Abstract
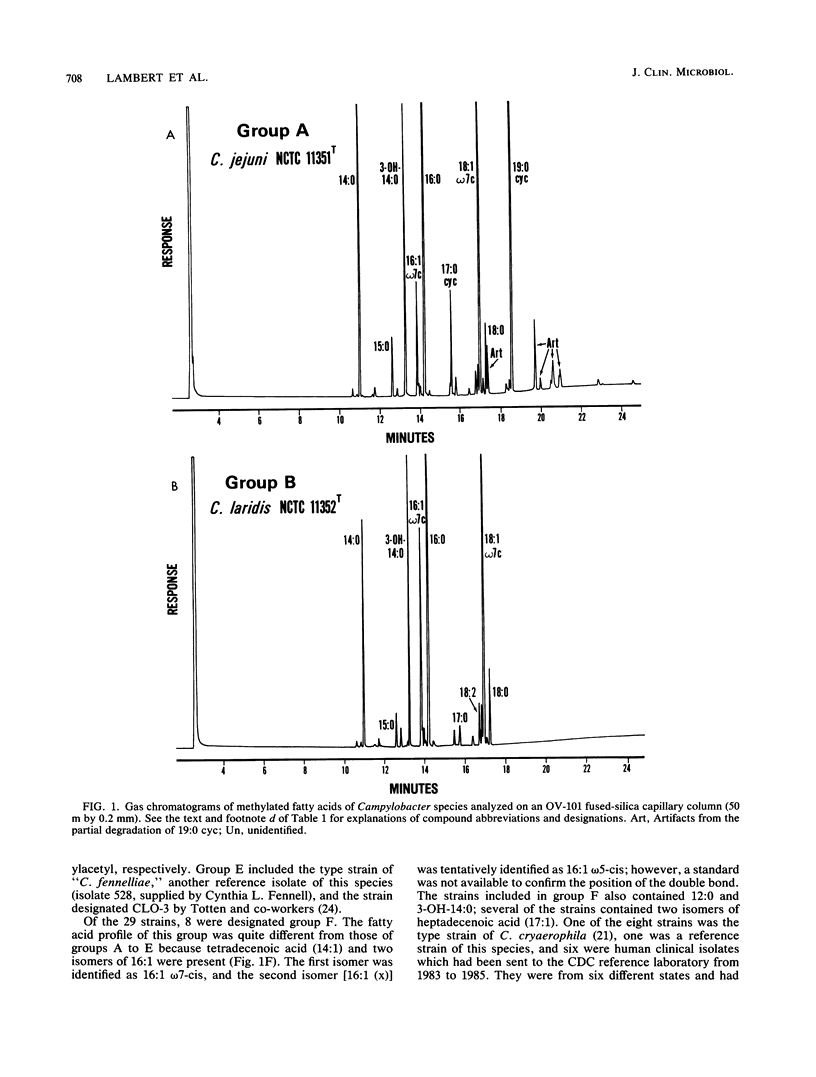
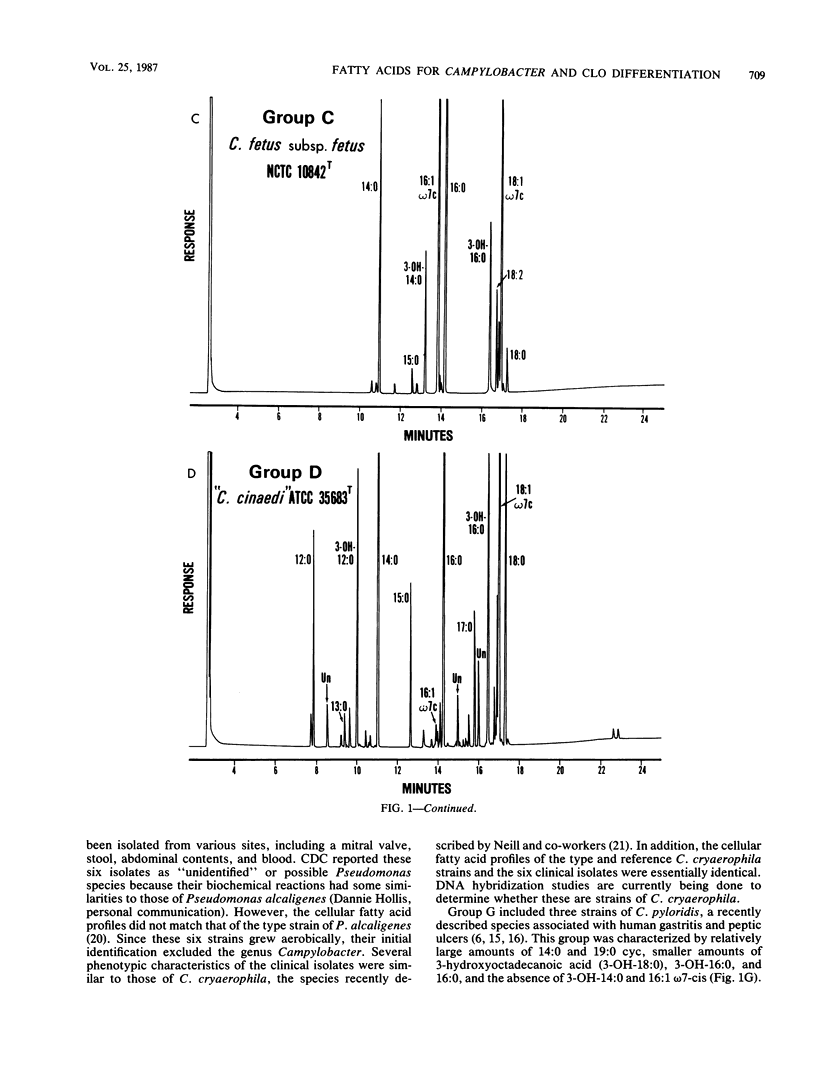
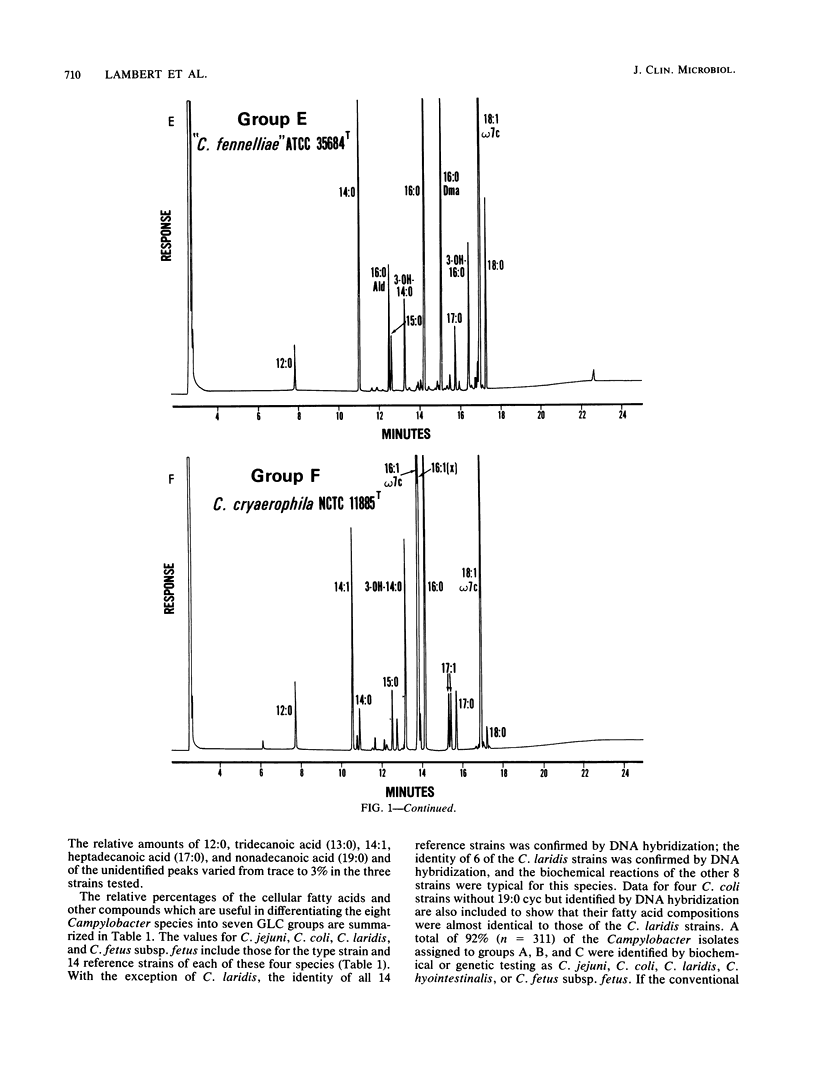
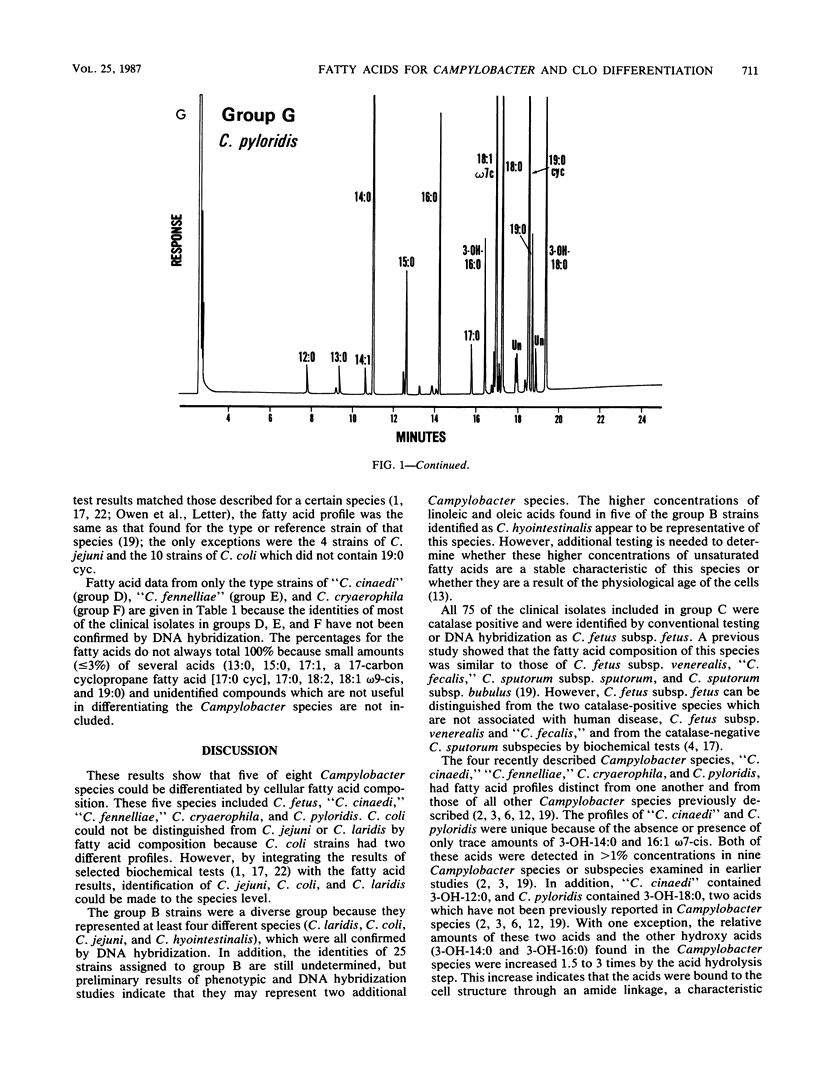
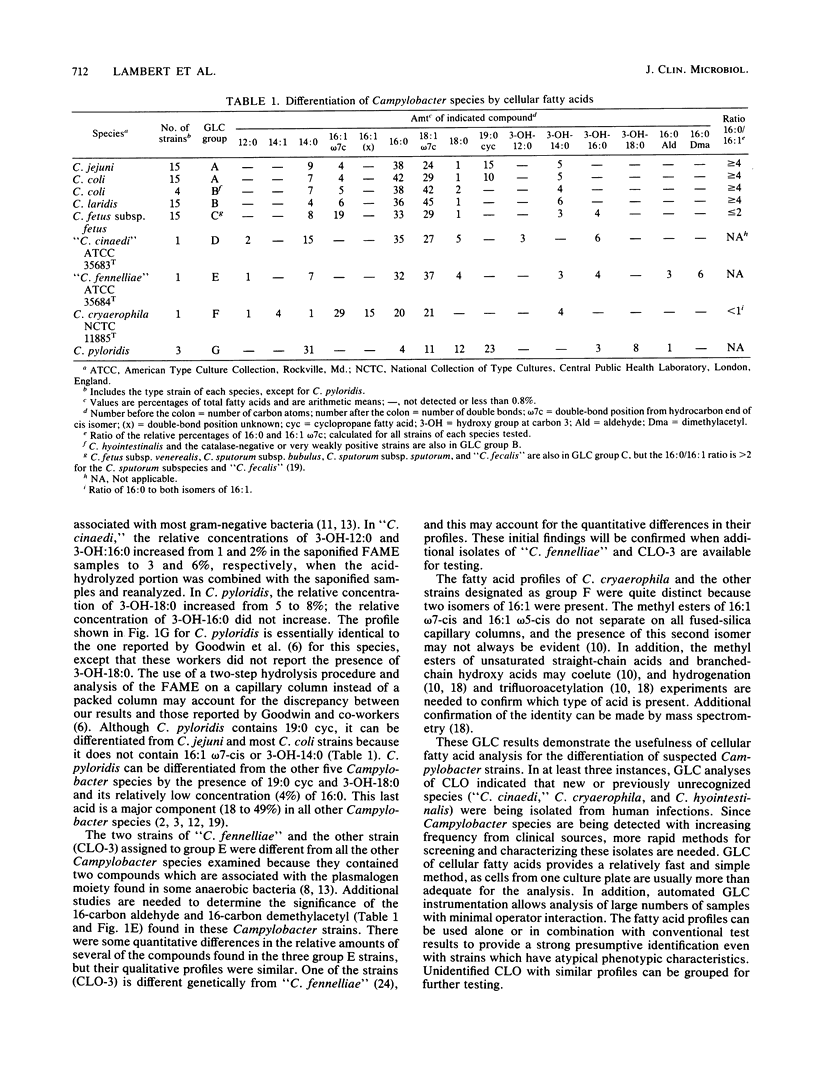
The cellular fatty acid compositions of 368 strains of Campylobacter species or Campylobacter-like organisms were determined by gas-liquid chromatography. Most of the strains (339) were placed in one of three groups based on differences in fatty acid profiles. Group A contained Campylobacter jejuni (97%) and most C. coli (83%) strains and was characterized by the presence of a 19-carbon cyclopropane fatty acid (19:0 cyc) and 3-hydroxytetradecanoic acid (3-OH-14:0). Group B included all C. laridis and some C. coli (17%) strains; its profile was similar to that of group A, except that 19:0 cyc was absent. Group C contained C. fetus subsp. fetus and C. fetus subsp. veneralis and was characterized by the presence of 3-OH-14:0 and 3-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid (3-OH-16:0) and the absence of 19:0 cyc. Twenty-nine isolates were placed in four additional groups. Group D included the type strain of "C. cinaedi" and 14 other isolates, which were differentiated by the presence of dodecanoic acid (12:0), 3-hydroxydodecanoic acid (3-OH-12:0), and 3-OH-16:0 and the absence of hexadecenoic acid (16:1) and 3-OH-14:0. Group E contained the type strain of "C. fennelliae" and two additional isolates, which were differentiated by the presence of a 16-carbon aldehyde and a 16-carbon dimethylacetyl and the absence of 16:1. Group F included the type strain and one reference strain of C. cryaerophila and six human isolates whose phenotypic characteristics were similar to those of this species; this group was distinguished by the presence of two isomers of 16:1, tetradecenoic acid (14:1), and 3-OH-14:0. Group G included three stains of C. pyloridis and was characterized by the presence of 19:0 cyc, 3-OH-16:0, and 3-hydroxyoctadecanoic acid (3-OH-18:0) and by the absence of 16:1 and 3-OH-14:0.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J., Moss C. W., Weaver R. E. Cellular fatty acid composition of Campylobacter fetus. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 May;11(5):448–451. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.5.448-451.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis M. A. Cellular fatty acid profiles of campylobacters. Med Lab Sci. 1983 Oct;40(4):333–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds P., Patton C. M., Barrett T. J., Morris G. K., Steigerwalt A. G., Brenner D. J. Biochemical and genetic characteristics of atypical Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus strains isolated from humans in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):936–940. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.936-940.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhart C. J., Edmonds P., Ward G. E., Kurtz H. J., Brenner D. J. "Campylobacter hyointestinalis" sp. nov.: a new species of Campylobacter found in the intestines of pigs and other animals. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):715–720. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.715-720.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., McCulloch R. K., Armstrong J. A., Wee S. H. Unusual cellular fatty acids and distinctive ultrastructure in a new spiral bacterium (Campylobacter pyloridis) from the human gastric mucosa. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Apr;19(2):257–267. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-2-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert G. A., Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N., McKinney R. M. Correlation of an expanded direct fluorescent-antibody system with an established passive hemagglutination system for serogrouping strains of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1064–1069. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1064-1069.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen E., Hofstad T. Fatty acids of Fusobacterium species: taxonomic implications. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Mar;123(1):163–171. doi: 10.1099/00221287-123-1-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krausse R., Ullmann U. Studies on the identification of Campylobacter species using biochemical tests and high-performance liquid chromatography. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Nov;260(3):342–360. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(85)80023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. A., Moss C. W. Comparison of the effects of acid and base hydrolyses on hydroxy and cyclopropane fatty acids in bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1370–1377. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1370-1377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., McGechie D. B., Rogers P. A., Glancy R. J. Pyloric Campylobacter infection and gastroduodenal disease. Med J Aust. 1985 Apr 15;142(8):439–444. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1985.tb113444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megraud F., Bonnet F., Garnier M., Lamouliatte H. Characterization of "Campylobacter pyloridis" by culture, enzymatic profile, and protein content. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):1007–1010. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.1007-1010.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Dees S. B. Identification of microorganisms by gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of cellular fatty acids. J Chromatogr. 1975 Oct 29;112:594–604. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)99988-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Kai A., Lambert M. A., Patton C. Isoprenoid quinone content and cellular fatty acid composition of Campylobacter species. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):772–776. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.772-776.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Samuels S. B., Weaver R. E. Cellular fatty acid composition of selected Pseudomonas species. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Oct;24(4):596–598. doi: 10.1128/am.24.4.596-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B., Benjamin J. Differentiation of enteropathogenic Campylobacter. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Nov;33(11):1122–1122. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.11.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauxe R. V., Patton C. M., Edmonds P., Barrett T. J., Brenner D. J., Blake P. A. Illness associated with Campylobacter laridis, a newly recognized Campylobacter species. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):222–225. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.222-225.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Fennell C. L., Tenover F. C., Wezenberg J. M., Perine P. L., Stamm W. E., Holmes K. K. Campylobacter cinaedi (sp. nov.) and Campylobacter fennelliae (sp. nov.): two new Campylobacter species associated with enteric disease in homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):131–139. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


