Abstract
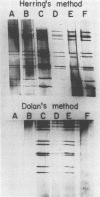
Detection of rotavirus by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in combination with silver staining and by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay showed 96.7% identical results in tests with 1,304 stool specimens from diarrheic patients. The polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis method can be modified to reduce cost and working time. Phenol extraction of stools, however, is essential in maintaining the sensitivity of the method.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastardo J. W., Holmes I. H. Attachment of SA-11 rotavirus to erythrocyte receptors. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1134–1140. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1134-1140.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan K. T., Twist E. M., Horton-Slight P., Forrer C., Bell L. M., Jr, Plotkin S. A., Clark H. F. Epidemiology of rotavirus electropherotypes determined by a simplified diagnostic technique with RNA analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):753–758. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.753-758.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herring A. J., Inglis N. F., Ojeh C. K., Snodgrass D. R., Menzies J. D. Rapid diagnosis of rotavirus infection by direct detection of viral nucleic acid in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):473–477. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.473-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The fractionation of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):251–257. doi: 10.1042/bj1020251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton P. J., Holdaway M. D., Petric M., Szymanski M. T., Tam J. S. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay for the detection of rotavirus. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):439–444. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.439-444.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Holmes I. H. Comparison of the genomes of simian, bovine, and human rotaviruses by gel electrophoresis and detection of genomic variation among bovine isolates. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):839–846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.839-846.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. S., Cai R. F., Chen J., Li R. J., Jiang R. S. Etiologic studies of the 1983 and 1984 outbreaks of epidemic diarrhea in Guangxi. Intervirology. 1985;24(3):140–146. doi: 10.1159/000149633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasi C., Louisirirotchanakul S., Thakerngpol K., Satrasook S., Surakhala M., Varavithya W., Thongcharoen P. The epidemiological study on viral diarrhoea in Thailand. J Med Assoc Thai. 1984 Jul;67(7):369–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Gust I. D., Holmes I. H. Human rotavirus and its antibody: their coexistence in feces of infants. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 May;7(5):405–409. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.5.405-409.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Kim H. W., Clem T., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1977 Aug 6;2(8032):263–267. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90951-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]