Abstract
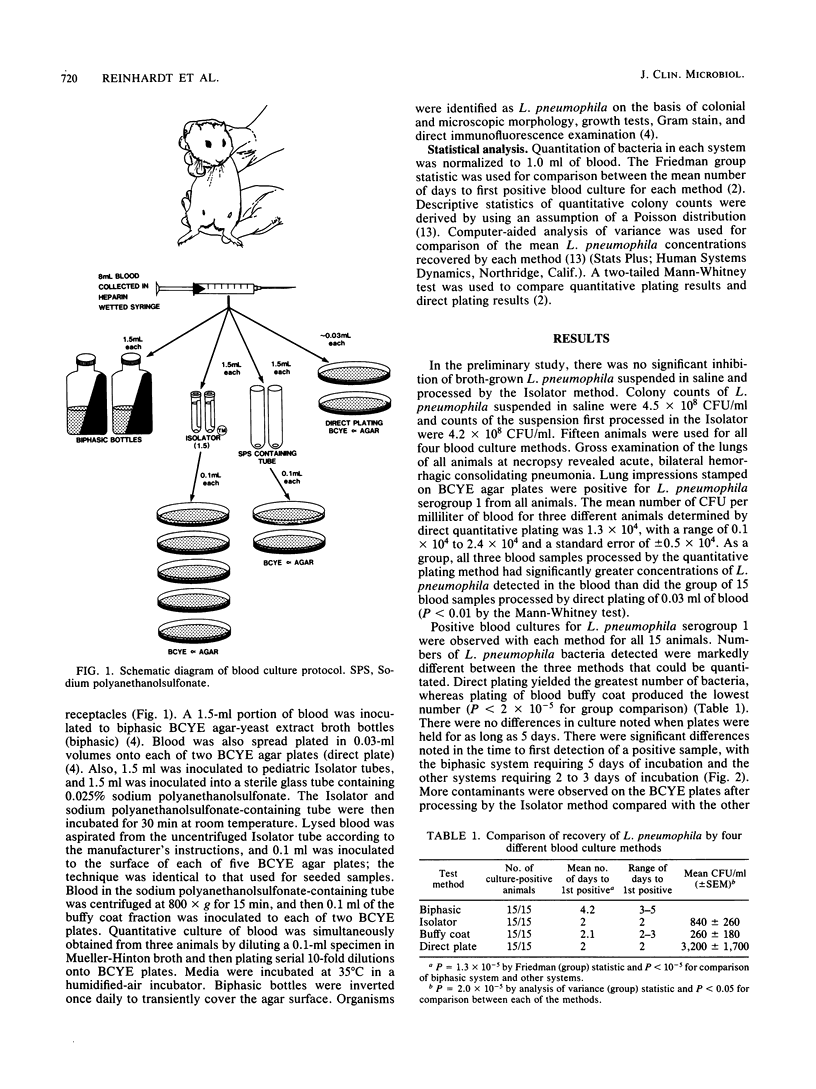
Blood was cultured from guinea pigs with experimental Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 pneumonia, using four different methods. A 0.03-ml amount was spread onto each of several plates of buffered charcoal-yeast extract supplemented with alpha-ketoglutarate (BCYE) (direct plate); 1.5 ml each was inoculated into a BCYE agar-yeast extract broth bottle (biphasic), a pediatric Isolator tube (E. I. du Pont de Nemours & Co., Inc., Wilmington, Del.), and a glass tube containing 0.025% sodium polyanethanolsulfonate. Blood processed in the Isolator tube was plated on BCYE, as was the buffy coat blood fraction, which was obtained by centrifugation of the tube containing sodium polyanethanolsulfonate and blood. Observations were made of the number of positive cultures, the time to detection of positive cultures, and the absolute bacterial concentrations. Each system was equally sensitive in detecting bacteremia. The biphasic method required 5 days for cultures to become positive, whereas the other systems required 2 to 3 days to detect all positive cultures (P = 1.3 X 10(-5) by Friedman group statistic, and P less than 10(-5) for comparison of the biphasic and other methods). The direct plating method demonstrated the best quantitative recovery of L. pneumophila in comparison to the other methods tested (P = 2.0 X 10(-5) by analysis of variance group statistic and P less than 0.05 for comparison between each of the methods). Quantitative recovery by the Isolator method was intermediate between the direct plating and buffy coat methods. The biphasic and Isolator blood culture methods performed poorly in comparison to the other methods, indicating the need for caution in choosing blood culture methods for Legionella isolation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chester B., Poulos E. G., Demaray M. J., Albin E., Prilucik T. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 from blood with nonsupplemented blood culture bottles. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):195–197. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.195-197.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn G. L., Barnes W. R. Rapid isolation of Legionella pneumophila from seeded donor blood. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):114–115. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.114-115.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Calarco K., Yasui V. K. Antimicrobial therapy of experimentally induced Legionnaires' disease in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Nov;130(5):849–856. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.5.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Meyer R. D., Finegold S. M. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from blood. Lancet. 1979 Apr 7;1(8119):750–751. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Interaction of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) with human phagocytes. I. L. pneumophila resists killing by polymorphonuclear leukocytes, antibody, and complement. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):386–397. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattimer G. L., Rhodes L. V., 3rd, Salventi J. F., Cepil B. R. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from clinical specimens: salutary effects of lung tissue dilution. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Jul;122(1):101–105. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrae A. D., Greaves P. W., Platts P. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from blood culture. Br Med J. 1979 Nov 10;2(6199):1189–1190. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6199.1189-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. S., Marrie T. J., Best L., Sumarah R. K., Peppard R. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from the blood of a patient with Legionnaires' disease. Can Med Assoc J. 1984 Nov 1;131(9):1085–1087. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D., Edelstein P. H., Kirby B. D., Louie M. H., Mulligan M. E., Morgenstein A. A., Finegold S. M. Legionnaires' disease: unusual clinical and laboratory features. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Aug;93(2):240–243. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-2-240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rihs J. D., Yu V. L., Zuravleff J. J., Goetz A., Muder R. R. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from blood with the BACTEC system: a prospective study yielding positive results. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):422–424. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.422-424.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr, Davis G. S., Gump D. W., Craighead J. E., Beaty H. N. Legionnaires' pneumonia after intratracheal inoculation of guinea pigs and rats. Lab Invest. 1982 Dec;47(6):568–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


