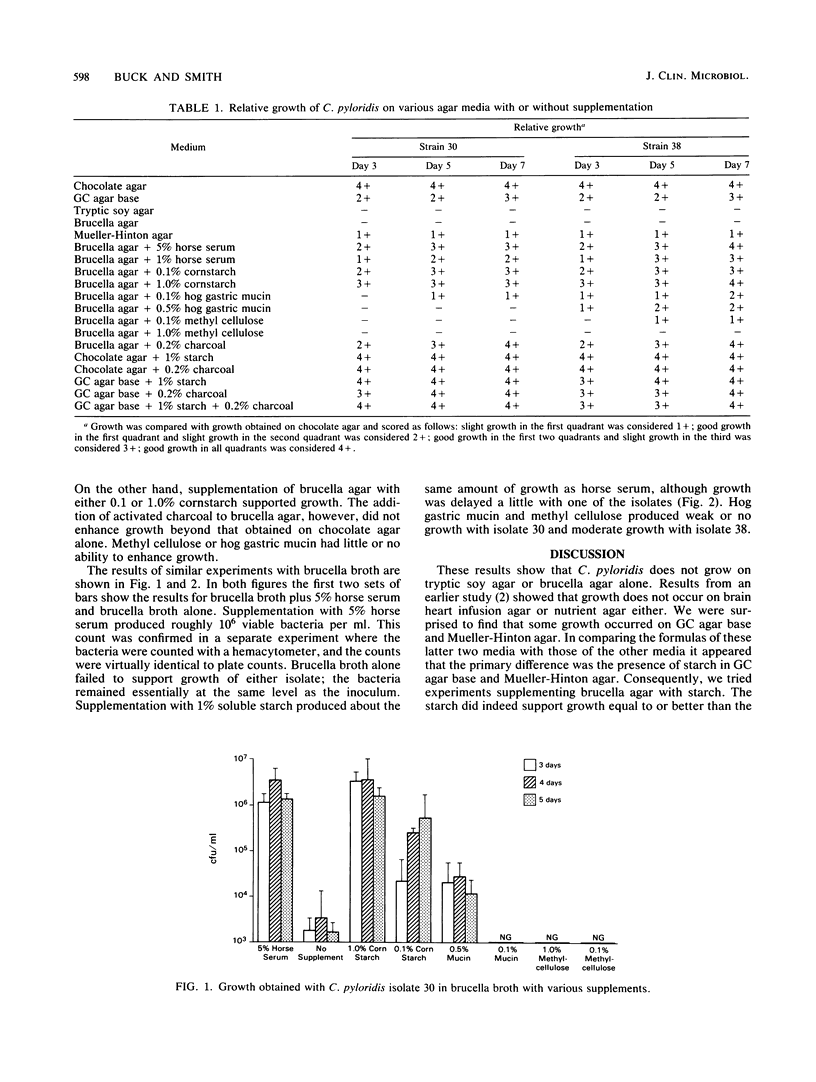
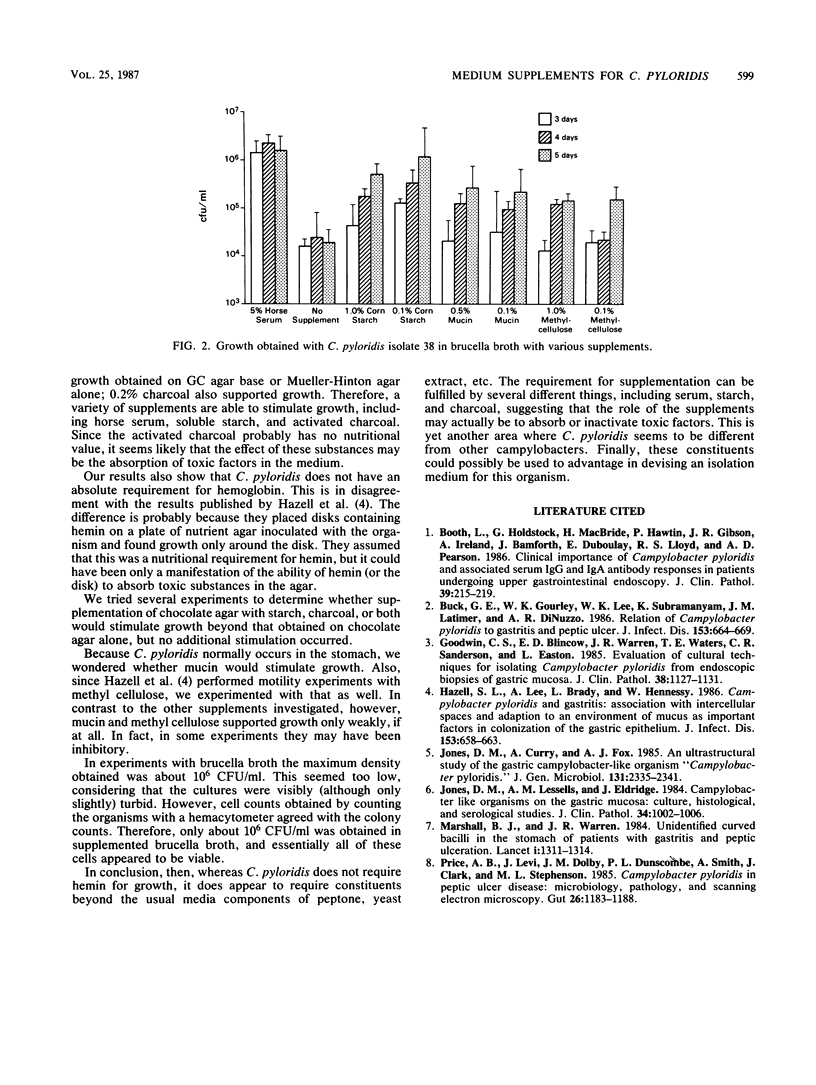
Experiments were conducted to define the growth requirements of Campylobacter pyloridis, a newly discovered organism associated with gastritis and peptic ulcers. Two clinical isolates were streaked onto various media, and growth was assessed semiquantitatively according to relative colony size and extent of growth through the streak. The growth obtained on fresh chocolate agar, composed of GC agar base (Difco Laboratories, Detroit, Mich.) plus 1% hemin, was used as a reference. The organism grew on both GC agar base and Mueller-Hinton agar without supplementation, but less well than on chocolate agar. No growth occurred on tryptic soy or brucella agar. Supplementation of brucella agar with 1 or 5% horse serum or 0.1 or 1.0% cornstarch supported growth to about the same level as GC agar base alone. Supplementation with hog gastric mucin or methyl cellulose supported weak growth. GC agar base with 1% starch or 0.2% charcoal supported growth as well as chocolate agar. Experiments with brucella broth provided similar results. Cornstarch and methyl cellulose partially replaced the requirement for serum, but methyl cellulose and hog gastric mucin did not. These results show that some form of supplementation is necessary for growth of C. pyloridis. This can be starch, serum, charcoal, or hemin, but hemin is not an absolute requirement for growth.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booth L., Holdstock G., MacBride H., Hawtin P., Gibson J. R., Ireland A., Bamforth J., DuBoulay C. E., Lloyd R. S., Pearson A. D. Clinical importance of Campylobacter pyloridis and associated serum IgG and IgA antibody responses in patients undergoing upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Feb;39(2):215–219. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck G. E., Gourley W. K., Lee W. K., Subramanyam K., Latimer J. M., DiNuzzo A. R. Relation of Campylobacter pyloridis to gastritis and peptic ulcer. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):664–669. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., Blincow E. D., Warren J. R., Waters T. E., Sanderson C. R., Easton L. Evaluation of cultural techniques for isolating Campylobacter pyloridis from endoscopic biopsies of gastric mucosa. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Oct;38(10):1127–1131. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.10.1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazell S. L., Lee A., Brady L., Hennessy W. Campylobacter pyloridis and gastritis: association with intercellular spaces and adaptation to an environment of mucus as important factors in colonization of the gastric epithelium. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):658–663. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Curry A., Fox A. J. An ultrastructural study of the gastric campylobacter-like organism 'Campylobacter pyloridis'. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Sep;131(9):2335–2341. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-9-2335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Lessells A. M., Eldridge J. Campylobacter like organisms on the gastric mucosa: culture, histological, and serological studies. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Sep;37(9):1002–1006. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.9.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Warren J. R. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984 Jun 16;1(8390):1311–1315. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91816-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. B., Levi J., Dolby J. M., Dunscombe P. L., Smith A., Clark J., Stephenson M. L. Campylobacter pyloridis in peptic ulcer disease: microbiology, pathology, and scanning electron microscopy. Gut. 1985 Nov;26(11):1183–1188. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.11.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


