Abstract
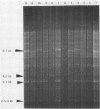
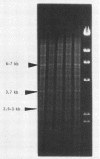
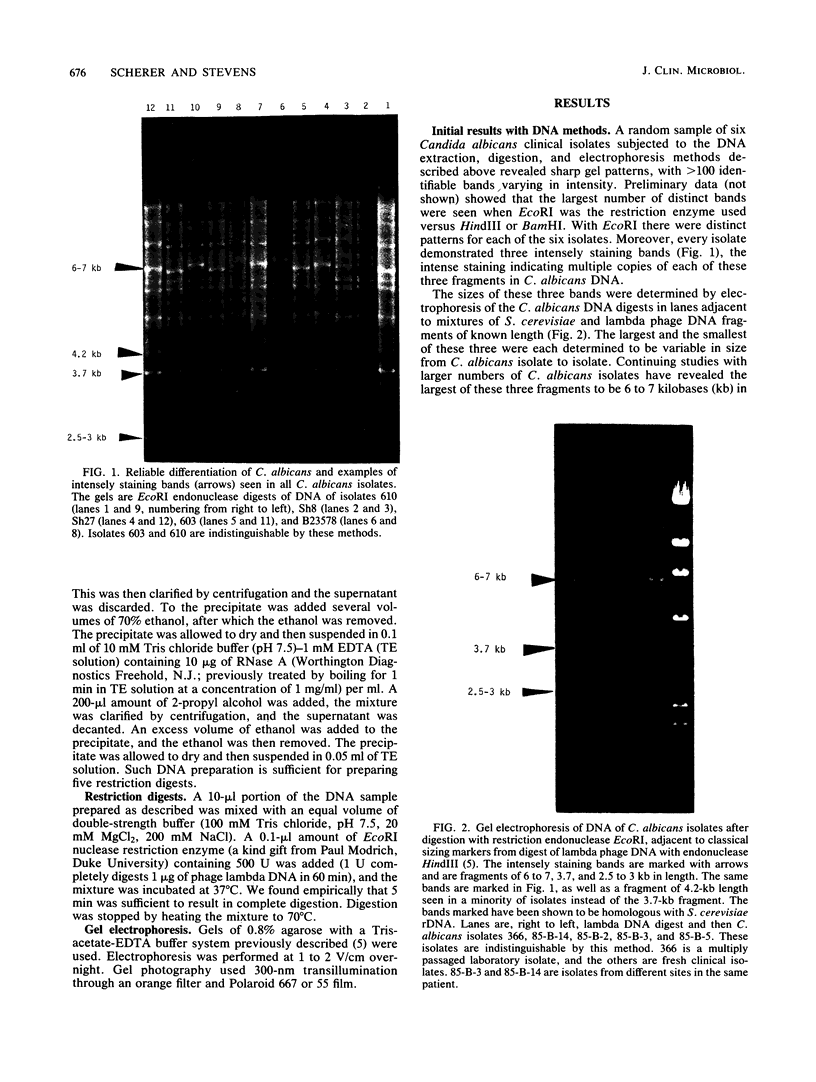
Methods are described for extraction of DNA from the yeast form of Candida spp., followed by digestion and electrophoresis of DNA fragments. The resulting gel patterns (greater than 100 bands) were used to type Candida isolates. Four intense bands identified, three of which are present in each isolate (6 to 7, 3.7 or 4.2, and 2.5 to 3 kilobases), appear to be DNA encoding the rRNA. The methods proved to be both simple and reproducible. The patterns were shown to be stable through several hundred doublings from multiple single colonies. A survey of isolates showed that, on the basis of similarity of gel patterns, several Candida species could be sorted into mutually exclusive groups, and subgroups could be created. Analyses of this survey suggested the possible epidemiologic and taxonomic applications of these methods. DNA typing methods appear to offer important potential advantages over phenotyping methods. The methods provide a base for further epidemiologic studies and for further development of techniques, such as the use of cloned probes for studies of DNA homology.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlson M., Osmond B. C., Botstein D. SUC genes of yeast: a dispersed gene family. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):799–803. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. W., Thomas M., Cameron J., St John T. P., Scherer S., Padgett R. A. Rapid DNA isolations for enzymatic and hybridization analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):404–411. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loose D. S., Stevens D. A., Schurman D. J., Feldman D. Distribution of a corticosteroid-binding protein in Candida and other fungal genera. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Aug;129(8):2379–2385. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-8-2379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCreight M. C., Warnock D. W. Enhanced differentiation of isolates of Candida albicans using a modified resistogram method. Mykosen. 1982 Nov;25(11):589–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1982.tb01926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinhof W. Demonstration of typical features of individual Candida albicans strains as a means of studying sources of infection. Chemotherapy. 1982;28 (Suppl 1):51–55. doi: 10.1159/000238153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Abbott A. B. A simple system for the presumptive identification of Candida albicans and differentiation of strains within the species. Sabouraudia. 1980 Dec;18(4):301–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Abbott A. B. Modification and extension of tests for differentiation of Candida species and strains. Sabouraudia. 1983 Mar;21(1):79–81. doi: 10.1080/00362178385380111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Abbott A. B., Stiller R. L., Scholer H. J., Polak A., Stevens D. A. Analysis of Candida albicans phenotypes from different geographical and anatomical sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):849–857. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.849-857.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen P., Thomas M., Kramer R. A., Davis R. W. Unique arrangement of coding sequences for 5 S, 5.8 S, 18 S and 25 S ribosomal RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae as determined by R-loop and hybridization analysis. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 15;123(3):387–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonelli L., Archibusacci C., Sestito M., Morace G. Killer system: a simple method for differentiating Candida albicans strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):774–780. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.774-780.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Román M. C., Linares Sicilia M. J. Preliminary investigation of Candida albicans biovars. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):430–431. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.430-431.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skorepová M., Hauck H. Differentiation of Candida albicans biotypes by the method of Odds and Abbott. Mykosen. 1985 Jul;28(7):323–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1985.tb02137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiller R. L., Bennett J. E., Scholer H. J., Wall M., Polak A., Stevens D. A. Susceptibility to 5-fluorocytosine and prevalence of serotype in 402 Candida albicans isolates from the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):482–487. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. W., Speller D. C., Day J. K., Farrell A. J. Resistogram method for differentiation of strains of Candida albicans. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;46(3):571–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb00857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. W. Typing of Candida albicans. J Hosp Infect. 1984 Sep;5(3):244–252. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(84)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson M. I., Samaranayake L. P., MacFarlane T. W. Biotypes of oral Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis isolates. J Med Vet Mycol. 1986 Feb;24(1):81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Lasker B. A., Sirotkin K., Riggsby W. S. Repetitive DNA of Candida albicans: nuclear and mitochondrial components. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):918–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.918-924.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]