Abstract
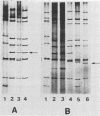
Swine rotaviruses displaying distinctive electropherotypes were isolated from the feces of diarrheic piglets in two swine herds in the province of Buenos Aires, Argentina. In one case all samples isolated showed abnormal electropherotypes. All samples were classified as group A reactive when assayed by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Three samples from this herd were adapted to grow in tissue culture. The electrophoretic pattern of the genomic RNA as well as the group A reactivity of one of these viruses was retained after cloning in MA-104 cells. In the other pig unit were found samples displaying both classical and abnormal electropherotypes. These viruses were also positive in the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; however, since they could not be adapted to grow in tissue culture, this classification must be considered tentative. The abnormal electropherotype exhibited by these pig viruses strongly resembles those of human origin called super short.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen A. M., Desselberger U. Reassortment of human rotaviruses carrying rearranged genomes with bovine rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2703–2714. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besselaar T. G., Rosenblatt A., Kidd A. H. Atypical rotavirus from South African neonates. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1986;87(3-4):327–330. doi: 10.1007/BF01315311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Agnes A. G., Cross R. F. Porcine pararotavirus: detection, differentiation from rotavirus, and pathogenesis in gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):312–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.312-319.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Clarke I. N., McCrae M. A. Characterization of an antigenically distinct porcine rotavirus. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1058–1062. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1058-1062.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasey D., Banks J. The commonest rotaviruses from neonatal lamb diarrhoea in England and Wales have atypical electropherotypes. Vet Rec. 1984 Sep 29;115(13):326–327. doi: 10.1136/vr.115.13.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasey D., Davies P. Atypical rotaviruses in pigs and cattle. Vet Rec. 1984 Jan 7;114(1):16–17. doi: 10.1136/vr.114.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. H., Estes M. K., Rangelova S. M., Shindarov L. M., Melnick J. L., Graham D. Y. Detection of antigenically distinct rotaviruses from infants. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):523–526. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.523-526.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan K. T., Twist E. M., Horton-Slight P., Forrer C., Bell L. M., Jr, Plotkin S. A., Clark H. F. Epidemiology of rotavirus electropherotypes determined by a simplified diagnostic technique with RNA analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):753–758. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.753-758.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Puerto F., Soler C., González N. Characterization of a human pararotavirus. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):112–116. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.112-116.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa A., Inouye S., Matsuno S., Yamaoka K., Eko R., Suharyono W. Isolation of human rotaviruses with a distinct RNA electrophoretic pattern from Indonesia. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(6):719–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herring A. J., Inglis N. F., Ojeh C. K., Snodgrass D. R., Menzies J. D. Rapid diagnosis of rotavirus infection by direct detection of viral nucleic acid in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):473–477. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.473-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hundley F., Biryahwaho B., Gow M., Desselberger U. Genome rearrangements of bovine rotavirus after serial passage at high multiplicity of infection. Virology. 1985 May;143(1):88–103. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90099-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung T., Chen G. M., Wang C. G., Yao H. L., Fang Z. Y., Chao T. X., Chou Z. Y., Ye W., Chang X. J., Den S. S. Waterborne outbreak of rotavirus diarrhoea in adults in China caused by a novel rotavirus. Lancet. 1984 May 26;1(8387):1139–1142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Hasegawa A., Mukoyama A., Inouye S. A candidate for a new serotype of human rotavirus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):623–624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.623-624.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Allan G. M., Todd D., McFerran J. B., McCracken R. M. Isolation from chickens of a rotavirus lacking the rotavirus group antigen. J Gen Virol. 1981 Aug;55(Pt 2):405–413. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-2-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas J. C., Cohen J., Fortier B., Lourenco M. H., Bricout F. Isolation of a human pararotavirus. Virology. 1983 Jan 15;124(1):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Brown J. F., McCrae M. A. Molecular characterization of rotaviruses with distinct group antigens. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2093–2101. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Hundley F., Chrystie I., McCrae M. A., Desselberger U. The genomes of rotaviruses isolated from chronically infected immunodeficient children. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jul;65(Pt 7):1141–1150. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-7-1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira H. G., Azeredo R. S., Leite J. P., Andrade Z. P., De Castro L. A combined enzyme immunoassay for rotavirus and adenovirus (EIARA). J Virol Methods. 1985 Jan;10(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(85)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira H. G., Leite J. P., Azeredo R. S., de Farias V., Sutmoller F. An atypical rotavirus detected in a child with gastroenteritis in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1983 Jul-Sep;78(3):245–250. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02761983000300002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., La Torre J., Kelley D. E., Greenberg J. R. On the lability of poly(A) sequences during extraction of messenger RNA from polyribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Bishop R. F., Holmes I. H. Detection of a rotavirus-like agent associated with diarrhea in an infant. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):724–726. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.724-726.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Cross R. F., House J. A. Rotavirus-like, calicivirus-like, and 23-nm virus-like particles associated with diarrhea in young pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.105-111.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inaba Y., Shinozaki T., Fujii R., Matumoto M. Isolation of human rotavirus in cell cultures: brief report. Arch Virol. 1981;69(2):155–160. doi: 10.1007/BF01315159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigolo de San Juan C., Bellinzoni R. C., Mattion N., La Torre J., Scodeller E. A. Incidence of group A and atypical rotaviruses in Brazilian pig herds. Res Vet Sci. 1986 Sep;41(2):270–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Herring A. J., Campbell I., Inglis J. M., Hargreaves F. D. Comparison of atypical rotaviruses from calves, piglets, lambs and man. J Gen Virol. 1984 May;65(Pt 5):909–914. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-5-909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino A., Scodeller E. A., Bellinzoni R., Muchinik G. R., La Torre J. L. Detection of an atypical rotavirus associated with diarrhoea in Chaco, Argentina. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1986;80(1):120–122. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(86)90209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Reynolds D. L., Saif Y. M. Isolation and serial propagation of turkey rotaviruses in a fetal rhesus monkey kidney (MA104) cell line. Avian Dis. 1986 Jan-Mar;30(1):93–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Saif L. J., Moorhead P. D., Whitmoyer R. E. Porcine rotavirus-like virus (group B rotavirus): characterization and pathogenicity for gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):340–345. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.340-345.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]