Abstract
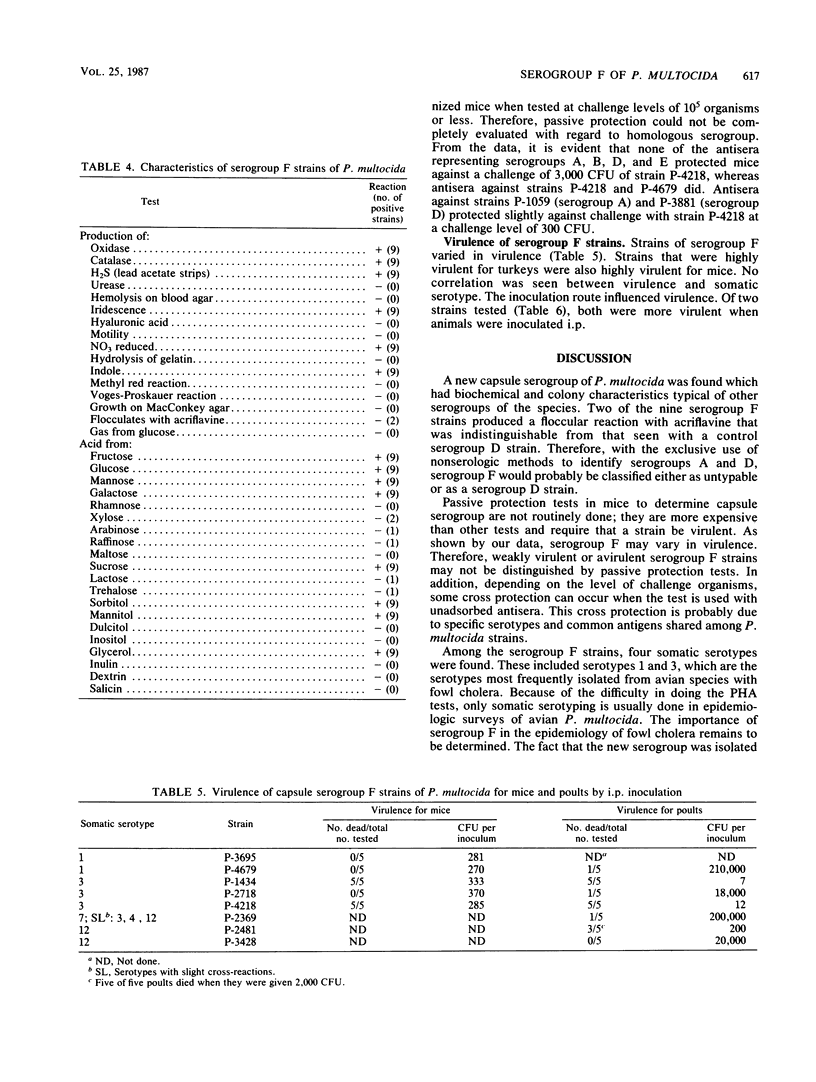
Four capsule serogroups (A, B, D, and E) have been described by using passive hemagglutination tests. Serogroups A and D predominant in pasteurelloses of avian species. A new capsule serogroup of Pasteurella multocida has been isolated from turkeys in Arkansas, California, Indiana, Iowa, Missouri, New Jersey, and Virginia. Strains belonging to the new serogroup were somatic serotype 1, 3, 7, or 12, and they varied in virulence for mice and poults. Antisera made in rabbits passively protected mice against challenge with the same serogroup regardless of somatic serotype.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CARTER G. R. CORRELATION BETWEEN HEMAGGLUTINATING ANTIBODY AND MOUSE PROTECTION IN ANTIPASTEURELLA (PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA) SERA. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Oct;10:753–756. doi: 10.1139/m64-095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTER G. R. Studies on Pasteurella multocida. I. A hemagglutination test for the identification of serological types. Am J Vet Res. 1955 Jul;16(60):481–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter G. R. Further Observations on Typing Pasteurella Multocida by the Indirect Hemagglutination Test. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1962 Oct;26(10):238–240. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter G. R., Rundell S. W. Identification of type A strains of P multocida using staphylococcal hyaluronidase. Vet Rec. 1975 Apr 12;96(15):343–343. doi: 10.1136/vr.96.15.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter G. R., Subronto P. Identification of type D strains of Pasteurella multocida with acriflavine. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Feb;34(2):293–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heddleston K. L., Gallagher J. E., Rebers P. A. Fowl cholera: gel diffusion precipitin test for serotyping Pasteruella multocida from avian species. Avian Dis. 1972 Jul-Sep;16(4):925–936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heddleston K. L., Wessman G. Characteristics of Pasteurella multocida of human origin. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Apr;1(4):377–383. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.4.377-383.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVACS N. Identification of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by the oxidase reaction. Nature. 1956 Sep 29;178(4535):703–703. doi: 10.1038/178703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimler R. B., Brogden K. A. Pasteurella multocida isolated from rabbits and swine: serologic types and toxin production. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Apr;47(4):730–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


