Abstract
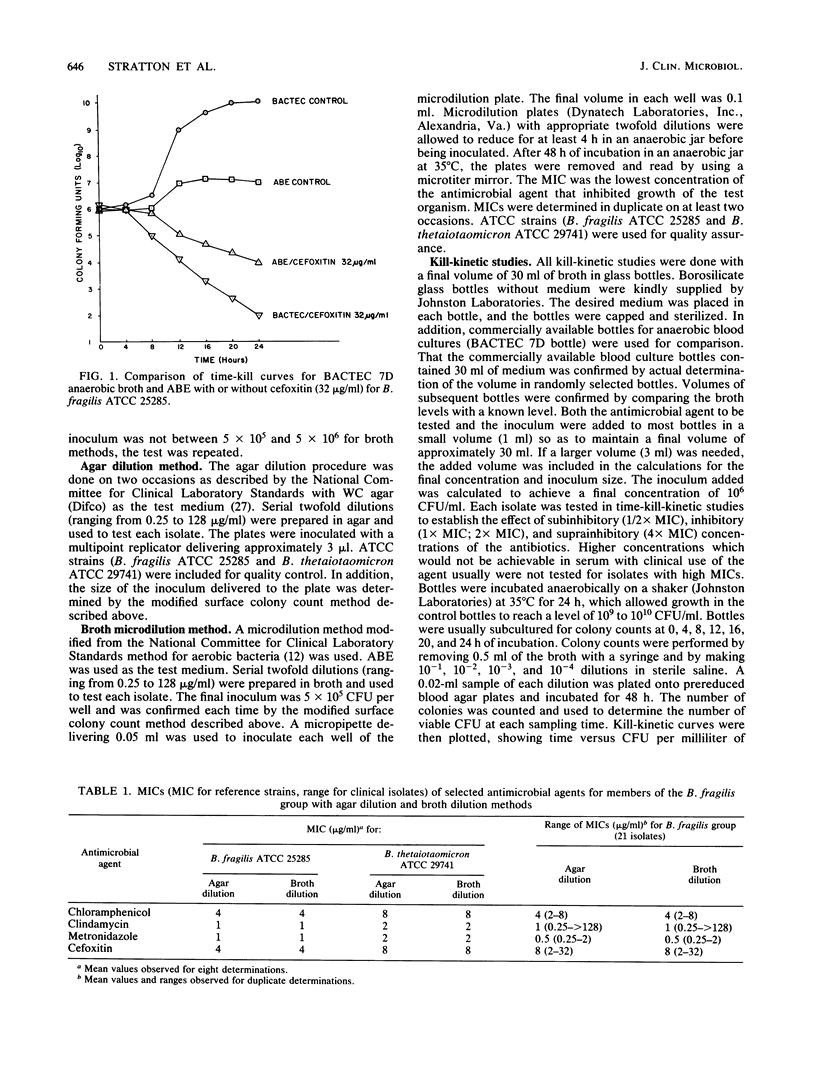
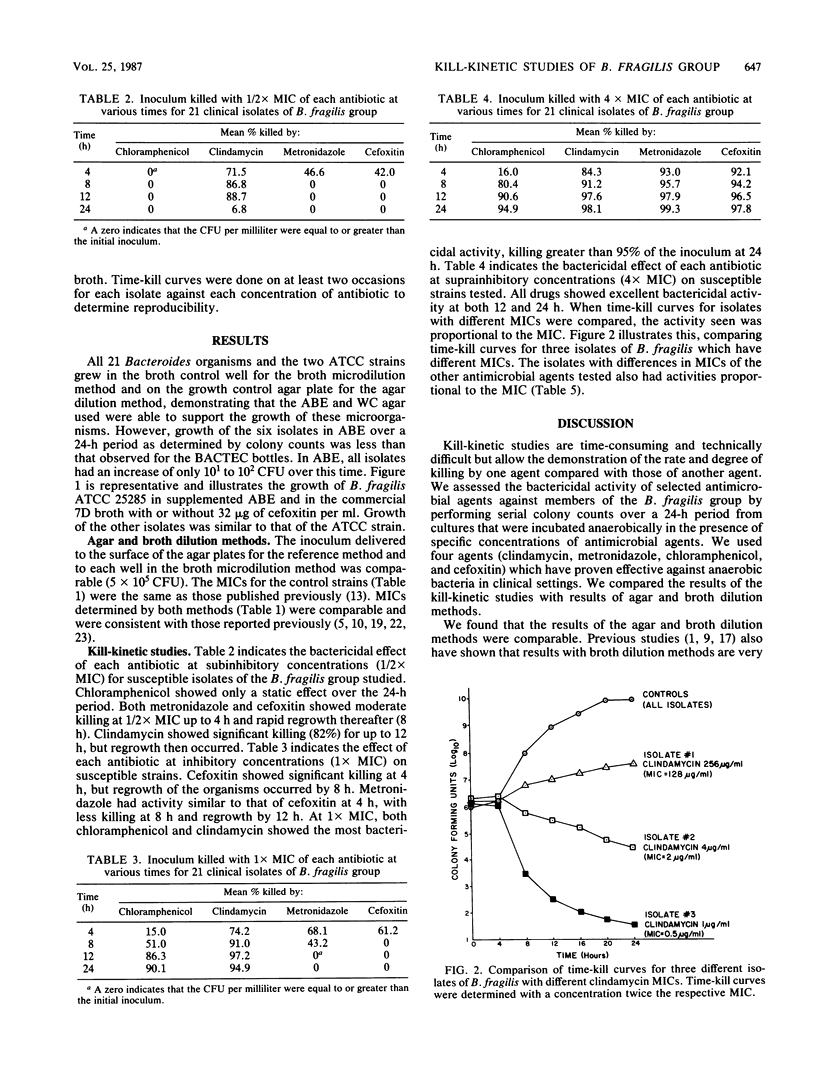
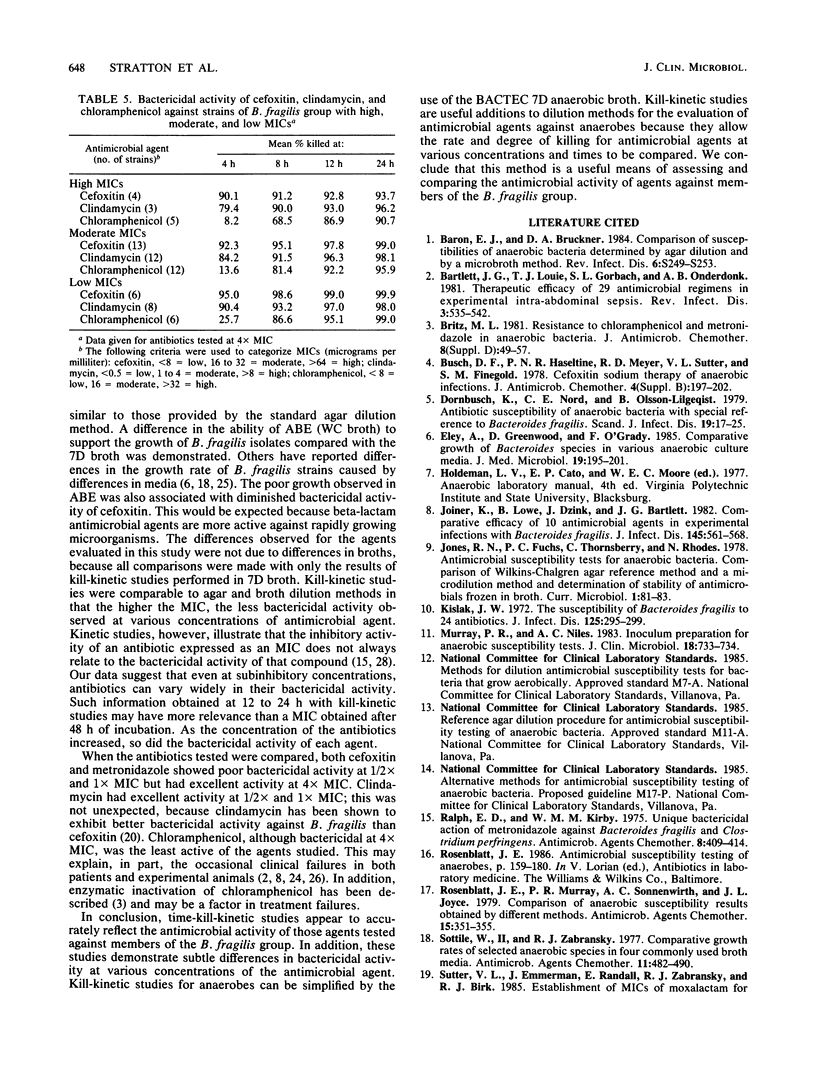
Kill-kinetic studies often are used to determine the rate and degree of killing of aerobic bacteria by antimicrobial agents. Few studies, however, make use of this method for determining antimicrobial activity against anaerobic bacteria. To evaluate kill-kinetic studies for anaerobes, kill-kinetic studies were performed for selected antimicrobial agents against members of the Bacteroides fragilis group and compared with MICs obtained by using a reference agar dilution method and a broth microdilution method. Results of the kill-kinetic studies showed that the degree of killing over a 24-h test period was related to the MIC for the test organism. In general, the higher the MIC of an antimicrobial agent for a test organism, the less the killing observed. In addition, these studies demonstrate subtle differences in bactericidal activity at various concentrations of the antimicrobial agents, which cannot be determined by agar or broth dilution methods. Kill-kinetic studies are a useful addition to dilution methods for the evaluation of antimicrobial agents against anaerobes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron E. J., Bruckner D. A. Comparison of susceptibilities of anaerobic bacteria determined by agar dilution and by a microbroth method. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;6 (Suppl 1):S249–S253. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_1.s249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Louie T. J., Gorbach S. L., Onderdonk A. B. Therapeutic efficacy of 29 antimicrobial regimens in experimental intraabdominal sepsis. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 May-Jun;3(3):535–542. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.3.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britz M. L. Resistance to chloramphenicol and metronidazole in anaerobic bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl 500):49–57. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_d.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch D. F., Heseltine P. N., Meyer R. D., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Cefoxitin sodium therapy of anaerobic infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Jul;4(B):197–202. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.suppl_b.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornbusch K., Nord C. E., Olsson-Liljeqvist B. Antibiotic susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria with special reference to Bacteroides fragilis. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1979;(19):17–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eley A., Greenwood D., O'Grady F. Comparative growth of Bacteroides species in various anaerobic culture media. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Apr;19(2):195–201. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner K., Lowe B., Dzink J., Bartlett J. G. Comparative efficacy of 10 antimicrobial agents in experimental infections with Bacteroides fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1982 Apr;145(4):561–568. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.4.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kislak J. W. The susceptibility of Bacteroides fragilis to 24 antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):295–299. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Niles A. C. Inoculum preparation for anaerobic susceptibility tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):733–734. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.733-734.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph E. D., Kirby W. M. Unique bactericidal action of metronidazole against Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium perfringens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Oct;8(4):409–414. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.4.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J. E., Murray P. R., Sonnenwirth A. C., Joyce J. L. Comparison of anaerobic susceptibility results obtained by different methods. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Mar;15(3):351–355. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.3.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottile W., 2nd, Zabransky R. J. Comparative growth rates of selected anaerobic species in four commonly used broth media. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):482–490. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Emmerman J., Randall E., Zabransky R. J., Birk R. J. Establishment of MICs of moxalactam for control and reference anaerobic organisms in agar dilution and microdilution techniques. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):424–426. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of Anaerobic bacteria to carbenicillin, cefoxitin, and related drugs. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):417–422. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson J. M., Thornsberry C. Preparing inoculum for susceptibility testing of anaerobes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):321–325. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.321-325.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Cuchural G. J., Jr, Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L., Aldridge K., Cleary T., Finegold S. M., Hill G., Iannini P., O'Keefe J. P. Nationwide study of the susceptibility of the Bacteroides fragilis group in the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):675–677. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Susceptibility of anaerobes to cefoxitin and other cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):128–132. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verweij-van Vught A., Sparrius M., Maclaren D. Loss of viability of Bacteroides fragilis and Bacteroides vulgatus in different media. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;4(4):433–434. doi: 10.1007/BF02148706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein W. M., Onderdonk A. B., Bartlett J. G., Louie T. J., Gorbach S. L. Antimicrobial therapy of experimental intraabdominal sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1975 Sep;132(3):282–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.3.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., Chalgren S. Medium for use in antibiotic susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Dec;10(6):926–928. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.6.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


