Abstract
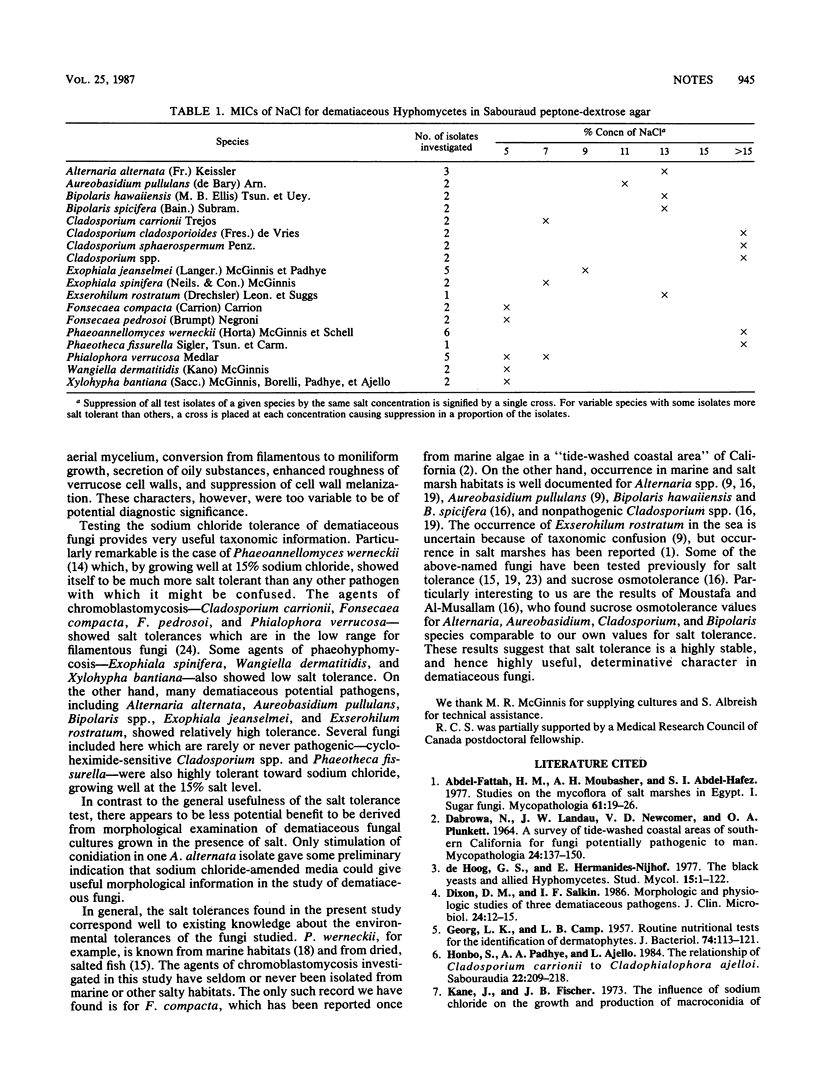
Seventeen taxa of dematiaceous fungi isolated from humans were tested to determine their responses to various concentrations of sodium chloride in vitro. Five groups of species were recognized on the basis of differing tolerances. Phaeoannellomyces werneckii was distinguished by its tolerance of greater than or equal to 15% NaCl; most dematiaceous pathogens were suppressed at less than or equal to 7% NaCl.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DABROWA N., LANDAU J. W., NEWCOMER V. D., PLUNKETT O. A. A SURVEY OF TIDE-WASHED COASTAL AREAS OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA FOR FUNGI POTENTIALLY PATHOGENIC TO MAN. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1964 Dec 15;24:136–150. doi: 10.1007/BF02075556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon D. M., Salkin I. F. Morphologic and physiologic studies of three dematiaceous pathogens. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):12–15. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.12-15.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEORG L. K., CAMP L. B. Routine nutritional tests for the identification of dermatophytes. J Bacteriol. 1957 Aug;74(2):113–121. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.2.113-121.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honbo S., Padhye A. A., Ajello L. The relationship of Cladosporium carrionii to Cladophialophora ajelloi. Sabouraudia. 1984;22(3):209–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J., Fischer J. B. The effect of sodium chloride on the growth and morphology of dermatophytes and some other keratolytic fungi. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jun;21(6):742–749. doi: 10.1139/m75-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis M. R., Borelli D., Padhye A. A., Ajello L. Reclassification of Cladosporium bantianum in the genus Xylohypha. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1148–1151. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1148-1151.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis M. R., Schell W. A., Carson J. Phaeoannellomyces and the Phaeococcomycetaceae, new dematiaceous blastomycete taxa. Sabouraudia. 1985 Jun;23(3):179–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padhye A. A., Ajello L. The taxonomic status of the hedgehog fungus Trichophyton erinacei. Sabouraudia. 1977 Jul;15(2):103–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawar V. H., Rahalkar P. W., Thirumalachar M. J. Cladosporium wernecki Horta isolated from marine habitat. Hindustan Antibiot Bull. 1965 Aug;8(1):19–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönborn C. NaCl-Toleranz bei Aspergillen und Dermatophyten der menschlichen Mikroflora. Mykosen. 1981 Dec;24(12):752–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönborn C. Uber die Kochsalz-Toleranz von Hefepilzen der menschlichen Mikroflora. Dermatol Monatsschr. 1976 Jul;162(7):564–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steadham J. E., Geis P. A., Simmank J. L. Use of carbohydrate and nitrate assimilations in the identification of dematiaceous fungi. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 May;5(1):71–75. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(86)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tresner H. D., Hayes J. A. Sodium chloride tolerance of terrestrial fungi. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Aug;22(2):210–213. doi: 10.1128/am.22.2.210-213.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



