Abstract
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation reportedly suppresses transcriptional activity of the cAMP-responsive element (CRE) in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase C (PEPCK-C) promoter and reduces hepatic PEPCK-C expression. Although a previous study found TORC2 phosphorylation to be involved in the suppression of AMPK-mediated CRE transcriptional activity, we herein present evidence that glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) phosphorylation induced by AMPK also plays an important role. We initially found that injecting fasted mice with 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleoside (AICAR) markedly increased Ser-9 phosphorylation of hepatic GSK3β within 15 min. Stimulation with AICAR or the GSK3β inhibitor SB-415286 strongly inhibited CRE-containing promoter activity in HepG2 cells. Using the Gal4-based transactivation assay system, the transcriptional activity of cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) was suppressed by both AICAR and SB415286, whereas that of TORC2 was repressed significantly by AICAR but very slightly by SB415286. These results show inactivation of GSK3β to directly inhibit CREB but not TORC2. Importantly, the AICAR-induced suppression of PEPCK-C expression was shown to be blunted by overexpression of GSK3β(S9G) but not wild-type GSK3β. In addition, AICAR stimulation decreased, whereas Compound C (AMPK inhibitor) increased CREB phosphorylation (Ser-129) in HepG2 cells. The time-courses of decreased CREB phosphorylation (Ser-129) and increased GSK3β phosphorylation were very similar. Furthermore, AMPK-mediated GSK3β phosphorylation was inhibited by an Akt-specific inhibitor in HepG2 cells, suggesting involvement of the Akt pathway. In summary, phosphorylation (Ser-9) of GSK3β is very likely to be critical for AMPK-mediated PEPCK-C gene suppression. Reduced CREB phosphorylation (Ser-129) associated with inactivation of GSK3β by Ser-9 phosphorylation may be the major mechanism underlying PEPCK-C gene suppression by AMPK-activating agents such as biguanide.
Hepatic PEPCK-C2 expression plays a critical role in the maintenance of glucose homeostasis, and activation of AMPK in the livers of fasted mice has been shown to reduce glucose production (1). The oral biguanide antidiabetic agent metformin and several factors including leptin and adiponectin reportedly activate AMPK, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce gluconeogenesis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (2–8). It was also reported that stimulation with the AMPK activator 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleoside (AICAR) suppresses hepatic PEPCK-C expression and the transcriptional activity of the cAMP-responsive element (CRE), which is present in the PEPCK-C promoter, actions similar to those of insulin (9).
AMPK achieves its downstream effects by immediate direct phosphorylation of enzyme substrates as well as long term effects on gene expression. For example, AMPK phosphorylates and inactivates acetyl-CoA carboxylase, resulting in suppression of the conversion of acetyl CoA to malonyl CoA (4). This malonyl CoA reduction allows entry of fatty acids into mitochondria and their subsequent oxidation (10, 11). Recently, as a molecular mechanism underlying AMPK-mediated PEPCK-C gene suppression, the phosphorylation of TORC2 (transducer of regulated CREB activity 2), a co-activator of cAMP-responsive element binding (CREB) protein, by AMPK was reported (12–15). TORC2 phosphorylated by AMPK or SIK binds to 14-3-3, and this complex is transported from inside the nucleus to the cytoplasm (16, 17). Thus, by reducing the association with TORC2 and CREB in the nucleus, CRE transcriptional activity and PEPCK-C expression are suppressed.
On the other hand, it has been revealed that CRE transcriptional activity is regulated not only by nuclear TORC2 but also by the phosphorylation of CREB. For example, forskolin stimulates cAMP production and enhances PEPCK-C gene expression by stimulating the protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation of CREB at Ser-133 and by promoting subsequent recruitment of the coactivator CREB-binding protein (CBP) to the promoter (18, 19). Furthermore, CREB has been regarded as one of the potential nuclear substrates of GSK3β, which were identified by in vitro phosphorylation and overexpression studies (20–22). Thus, it has been suggested that GSK3β phosphorylates CREB at Ser-129, leading to a stimulatory effect on CREB activity, and that CREB is involved in the cAMP-mediated activation of PEPCK-C expression (22–24). Because Akt/protein kinase B phosphorylates and inactivates GSK3β, insulin-induced suppression of CRE transcriptional activity is likely to be mediated by Akt-induced GSK3β phosphorylation at Ser-129. The phosphorylations of either CREB or TORC2 could,, thus, regulate transcriptional activity and thereby the gene expression of PEPCK-C.
In this study we observed that AMPK activation increases GSK3β phosphorylation rapidly and markedly in the mouse liver. Then, we performed experiments to determine whether AMPK-induced PEPCK-C gene suppression is indeed mediated by increased GSK3β phosphorylation. Herein, we present evidence showing a critical role of GSK3β phosphorylation in the AMPK-induced suppression of hepatic gluconeogenesis.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Reagents—AMPK inhibitor Compound C and Akt inhibitor IV were purchased from Calbiochem. Phospho-ACC (Ser-79), phospho-Akt (Thr-308), and phospho-GSK3β(Ser-9) antibodies were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA). Anti-rabbit horseradish peroxidase antibodies conjugated to horseradish peroxidase were obtained from Amersham Biosciences. Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium and fetal bovine serum were purchased from Invitrogen. All other reagents were of analytical grade. A rabbit polyclonal antibody was raised against a SIK(C) fragment (amino acid residues 1–343) or TORC2 peptide (563–699) in rabbits as described previously (25).
Preparation of Tissue Extracts—After an overnight fast or injection of AICAR (250 mg/kg), the animal was killed by cervical dislocation before removal of the liver. One part of the liver was homogenized in 10 volumes of ice-cold lysis buffer (20 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 1% Triton, 1 mm EDTA, 1 mm EGTA, 1 mm sodium orthovanadate, 1 mm dithiothreitol, 1 mm phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, and 2 μg/ml leupeptin). The solution was then centrifuged at 10,000 × g at 4 °C. The supernatant was collected, and the protein concentration was measured using a Bio-Rad protein assay kit.
Cell Culture—Human hepatoma HepG2 cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA). HepG2 cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 units/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin, and 5.5 mm d-glucose. The cells were incubated in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 at 37 °C and passaged every 3 days by trypsinization. Primary hepatocytes were isolated from male C57B6 mice by the collagenase method. Cells were suspended in William's E medium (Sigma) containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 1 nm insulin, 75 mg/liter penicillin, and 50 mg/liter streptomycin and then plated. After 12 h, serum was removed, and the cells were divided into control or dexamethasone (1 μm) groups. The medium was the same as that described above except that 0.1% bovine serum albumin was added instead of fetal bovine serum.
Construction and Luciferase Assay—The following plasmids were obtained from commercial sources: pTAL, pTAL-CRE and pM from Clontech (Palo Alto, CA) and pGL4.10 and pRL-TK from Promega (Madison, WI). The PEPCK-C promoter (–450 to –1) was inserted into a pGL4.10 vector (Promega). HepG2 cells in a 12-well collagen-coated plate were cotransfected with PEPCK-C-LUC vector (0.5 μg/well) with an internal reporter, pRL-TK (0.03 μg). For the CREB or TORC2 reporter assay, cells were transformed with Gal4 DNA binding domain-linked CREB expression vectors (pM-CREB, pM-TORC2, or pM, empty vector, 0.15 μg) and reporter vectors (UAS-linked luciferase reporter (pTAL-5x UAS, 0.15 μg) and an internal reporter, pRL-TK (0.03 μg)). pM was used to express a fusion protein that possessed the GAL4 DNA binding domain at the N terminus of a protein of interest. The fusion protein was transported into the nucleus by the SV40 nuclear localization sequence created in the GAL4 DNA binding domain. The luciferase reporter construct containing five copies of the GAL4 DNA binding site (UAS) upstream from the c-fos minimal promoter (FR-luc) was obtained from Stratagene. Because luciferase activity derived from FR-luc was low, the BamHI/XbaI fragment containing five copies of UAS elements of FR-Luc was transferred to the BglII/NheI site of pTAL, and the resultant reporter was named pTAL-5× UAS (26). After 48 h of transfection, cells were treated with or without forskolin (10 μm) or AICAR (2 mm) for 6 h and harvested to measure luciferase activities by the Dual-luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega Corp.). Specific promoter activities of PEPCK-C, CRE, CREB, or TORC2 genes were expressed as -fold expression compared with the reporter activity of the empty vector. Luciferase activities were measured and normalized by Renilla luciferase activity.
Site-directed Mutagenesis and Generation of Recombinant Adenovirus—Ser-9 of the wild-type GSK3β construct was mutated to a glycine to generate the GSK3β-S9G mutant construct using site-directed mutagenesis. Template DNA (5 ng) was mixed with 20 pmol of each primer (GSK3β-S9G: forward primer, 5′-ACCACCGCCTTTGGCGAGAGCTG-3′; GSK3β-S9G reverse primer, 5′-CAGCTCTCGCCAAAGGCGGTGGT-3′), and the PCR was run (94 °C, 30 s; 55 °C, 1 min; 68 °C, 5 min; 12 cycles). The product was transformed into DH5α competent Escherichia coli. Recombinant adenoviruses used to express wild-type GSK3β(WT) and constitutive active GSK3β(S9G) were constructed by homologous recombination of the expression cosmid cassettes containing the corresponding cDNAs and the parental virus genome, as described previously (27).
Adenoviral Gene Transfer—Recombinant adenovirus expressing wild-type and dominant negative mutant forms of AMPKα, wild-type GSK3β(WT), SIK1 and constitutive active GSK3β(S9G) were generated, purified, and concentrated using cesium chloride ultracentrifugation as reported previously (27). Adenovirus encoding LacZ served as a control, and the adenoviral gene transfer was performed as reported previously (27).
Western Blot Analysis—Western blot analysis was carried out as described previously (27). In brief, HepG2 cells were lysed in lysis buffer as shown above. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 12,000 × g for 15 min at 4 °C, and the resulting supernatant (cell lysate) was used for Western blotting and lipid content analysis. For Western blotting, 10 μg of protein were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE and electrophoretically transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes in a transfer buffer consisting of 20 mm Tris-HCl, 150 mm glycine, and 20% methanol. The membranes were blocked with 5% nonfat dry milk in Tris-buffered saline with 0.1% Tween 20 and incubated with specific antibodies followed by incubation with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies. The antigen-antibody interactions were visualized by incubation with ECL chemiluminescence reagent (Amersham Biosciences).
Immunoprecipitations—For the immunoprecipitation experiments, HepG2 cells were transfected with 1 μg of GST-tagged CREB. Whole-cell extracts were prepared from HepG2 cells in lysis buffer, as described above. Cell extracts were incubated for 4 h at 4 °C with anti-GST antibody (5 μg) and then for 1 h with 30 μl of protein G-Sepharose beads. The pellets were washed 5 times with 1 ml of lysis buffer, then resuspended in Laemmli sample buffer, boiled for 3 min, and analyzed on SDS/8% polyacrylamide gels.
RESULTS
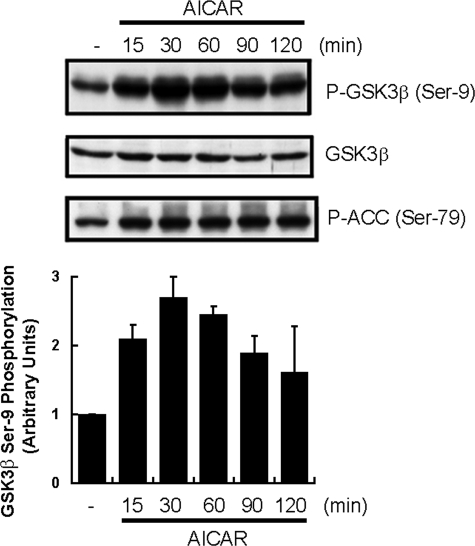
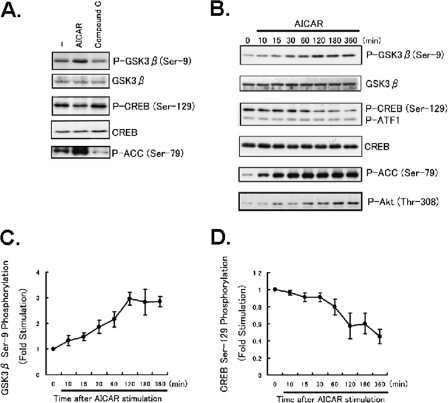
AICAR Stimulation Increases the Phosphorylations of GSK3β and ACC in Mouse Liver—AICAR was intraperitoneally injected into fasted mice, and the Ser-9 phosphorylation level of hepatic GSK3β was monitored at the indicated times (Fig. 1). As reported previously, AICAR stimulation increased ACC phosphorylation (lowest panel of Fig. 1). Interestingly, GSK3β phosphorylation was also markedly increased by AICAR injection, whereas the level of GSK3β protein expression was unchanged in the livers of fasted mice. This increase took place within 15 min of injecting AICAR, peaked at 30 min, and persisted for 2 h. Thus, AICAR stimulation was revealed to enhance not only ACC but also GSK3β, probably more markedly than ACC.
FIGURE 1.
AICAR induced GSK3β phosphorylation in livers of fasted mice. Ten-week-old C57BL6 mice were fasted overnight, then given an intraperitoneal injection of AICAR (250 mg/kg) before sacrifice followed by excision of the liver. Ser-9 phosphorylation (P-) of GSK3β was assessed by Western blotting. The phospho-GSK3β was quantified densitometrically, and the results are presented in the lower panel. The results are presented as the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments.
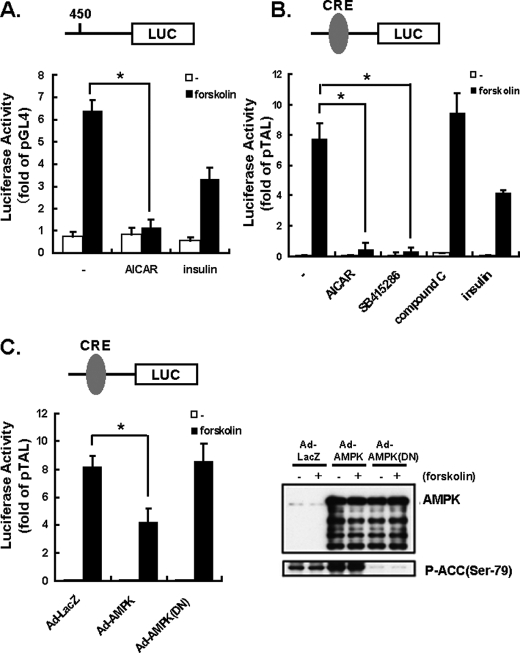
AMPK Activation Reduces Transcriptional Activities of PEPCK-C Gene Promoter and CRE—PEPCK-C regulation in vivo occurs mainly at the level of gene expression (28–32). Expression of the luciferase gene located downstream from the PEPCK-C gene promoter was markedly increased by forskolin in HepG2 cells, and this increase was suppressed by AICAR or insulin stimulation (Fig. 2A). Because the domain responsible for the forskolin-induced PEPCK-C up-regulation is reportedly that of CRE, we subsequently performed a luciferase assay using a plasmid containing the CRE domain upstream from the luciferase gene (Fig. 2B). Forskolin markedly enhanced CRE transcriptional activity, whereas AICAR almost completely abolished it, and the AMPK inhibitor Compound C had no effect. Interestingly, the GSK3β inhibitor SB415286 also very strongly inhibited the forskolin-induced increase in CRE activity (Fig. 2B). Furthermore, to confirm that the effect of AICAR is mediated by increased AMPK activity, the wild-type and dominant negative mutant of AMPK were overexpressed, employing adenovirus-mediated gene transfer. The overexpressed proteins were detected by immunoblotting (upper blot in the right panel of Fig. 2C). As predicted, AMPK overexpression increased ACC phosphorylation, whereas a dominant negative form suppressed it (lower blot in the right panel of Fig. 2C). Under these conditions, AMPK was revealed to suppress forskolin-induced CRE transcriptional activity (left panel of Fig. 2C).
FIGURE 2.
Inhibition of PEPCK-C reporter by AICAR in HepG2 cells in the presence and the absence of forskolin. AICAR or the GSK3β inhibitor SB-415286 has the potential to down-regulate CRE-dependent transcription in the presence and in the absence of 10 μm forskolin. HepG2 cells were transfected with the PEPCK-C promoter fused to the luciferase reporter plasmid (pGL4.10-PEPCK-C: 0.5 μg) with an internal reporter, pRL-TK (0.03 μg). HepG2 cells were serum-starved overnight before incubation with AICAR (2 mm) or insulin (10 nm) with or without 10 μm forskolin. After a 6-h incubation, cells were harvested for the reporter assay. A, the PEPCK-C-dependent reporter activities that had been normalized with internal reporter activities were expressed as -fold activities of the empty reporter (pGL4.10). B, HepG2 cells were transfected with the CRE-reporter plasmid (pTAL-CRE: 0.25 μg) with the internal reporter pRL-TK (0.03 μg). HepG2 cells were serum-starved overnight before incubation with AICAR (2 mm), insulin (10 nm), the selective AMPK inhibitor Compound C (20 μm), GSK3β inhibitor, or SB-415286 (30 μm) with or without 10 μm forskolin. After a 6-h incubation, cells were harvested for the reporter assay. C, AMPK (WT, DN) was overexpressed by adenoviral (Ad) gene transfer, and expressions were detected by anti-AMPK antibody (upper blot in the right panel). AMPK activity was monitored by antiphospho-Ser79-ACC (lower blot in the right panel). The cells were transfected with the CRE-reporter plasmid (pTAL-CRE, 0.25 μg) with the internal reporter pRL-TK (0.03 μg), and the reporter assay was performed.
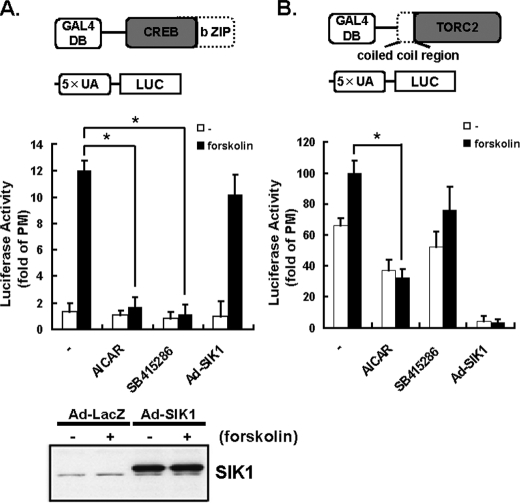
Contribution of CREB and TORC2 in the AMPK-, SIK1-, and GSK3β-mediated Suppression of CRE Activity—Because both AICAR and SB415286 repressed CRE-dependent reporter activity (Fig. 2B), we performed the experiments to determine which of these molecules (CREB or TORC2) is involved in the AICAR- and SB415286-induced suppression of the CRE transcriptional activity, using a GAL4-based transactivation assay system in HepG2 cells. Expression vectors encoding the DNA binding domain of the yeast transcription factor GAL4 fused to CREB were co-transfected with a GAL4-binding site (UAS)-driven luciferase reporter gene. To eliminate the interaction between the bZIP domain of CREB and the N-terminal coiled-coil region of TORC2, the transactivation domains of CREB and TORC2 were separated from the bZIP domain and the N-terminal coiled-coil region, respectively (upper diagram of Fig. 3, A and B). This allowed investigation of the transactivation potential of the transcription factor, independently of its DNA binding and endogenous background.
FIGURE 3.
Contributions of CREB and TORC2 to AMPK-, SIK1-, and GSK3β-mediated suppressions of CRE activity. HepG2 cells were cotransfected with the expression plasmids for GAL4-truncated CREB (bZIP domain) (0.25 μg) or GAL4-truncated TORC2 (coiled coil region) (0.25 μg) and a pTAL-5× UAS reporter plasmid (0.25 μg) with the internal reporter pRL-TK (0.03 μg) (A and B). HepG2 cells were serum-starved overnight before incubation with AICAR (2 mm), insulin (10 nm), and GSK3β inhibitor or SB-415286 (30 μm) with or without 10 μm forskolin. Adenovirus (Ad)-mediated overexpressions of SIK1 proteins were detected using an anti-SIK1 immunoblot (lower panel). The specific transactivation activities of TORCs were expressed as the -fold activation of the empty Gal4 vector, pM. Means and S.D. are indicated (n = 3). *, p < 0.05.
As shown in Fig. 3A, the transcriptional activity of CREB was inhibited by both AICAR and SB415286, whereas that of TORC2 was repressed by AICAR significantly and by SB415286 slightly. These results suggested that AMPK might inhibit the activities of both CREB and TORC2, whereas GSK-3β might up-regulate the activity of only CREB. The zero effect of SB415286 on the level of phosphorylation of TORC2 (Fig. 4) might also support this hypothesis.
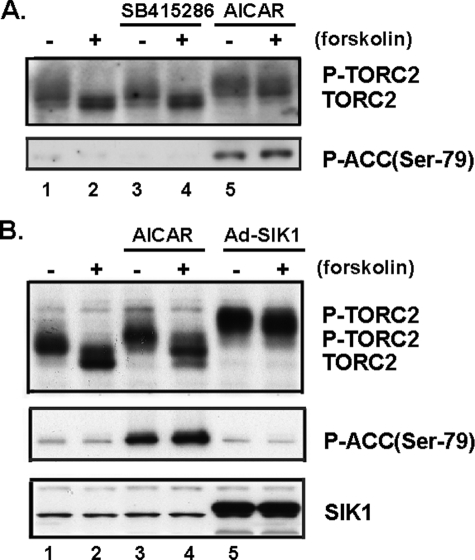
FIGURE 4.
Effect of GSK3β inhibitor SB-415286-, AICAR-, or adenovirus-expressed SIK1 (Ad-SIK1) on P-TORC2 levels in primary hepatocytes in the presence and the absence of forskolin. A, stimulation of hepatocytes with GSK3β inhibitor, SB415286, did not shift the mobility of TORC2 in response to the presence or absence of forskolin. Primary hepatocytes were serum-starved overnight before a 2-h incubation with 30 μm SB-415286 (lanes 3 and 4) or 2 mm AICAR (lanes 5 and 6) with or without 10 μm forskolin. TORC2 phosphorylation was detected by Western blotting as a phosphorylation-dependent mobility shift (TORC2, dephosphorylated; P-TORC2, phosphorylated) in primary hepatocytes. AMPK activity was monitored by antiphospho-Ser-79-ACC (lower panel). B, TORC2 was strongly phosphorylated in adenovirus-expressing SIK1. Primary hepatocytes were stimulated with 2 mm AICAR (lanes 3 and 4) and adenovirus-mediated overexpressions of SIK1(lanes 5 and 6) with or without 10 μm forskolin. AMPK activity was monitored by antiphospho-Ser-79-ACC (middle panel). SIK1 proteins were detected using an anti-SIK1 immunoblot (lower panel). Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.
On the other hand, TORC2 is known to be highly phosphorylated and inactivated by SIK1, a member of the AMPK family of Ser/Thr kinases. SIK1 phosphorylates TORC2 and blocks its nuclear accumulation (16). Indeed, when SIK1 was overexpressed, the forskolin-induced increase in GAL4-TORC2 activity was completely abolished (Fig. 3B). In addition, TORC2 was strongly phosphorylated in adenovirus-expressing SIK1 (Ad-SIK1) cells (Fig. 4B). Thus, as shown with the GAL4-system and phosphorylation-dependent mobility shift of TORC2, CREB appears to be crucial for exerting the effects of SB415286 and AICAR, whereas TORC2 appears to be crucial for manifestation of the effects of AICAR stimulation and SIK overexpression.
Phosphorylation of TORC2 and ACC by AMPK and SIK1—AMPK and SIK1 reportedly phosphorylate TORC2 (Ser-171), and phosphorylated TORC2 is transported from within the nucleus to the cytoplasm (12). As shown in Fig. 4, endogenous hepatic TORC2 was markedly dephosphorylated upon stimulation with forskolin (lanes 1 and 2 of Fig. 4, A and B). Stimulation of hepatocytes with AICAR resulted in a slight shift in the mobility of TORC2, indicating phosphorylation (lanes 1 and 5 or lanes 2 and 6 of Fig. 4A and lanes 1 and 3 or lanes 2 and 4 of Fig. 4B), whereas stimulation with a GSK3β specific inhibitor, SB415286, did not produce a shift in response to the presence or absence of forskolin (lanes 3 and 4 of Fig. 4A). On the other hand, TORC2 was strongly phosphorylated in adenovirus-expressing SIK1 (Ad-SIK1) cells (bottom panel of Fig. 4B), i.e. more than with AICAR stimulation (lanes 5 and 6 of Fig. 4B). These results suggest that whereas AICAR stimulation induces TORC2 phosphorylation, SIK1 is likely to phosphorylate more serine residues than AMPK. In contrast, ACC was phosphorylated by AICAR but not by SIK1 (middle panel of Fig. 4B).
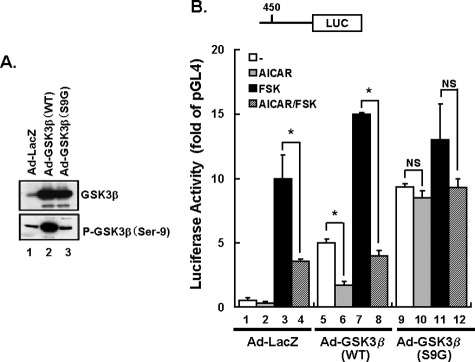
Active Mutant of GSK3β Inhibits AICAR-induced Suppression of Transcriptional Activity of PEPCK-C Promoter—Phosphorylation of GSK3β on Ser-9 inhibits its catalytic activity. In examining whether AICAR-induced suppression of the PEPCK-C gene occurs via GSK3β phosphorylation, we created non-phosphorylatable, constitutively active mutants of the GSK3β(S9G) and GSK3β(WT) adenoviruses. Western blots of total extracts from infected cells treated for 48 h revealed marked overexpressions of GSK3β(S9G) and GSK3β(WT) compared with endogenously expressed GSK3β (upper panel of Fig. 5A). Furthermore, GSK3β(WT) was detected by antiphospho-Ser-9 GSK3β antibody, whereas GSK3β(S9G) was not (lower panel of Fig. 5A). HepG2 cells were incubated with 1.4 × 108 plaque-forming units/well (12-well plate) of adenovirus particles in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium. Infection of HepG2 cells with an adenovirus-expressing GSK3β produced a 10–20-fold increase.
FIGURE 5.
Mutant GSK3β(S9G) overexpression affects PEPCK-C transcriptional activity in HepG2 cells. HepG2 cells were transiently transfected with pGL4.10-PEPCK-C (0.5 μg) with the internal reporter pRL-TK (0.03 μg). After 5 h of transfection, HepG2 cells were infected with LacZ, GSK3β(WT), or GSK3β(S9G) adenovirus. After 48 h of transfection, the cells were stimulated with or without 2 mm AICAR or 10 μm forskolin for 6 h. A, adenovirus-mediated overexpression of GSK3β(WT, S9G) was detected by anti-GSK3β antibody or anti-phospho-(P-)Ser-9-GSK3β. B, the cells were incubated in the presence and in the absence of 2 mm AICAR or 10 μm forskolin, and the reporter assays were then performed. The results are presented as mean relative luciferase (LUC) units (±S.E.), normalized to Renilla LUC activity, derived from three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05.
In control-LacZ-overexpressing HepG2 cells, forskolin enhances PEPCK-C promotor transcriptional activity, and co-stimulation with AICAR blunted this forskolin-induced increase (bars 1–4 of Fig. 5B). In wild-type GSK3β-overexpressing cells, although basal PEPCK-C transcriptional activity was increased as compared with that in LacZ-cells (bars 1 and 5 of Fig. 5B), responses to forskolin and AICAR were quite similar (bars 5–8 of Fig. 5B). However, in active mutant of GSK3β(S9G)-overexpressing cells, PEPCK-C promotor transcriptional activities under basal and AICAR-stimulated conditions were both significantly increased (bars 9–12 of Fig. 5B), as compared with that in wild-type GSK3β-overexpressing cells. In addition, it should be noted that AICAR-induced suppression of PEPCK-C promotor transcriptional activity was observed in wild-type GSK3β-overexpressing cells, but this effect was nearly abolished in the GSK3β(S9G)-overexpressing cells (bars 9 and 10 of Fig. 5B). Thus, it was revealed that expression of constitutively active GSK3β(S9G) enhanced PEPCK-C transcription in HepG2 cells, which suggests phosphorylation of Ser-9 of GSK3β is involved in the mechanism underlying AMPK or AICAR-induced PEPCK-C gene suppression.
AMPK Increases GSK3β(Ser-9) Phosphorylation but Decreases CREB Phosphorylation (Ser-129) in HepG2 Cells—To test whether activators of AMPK have a regulatory influence on GSK3β, HepG2 cells were treated with the AMPK activator AICAR, and phosphorylations of CREB and GSK3β were measured using immunoblot analyses with the corresponding phospho-specific antibodies. When cells were treated with 2 mm AICAR for 1 h, phosphorylation of GSK3β was significantly increased, whereas CREB phosphorylation was reduced (Fig. 6A). In contrast, when the cells were treated with the selective AMPK inhibitor Compound C, phosphorylation of GSK3β at Ser-9 was reduced, and that of CREB at Ser-129 was slightly increased (Fig. 6A). Thus, AMPK activation caused phosphorylation of GSK3β via a mechanism that was blocked by the AMPK inhibitor Compound C, indicating that an AMPK-dependent effect contributes to this response to AICAR. Panel B of Fig. 6 shows the time-courses of AICAR-induced phosphorylation of GSK3β at Ser-9, CREB phosphorylation at Ser-129, ACC phosphorylation at Ser-79, and Akt phosphorylation at Thr-308. The time-courses of decreased CREB phosphorylation (Ser-129) and increased GSK3β phosphorylation were very similar (panels C and D of Fig. 6). These actions were evident within 10 min of treatment and were maintained for 360 min. Phosphorylation of Ser-133 was unchanged by AICAR stimulation in HepG2 cells (data not shown). The data suggest GSK3β integrate AMPK signaling pathways to promote CREB Ser-129 phosphorylation. We also did these experiments in primary hepatocytes (supplemental Fig. 1). With only AICAR treatment, i.e. no activation of AMPK, there was neither phosphorylation of GSK3β nor dephosphorylation of CREB. However, in the presence of dibutyryl-cAMP, AICAR treatment induced phosphorylation of Ser-9-GSK3β and reduced that of Ser-129-CREB. These results demonstrate that AICAR triggers phosphorylation of GSK3β in the presence of dibutyryl-cAMP-increased protein kinase A activation and suggest that AICAR regulates the phosphorylations of GSK3β in parallel with its effects on gluconeogenesis.
FIGURE 6.
AMPK activation increased phosphorylation of GSK3β in HepG2 cells. HepG2 cells were treated with AICAR (2 mm) or the selective AMPK inhibitor Compound C (20 μm). A, immunoblot analyses were performed with HepG2 cell extracts prepared using anti-GSK3β, anti-phospho (P-)-GSK3β (Ser-9), anti-CREB, antiphospho-CREB (Ser-129), or anti-phospho-ACC (Ser-79) antibody as indicated. B, Western blot analyses of time-dependent effects were performed with HepG2 cell extracts prepared using anti-GSK3β, anti-phospho-GSK3β (Ser-9), anti-CREB, anti-phospho-CREB (Ser-129), anti-phospho-Akt (Thr-308), or anti-phospho-ACC (Ser-79) antibody. Panels C and D, show the results of densitometric analysis of phospho-GSK3β (Ser-9) and phospho-CREB (Ser-129) as the mean ± S.E. of three samples.
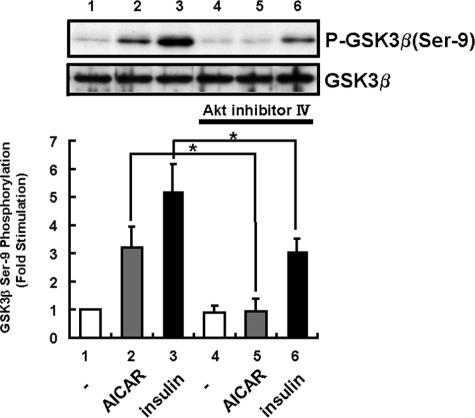
Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Pathway Is Necessary for AMPK-induced GSK3β Phosphorylation—To examine whether phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt activations are necessary for AMPK-mediated GSK3β phosphorylation, HepG2 cells were stimulated with AICAR with or without pretreatment with 10 μm Akt inhibitor IV ((Fig. 7). Both insulin-induced and AICAR-induced GSK3β phosphorylations were inhibited by preincubation with Akt inhibitor IV. Akt phosphorylation on Thr-308 was increased in a time-dependent manner (Fig. 6B). Thus, AMPK-induced GSK3β phosphorylation is likely to be mediated by the Akt pathway.
FIGURE 7.
Western blot analysis in AICAR-treated HepG2 cells in the absence or the presence of Akt inhibitor. The Ser-9 phosphorylation (P-) levels of GSK3β were detected by Western blotting using an anti-P-Ser-9-GSk3β antibody (upper panel). HepG2 cells were detected by treatment with AICAR (2 mm) for 1 h or insulin (1 μm) for 15 min after pretreatment with or without 10 μm Akt inhibitor IV. Pretreatment with 10 μm Akt inhibitor IV inhibited AICAR-induced GSK3β phosphorylation (P). The lower panel shows the results of densitometric analysis of phospho-GSK3β (Ser-9) as the mean ± S.E. of three samples. *, p < 0.05.
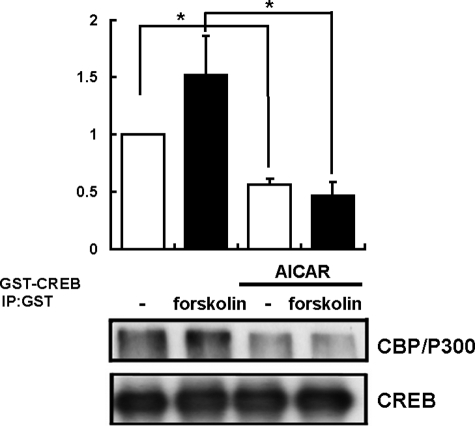
AICAR Suppresses CREB-CBP Interactions—Protein kinase A reportedly phosphorylates CREB at Ser-133, and phosphorylation of CREB increases its affinity for CREs. Ser-129, a consensus GSK3β phospho-accepter site, has been proposed to regulate CREB activity in conjunction with Ser-133 after cAMP induction. Because the CREB transcriptional coactivator, CREB-binding protein (CBP/P300), is a nuclear protein that binds specifically to the protein kinase A-phosphorylated form of CREB and can activate transcription (33), we examined how the forskolin-promoted CREB-CBP interaction was regulated via AICAR stimulation.
Forskolin treatment increased the interaction between endogenous CBP/P300 and transfected GST-CREB in HepG2 cells as previously reported (Fig. 8). It was revealed that AICAR treatment markedly decreased this interaction (Fig. 8). This result suggested that the affinity of CREB for CBP/P300 was negatively regulated by suppression of CREB Ser-129 phosphorylation in response to AICAR stimulation.
FIGURE 8.
AICAR stimulation inhibited CREB-CBP/P300 interaction. Amounts of CBP associated with CREB were determined by immunoprecipitation with extracts obtained from transfected HepG2 cells. HepG2 cells transfected with GST-tagged CREB were serum-starved overnight before incubation with AICAR (2 mm) with or without 10 μm forskolin for 1 h. HepG2 cells transfected with GST-tagged CREB were extracted and subjected to immunoprecipitation using GST-specific antibody. Shown is a Western blot of GST-tagged CREB-transfected HepG2 cell lysates with a CBP/P300-specific antibody showing immunoprecipitation of exogenously expressed GST-tagged CREB with endogenous CBP/P300 (upper lanes, immunoprecipitation of endogenous CBP/P300 from GST-tagged CREB transfected cells with the CBP/P300-specific antibody; lower lane, immunoprecipitation (IP) of GST-tagged CREB with the anti-CREB antibody). The results are presented as the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments.
DISCUSSION
Hepatic gluconeogenesis is strictly regulated to maintain whole-body glucose homeostasis, and several hormones such as insulin and glucagons are involved in this regulation. PEPCK-C has been regarded as the key enzyme determining the rate of hepatic gluconeogenesis, but recent studies on PEPCK-C gene knock-out mice suggest that PEPCK-C functions as an integrator of hepatic energy metabolism, including those of lipid and glycogen (34–36). The promoter region of the PEPCK-C gene contains the CRE domain, which was shown to play an important role in PEPCK-C gene expression (30, 31, 37–39). Glucagon and forskolin, via increased cAMP, reportedly increase PEPCK-C gene expression by stimulating protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation of CREB at Ser-133 (40–43). Recently, the coactivator of CREB termed TORC2 was reported to be important for the regulation of CRE transcriptional activity and PEPCK-C gene expression (12). TORC2 is reportedly phosphorylated by AMPK and SIK, and phosphorylated TORC2 binds to 14-3-3 protein and is thereby removed from the nucleus to the cytoplasm (16). Depletion of nuclear TORC2 led to the suppression of CRE transcriptional activity (44). Thus, AMPK-induced PEPCK-C gene suppression is likely to be mediated by TORC2 phosphorylation. However, in this study we demonstrated another mechanism to underlie AMPK-induced PEPCK-C gene suppression. This novel mechanism involves GSK3β phosphorylation and subsequent CREB dephosphorylation.
We demonstrated for the first time that AMPK activation increases GSK3β phosphorylation in not only cultured cells such as HepG2 but also in the mouse liver. This phosphorylation in the liver was rapidly induced (within 15 min of AICAR stimulation) and persisted for at least 2 h, indicating physiological significance. In addition, suppression of AMPK with the selective inhibitor Compound C blocked GSK3β phosphorylation induced by AICAR. Because the Akt inhibitor attenuated AICAR-induced GSK3β phosphorylation, it seems unlikely that AMPK directly phosphorylates GSK3β. Indeed, AICAR stimulation does not activate phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (data not shown) but does increase Akt phosphorylation. Thus, although the exact molecular mechanism cannot be identified from our data, several possibilities can be considered. For example, AMPK activation may affect the activity of PDK1 or the mTOR-Rictor complex (45, 46). Another possibility is that the dephosphorylation of Akt or GSK3β is suppressed by AMPK activation. Indeed, a recent study also found Akt to be dephosphorylated after AICAR treatment in differentiated hippocampal neurons (47). Alternatively, inhibition of other kinases might be involved in the effects of AICAR because it was recently reported that AICAR inhibits the Ser-9 phosphorylation of GSK3β induced by co-treatment with a phorbol ester activator of protein kinase C plus the calcium ionophore ionomycin. Further studies are necessary to clarify this issue.
Phosphorylation of GSK3 at an NH2-terminal serine residue (Ser-21 and Ser-9 in GSK-3α and -3β, respectively) renders it inactive. Administration of specific inhibitors of GSK3β such as L803-mts reportedly not only increases hepatic glycogen synthesis but also decreases glucose production with decreased levels of PEPCK-C mRNA in fa/fa rats (48) and ob/ob mice (49). However, the molecular events underlying the regulation of PEPCK-C gene expression by GSK3β remain unclear. Because a previous study showed that GSK3β phosphorylates CREB at Ser-129 (20), we considered the possibility that GSK3β phosphorylation contributes to AMPK-induced PEPCK-C gene suppression. AICAR stimulation induced GSK3β phosphorylation and CREB dephosphorylation in HepG2 cells with very similar time-courses (Fig. 6). In addition, AMPK stimulation reduced PEPCK-C promoter activity in HepG2 cells, and the GSK3β inhibitor SB-415286 and AICAR both strongly suppressed CRE activity. Importantly, AICAR-induced suppression of PEPCK-C promoter activity was significantly attenuated by overexpressing the constitutively active mutant of GSK3β(S9G). These findings strongly suggest that inactivation of GSK3β is necessary for AMPK-induced PEPCK-C promoter and CRE activity suppressions. We also performed reporter assays using Gal4-CREB and Gal4-TORC2 reporter systems. SB-415286 suppressed CREB reporter activities while only slightly affecting those of TORC2 (Fig. 3, A and B). Stimulation of hepatocytes with SB415286 did not shift the mobility of TORC2 according to the presence or absence of forskolin (Fig. 4A). These results showed GSK3β inactivation to directly inhibit CREB.
The importance of Ser-133 phosphorylation in stimulating CREB activity has been recognized (50, 51). Phosphorylation of CREB at Ser-133 also creates a consensus site for phosphorylation by GSK3β at Ser-129 (21). Substitution of Ser-129 by Ala strongly impaired forskolin-induced CREB-dependent transcription in PC12 cells (21). We observed the suppression of Ser-129 phosphorylation by AICAR stimulation to decrease CREB-CBP interactions. These results showed double-phosphorylated CREB (Ser-129 and -133) to promote the TORC2-CBP interaction. GSK3β may also play a physiological role in cAMP signaling, as cAMP-induced stimulation of CREB activity depended on the phosphorylation of Ser-129 (Fig. 9).
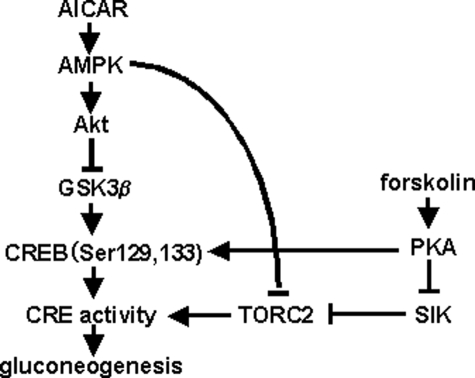
FIGURE 9.
A model of the role of the AMPK-GSK3β-CREB signaling pathway in gluconeogenesis. PKA, protein kinase A.
Taken together, our findings indicate that pathways activated in parallel by this agent then concomitantly activate AMPK and phosphorylate Akt and, consequently, GSK3β. These results indicate that actions ascribed to AMPK after AICAR treatment may be influenced by the concomitant modulatory actions of this drug on Akt and GSK3β. AMPK and Akt generally have opposing roles in cellular metabolism. AMPK is activated when AMP levels increase in conjunction with decreased ATP levels, and activated AMPK inhibits anabolic processes and promotes catabolism to minimize ATP utilization while promoting ATP production. On the other hand, Akt generally promotes anabolic cellular functions that utilize ATP, such as proliferation and cell growth, although Akt may share with AMPK the ability to promote ATP synthesis by different mechanisms. Thus, the combined effects of AICAR on AMPK and Akt may enhance the outcomes that have been ascribed to their activating effects on AMPK.
In conclusion, AMPK activation increases GSK3β phosphorylation in vivo. Reduced CREB phosphorylation (Ser-129) associated with inactivation of GSK3β by Ser-9 phosphorylation may be the major mechanism underlying PEPCK-C gene suppression by AMPK-activating agents such as biguanide, leptin, and adiponectin. Thus, it is very likely that two mechanisms independently mediate the AMPK-induced suppression of PEPCK-C expression. We agree that TORC2 phosphorylation by AMPK is important, but the GSK3β-mediated pathway plays an additional, possibly critical, role in PEPCK-C gene suppression.
Supplementary Material
The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
The on-line version of this article (available at http://www.jbc.org) contains supplemental Fig. 1.
Footnotes
The abbreviations used are: PEPCK-C, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase C; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; AICAR, 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleoside; CREB, CRE, cAMP-response element; CREB, CRE-binding protein; TORC2, transducer of regulated CREB activity 2; WT, wild type; GST, glutathione S-transferase; CBP, CREB-binding protein; UAS, upstream activating sequence; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; SIK, salt-inducible kinase.
References
- 1.Vincent, M. F., Erion, M. D., Gruber, H. E., and Van den Berghe, G. (1996) Diabetologia 39 1148–1155 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Stapleton, D., Mitchelhill, K. I., Gao, G., Widmer, J., Michell, B. J., Teh, T., House, C. M., Fernandez, C. S., Cox, T., Witters, L. A., and Kemp, B. E. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271 611–614 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Winder, W. W., and Hardie, D. G. (1999) Am. J. Physiol. 277 E1–E10 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zhou, G., Myers, R., Li, Y., Chen, Y., Shen, X., Fenyk-Melody, J., Wu, M., Ventre, J., Doebber, T., Fujii, N., Musi, N., Hirshman, M. F., Goodyear, L. J., and Moller, D. E. (2001) J. Clin. Investig. 108 1167–1174 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yamauchi, T., Kamon, J., Minokoshi, Y., Ito, Y., Waki, H., Uchida, S., Yamashita, S., Noda, M., Kita, S., Ueki, K., Eto, K., Akanuma, Y., Froguel, P., Foufelle, F., Ferre, P., Carling, D., Kimura, S., Nagai, R., Kahn, B. B., and Kadowaki, T. (2002) Nat. Med. 8 1288–1295 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lochhead, P. A., Salt, I. P., Walker, K. S., Hardie, D. G., and Sutherland, C. (2000) Diabetes 49 896–903 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cool, B., Zinker, B., Chiou, W., Kifle, L., Cao, N., Perham, M., Dickinson, R., Adler, A., Gagne, G., Iyengar, R., Zhao, G., Marsh, K., Kym, P., Jung, P., Camp, H. S., and Frevert, E. (2006) Cell Metab. 3 403–416 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Towler, M. C., and Hardie, D. G. (2007) Circ. Res. 100 328–341 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bady, I., Marty, N., Dallaporta, M., Emery, M., Gyger, J., Tarussio, D., Foretz, M., and Thorens, B. (2006) Diabetes 55 988–995 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Winder, W. W., Wilson, H. A., Hardie, D. G., Rasmussen, B. B., Hutber, C. A., Call, G. B., Clayton, R. D., Conley, L. M., Yoon, S., and Zhou, B. (1997) J. Appl. Physiol. 82 219–225 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Munday, M. R., Campbell, D. G., Carling, D., and Hardie, D. G. (1988) Eur. J. Biochem. 175 331–338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Koo, S. H., Flechner, L., Qi, L., Zhang, X., Screaton, R. A., Jeffries, S., Hedrick, S., Xu, W., Boussouar, F., Brindle, P., Takemori, H., and Montminy, M. (2005) Nature 437 1109–1111 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Conkright, M. D., Canettieri, G., Screaton, R., Guzman, E., Miraglia, L., Hogenesch, J. B., and Montminy, M. (2003) Mol. Cell 12 413–423 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Iourgenko, V., Zhang, W., Mickanin, C., Daly, I., Jiang, C., Hexham, J. M., Orth, A. P., Miraglia, L., Meltzer, J., Garza, D., Chirn, G. W., McWhinnie, E., Cohen, D., Skelton, J., Terry, R., Yu, Y., Bodian, D., Buxton, F. P., Zhu, J., Song, C., and Labow, M. A. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100 12147–12152 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shaw, R. J., Lamia, K. A., Vasquez, D., Koo, S. H., Bardeesy, N., Depinho, R. A., Montminy, M., and Cantley, L. C. (2005) Science 310 1642–1646 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Screaton, R. A., Conkright, M. D., Katoh, Y., Best, J. L., Canettieri, G., Jeffries, S., Guzman, E., Niessen, S., Yates, J. R., III, Takemori, H., Okamoto, M., and Montminy, M. (2004) Cell 119 61–74 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bittinger, M. A., McWhinnie, E., Meltzer, J., Iourgenko, V., Latario, B., Liu, X., Chen, C. H., Song, C., Garza, D., and Labow, M. (2004) Curr. Biol. 14 2156–2161 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhou, X. Y., Shibusawa, N., Naik, K., Porras, D., Temple, K., Ou, H., Kaihara, K., Roe, M. W., Brady, M. J., and Wondisford, F. E. (2004) Nat. Med. 10 633–637 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chrivia, J. C., Kwok, R. P., Lamb, N., Hagiwara, M., Montminy, M. R., and Goodman, R. H. (1993) Nature 365 855–859 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fiol, C. J., Williams, J. S., Chou, C. H., Wang, Q. M., Roach, P. J., and Andrisani, O. M. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269 32187–32193 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tyson, D. R., Swarthout, J. T., Jefcoat, S. C., and Partridge, N. C. (2002) Endocrinology 143 674–682 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tullai, J. W., Chen, J., Schaffer, M. E., Kamenetsky, E., Kasif, S., and Cooper, G. M. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282 9482–9491 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yeagley, D., Agati, J. M., and Quinn, P. G. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273 18743–18750 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lipina, C., Huang, X., Finlay, D., McManus, E. J., Alessi, D. R., and Sutherland, C. (2005) Biochem. J. 392 633–639 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ogihara, T., Shin, B. C., Anai, M., Katagiri, H., Inukai, K., Funaki, M., Fukushima, Y., Ishihara, H., Takata, K., Kikuchi, M., Yazaki, Y., Oka, Y., and Asano, T. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272 12868–12873 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Doi, J., Takemori, H., Lin, X. Z., Horike, N., Katoh, Y., and Okamoto, M. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277 15629–15637 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sakoda, H., Gotoh, Y., Katagiri, H., Kurokawa, M., Ono, H., Onishi, Y., Anai, M., Ogihara, T., Fujishiro, M., Fukushima, Y., Abe, M., Shojima, N., Kikuchi, M., Oka, Y., Hirai, H., and Asano, T. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278 25802–25807 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lochhead, P. A., Coghlan, M., Rice, S. Q., and Sutherland, C. (2001) Diabetes 50 937–946 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sasaki, K., Cripe, T. P., Koch, S. R., Andreone, T. L., Petersen, D. D., Beale, E. G., and Granner, D. K. (1984) J. Biol. Chem. 259 15242–15251 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Short, J. M., Wynshaw-Boris, A., Short, H. P., and Hanson, R. W. (1986) J. Biol. Chem. 261 9721–9726 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hanson, R. W., and Reshef, L. (1997) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 66 581–611 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Croniger, C., Leahy, P., Reshef, L., and Hanson, R. W. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273 31629–31632 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Vo, N., and Goodman, R. H. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276 13505–13508 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.She, P., Shiota, M., Shelton, K. D., Chalkley, R., Postic, C., and Magnuson, M. A. (2000) Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 6508–6517 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.She, P., Burgess, S. C., Shiota, M., Flakoll, P., Donahue, E. P., Malloy, C. R., Sherry, A. D., and Magnuson, M. A. (2003) Diabetes 52 1649–1654 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hakimi, P., Johnson, M. T., Yang, J., Lepage, D. F., Conlon, R. A., Kalhan, S. C., Reshef, L., Tilghman, S. M., and Hanson, R. W. (2005) Nutr. Metab. 2 33–44 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Foretz, M., Ancellin, N., Andreelli, F., Saintillan, Y., Grondin, P., Kahn, A., Thorens, B., Vaulont, S., and Viollet, B. (2005) Diabetes 54 1331–1339 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Roesler, W. J., Vandenbark, G. R., and Hanson, R. W. (1989) J. Biol. Chem. 264 9657–9664 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Klemm, D. J., Roesler, W. J., Liu, J. S., Park, E. A., and Hanson, R. W. (1990) Mol. Cell. Biol. 10 480–485 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Leahy, P., Crawford, D. R., Grossman, G., Gronostajski, R. M., and Hanson, R. W. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274 8813–8822 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Herzig, S., Long, F., Jhala, U. S., Hedrick, S., Quinn, R., Bauer, A., Rudolph, D., Schutz, G., Yoon, C., Puigserver, P., Spiegelman, B., and Montminy, M. (2001) Nature 413 179–183 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Parker, D., Ferreri, K., Nakajima, T., LaMorte, V. J., Evans, R., Koerber, S. C., Hoeger, C., and Montminy, M. R. (1996) Mol. Cell. Biol. 16 694–703 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sassone-Corsi, P. (1998) Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 30 27–38 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Boer, U., Eglins, J., Krause, D., Schnell, S., Schofl, C., and Knepel, W. (2007) Biochem. J. 408 69–77 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sarbassov, D. D., Guertin, D. A., Ali, S. M., and Sabatini, D. M. (2005) Science 307 1098–1101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tzatsos, A., and Kandror, K. V. (2006) Mol. Cell. Biol. 26 63–76 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.King, T. D., Song, L., and Jope, R. S. (2006) Biochem. Pharmacol. 71 1637–1647 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Cline, G. W., Johnson, K., Regittnig, W., Perret, P., Tozzo, E., Xiao, L., Damico, C., and Shulman, G. I. (2002) Diabetes 51 2903–2910 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kaidanovich-Beilin, O., and Eldar-Finkelman, H. (2006) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 316 17–24 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sands, W. A., and Palmer, T. M. (2008) Cell. Signal. 20 460–466 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Johannessen, M., and Moens, U. (2007) Front. Biosci. 12 1814–1832 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.