Abstract
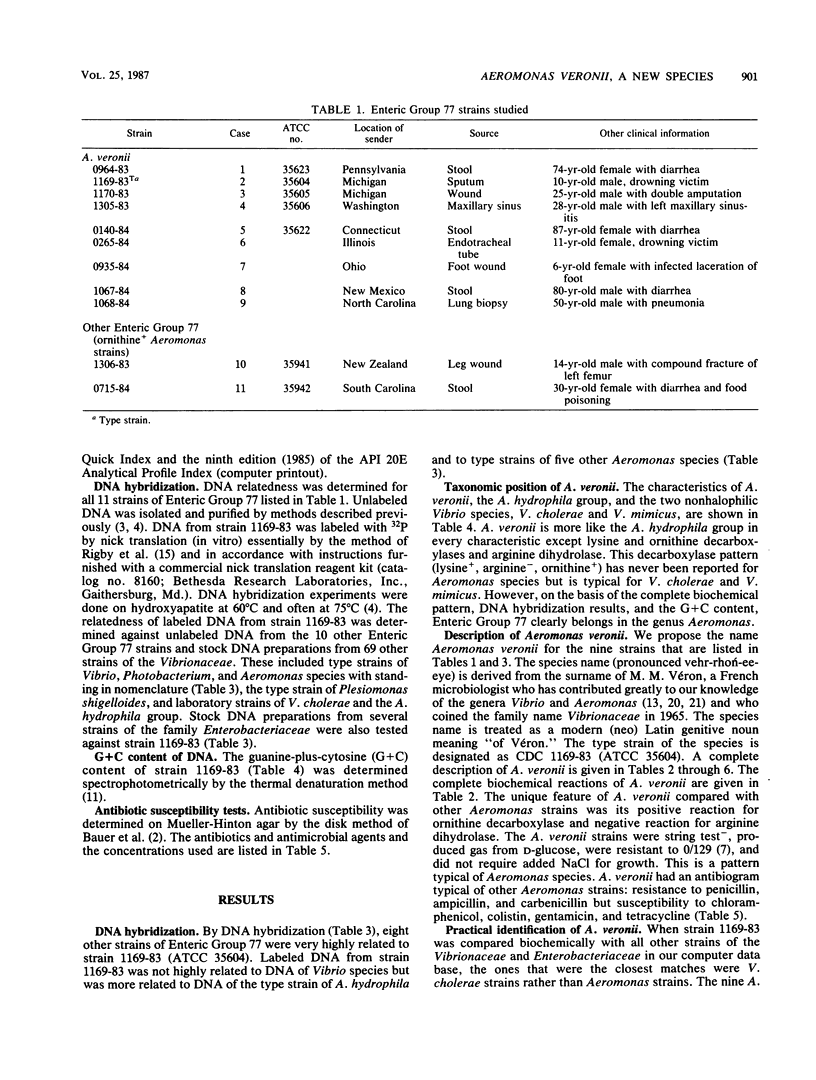
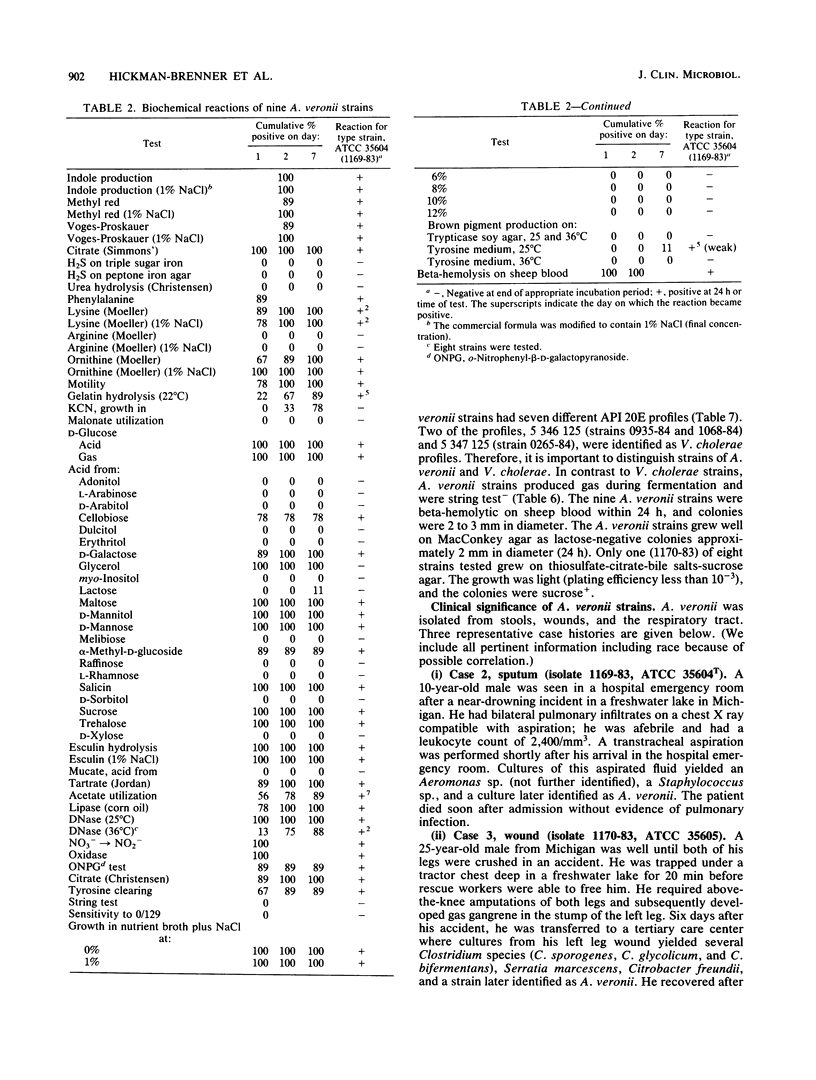
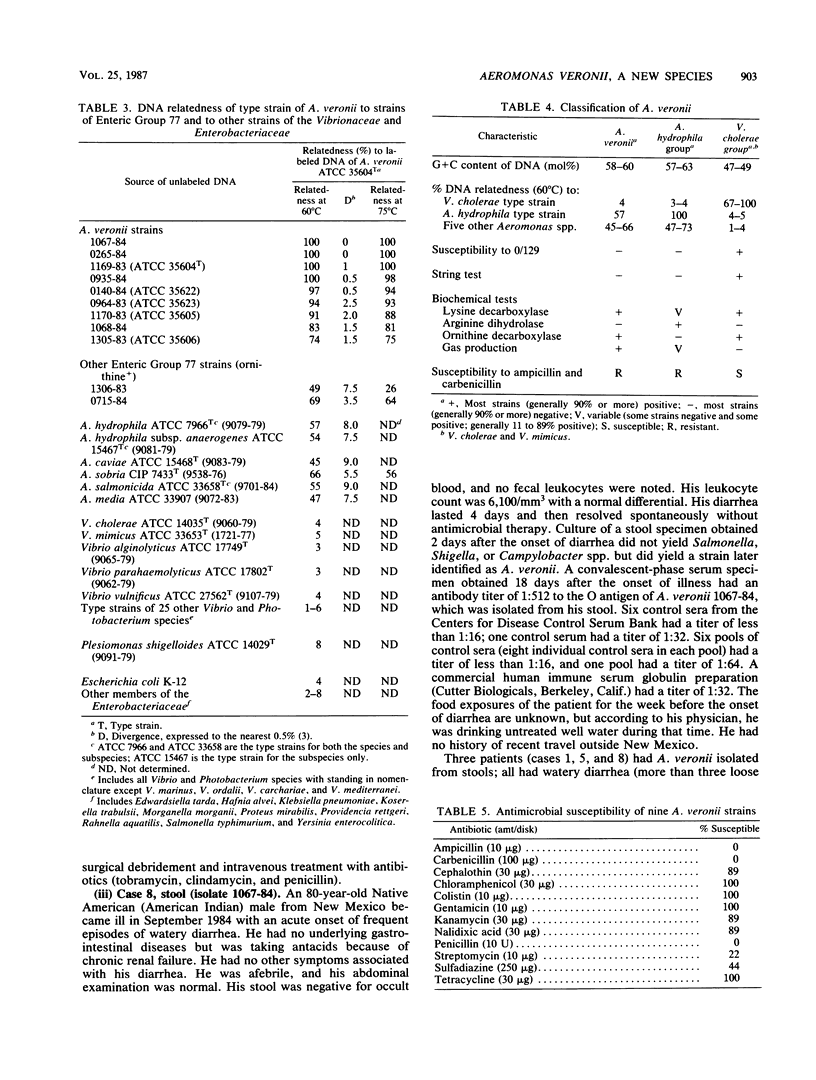
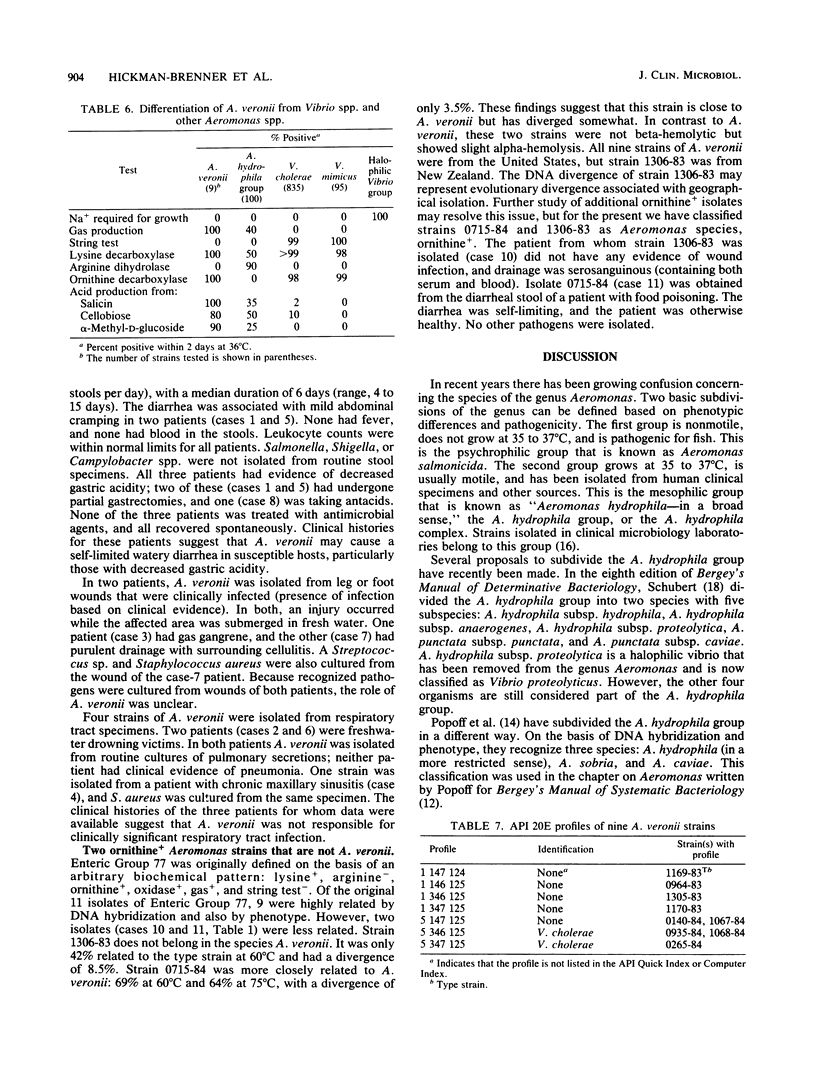
In 1983, the vernacular name Enteric Group 77 was coined for a group of strains that had been referred to our laboratory as "possible Vibrio cholerae except for gas production." By DNA-DNA hybridization (hydroxyapatite, 32P), 8 of 10 strains of Enteric Group 77 were very highly related to the labeled strain 1169-83 (74 to 100% at 60 degrees C and 75 to 100% at 75 degrees C; percent divergence, 0.0 to 2.5). Type strains of six other Aeromonas species were 45 to 66% related (60 degrees C) to strain 1169-83, but type strains of 27 Vibrio species were only 2 to 6% related. The name Aeromonas veronii is proposed for the highly related group of nine strains formerly known as Enteric Group 77. The type strain is designated as ATCC 35604 (CDC 1169-83). Strains of A. veronii grew well at 36 degrees C and had positive reactions at this temperature for indole, methyl red, Voges-Proskauer, citrate, lysine and ornithine decarboxylases, DNase, lipase, and motility; the strains had negative reactions for arginine decarboxylase, H2S, urea, and malonate. The following sugars were fermented: D-glucose (acid and gas), cellobiose (seven of nine strains), D-galactose, maltose, D-mannitol, D-mannose, alpha-methyl-D-glucoside (eight of nine strains), salicin, sucrose, and trehalose. The following sugars were not fermented: adonitol, L-arabinose, D-arabitol, dulcitol, erythritol, myo-inositol, lactose, raffinose, L-rhamnose, D-sorbitol, and D-xylose. The positive ornithine decarboxylase reaction differentiates A. veronii from other Aeromonas species. The antibiogram of A. veronii is typical of other Aeromonas strains (resistance to ampicillin and carbenicillin and susceptibility to most other agents). A. veronii strains were isolated from three clinical sources: respiratory secretions of four victims of drowning or near drowning in fresh water (probably not clinically significant); infected wounds of two patients previously exposed to fresh water (unknown clinical significance); and stools from three patients with diarrhea (probably clinically significant).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Fanning G. R., Johnson K. E., Citarella R. V., Falkow S. Polynucleotide sequence relationships among members of Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):637–650. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.637-650.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman-Brenner F. W., Huntley-Carter G. P., Fanning G. R., Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Koserella trabulsii, a new genus and species of Enterobacteriaceae formerly known as Enteric Group 45. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):39–42. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.39-42.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman F. W., Farmer J. J., 3rd, Hollis D. G., Fanning G. R., Steigerwalt A. G., Weaver R. E., Brenner D. J. Identification of Vibrio hollisae sp. nov. from patients with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):395–401. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.395-401.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman F. W., Farmer J. J., 3rd Salmonella typhi: identification, antibiograms, serology, and bacteriophage typing. Am J Med Technol. 1978 Dec;44(12):1149–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman F. W., Framer J. J., 3rd, Steigerwalt A. G., Brenner D. J. Unusual groups of Morganella ("Proteus") morganii isolated from clinical specimens: lysine-positive and ornithine-negative biogroups. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):88–94. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.88-94.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M., Véron M. A taxonomic study of the Aeromonas hydrophila-Aeromonas punctata group. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):11–22. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


