Abstract
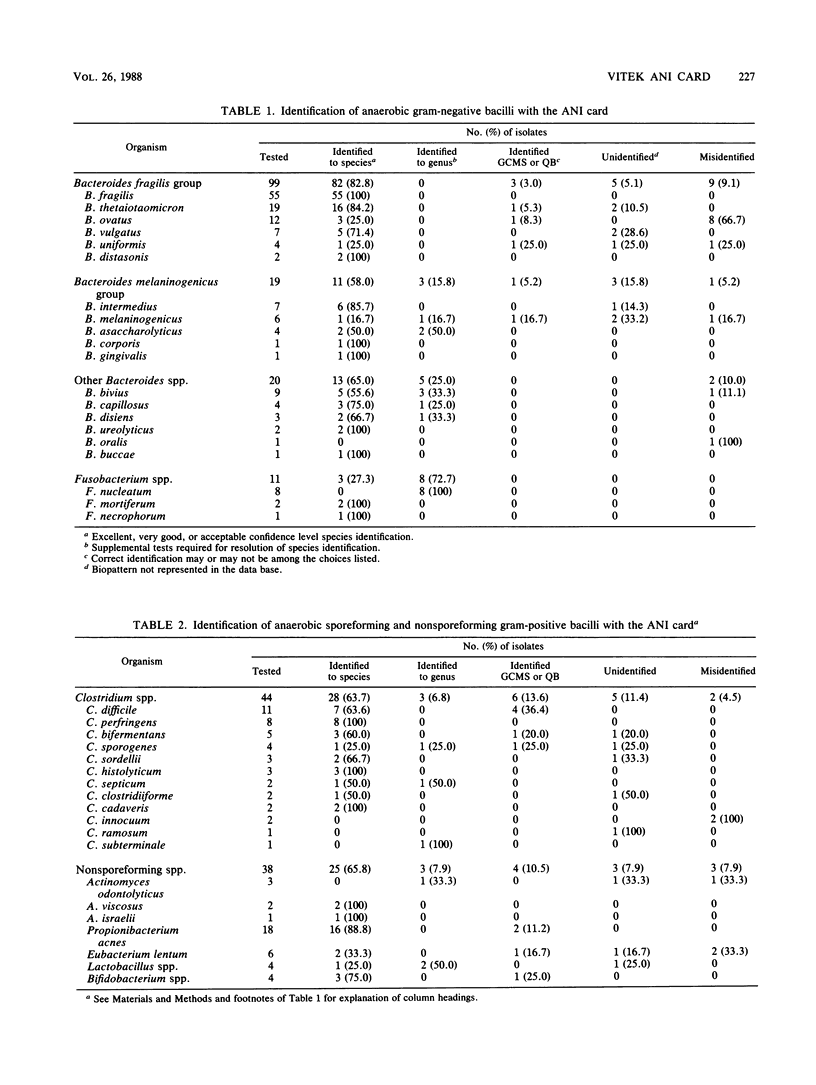
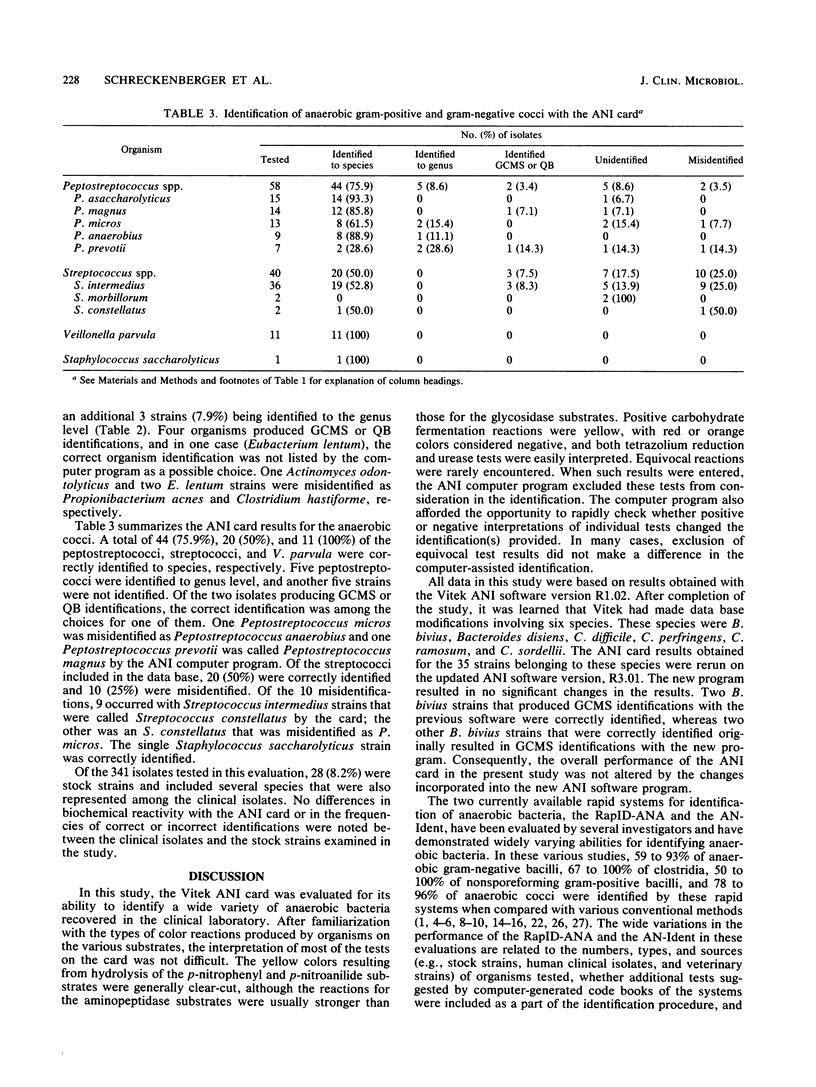
An evaluation of the Vitek Anaerobe Identification (ANI) card was performed with 341 bacterial isolates, including 313 clinical isolates and 28 stock strains of anaerobic microorganisms. Identifications obtained with the ANI card were compared with those determined by conventional methods. The card identified 73.2% of 149 anaerobic gram-negative bacilli, 63.6% of 44 Clostridium spp., 65.8% of 38 anaerobic nonsporeforming gram-positive bacilli, and 69.1% of 110 anaerobic cocci, with no further testing required. When genus-level identifications were included, 83.9% of the anaerobic gram-negative bacilli, 70.5% of Clostridium spp., 73.7% of the anaerobic nonsporeforming gram-positive bacilli, and 73.6% of the anaerobic cocci were identified. Nineteen isolates (5.6%) produced identifications of good confidence but marginal separation or questionable biotype, in which the correct identification was listed with one or two other possible choices and extra tests were required and suggested. A total of 28 (8.2%) were not identified and 29 isolates (8.5%) were misidentified by the ANI card. Among the commonly isolated clinically significant anaerobes, the ANI card identified 100% of 55 Bacteroides fragilis and 100% of 8 Clostridium perfringens. Use of supplemental tests and expansion of the data base to include additional strains of organisms that are difficult to separate even with conventional methods may improve the accuracy of the ANI card as a method for identification of anaerobic bacteria in the clinical laboratory.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adney W. S., Jones R. L. Evaluation of the RapID-ANA system for identification of anaerobic bacteria of veterinary origin. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):980–983. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.980-983.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Jumaili I. J., Bint A. J. Simple method for isolation and presumptive identification of Clostridium difficile. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1981;250(1-2):142–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelbaum P. C., Kaufmann C. S., Depenbusch J. W. Accuracy and reproducibility of a four-hour method for anaerobe identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):894–898. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.894-898.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate G. Comparison of Minitek Anaerobe II, API An-Ident, and RapID ANA systems for identification of Clostridium difficile. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jun;85(6):716–718. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/85.6.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlage R. S., Ellner P. D. Comparison of the PRAS II, AN-Ident, and RapID-ANA systems for identification of anaerobic bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):32–35. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.32-35.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. W., Pfeiffer D. G., Tally F. P. Evaluation of xylan fermentation for the identification of Bacteroides ovatus and Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):125–126. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.125-126.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellinger C. A., Moore L. V. Use of the RapID-ANA System to screen for enzyme activities that differ among species of bile-inhibited Bacteroides. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):289–293. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.289-293.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulletta E., Amato G., Nani E., Covelli I. Comparison of two systems for identification of anaerobic bacteria. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;4(3):282–285. doi: 10.1007/BF02013653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstad T. Evaluation of the API ZYM system for identification of Bacteroides and Fusobacterium species. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1980;168(3):173–177. doi: 10.1007/BF02122851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain Z., Lannigan R., Schieven B. C., Stoakes L., Kelly T., Groves D. Comparison of RapID-ANA and Minitek with a conventional method for biochemical identification of anaerobes. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 May;7(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston B. L., Edelstein M. A., Holloway E. Y., Finegold S. M. Bacteriologic and clinical study of Bacteroides oris and Bacteroides buccae. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):491–493. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.491-493.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karachewski N. O., Busch E. L., Wells C. L. Comparison of PRAS II, RapID ANA, and API 20A systems for identification of anaerobic bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):122–126. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.122-126.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. W. Phenotypic differentiation of some of the Veillonella species with the API ZYM system. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Jun;28(6):703–705. doi: 10.1139/m82-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M. Rapid identification of Actinomycetaceae and related bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):127–133. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.127-133.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon B. E., Syed S. A., Loesche W. J. API ZYM system for identification of Bacteroides spp., Capnocytophaga spp., and spirochetes of oral origin. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):97–102. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.97-102.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levett P. N. Identification of Clostridium difficile using the API ZYM system. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;4(5):505–507. doi: 10.1007/BF02014434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Weber C. J., Niles A. C. Comparative evaluation of three identification systems for anaerobes. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):52–55. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.52-55.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreckenberger P. C., Blazevic D. J. Rapid methods for biochemical testing of anaerobic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Nov;28(5):759–762. doi: 10.1128/am.28.5.759-762.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan O. Biochemical, enzymatic, and serological differentiation of Peptococcus indolicus (Christiansen) Sørensen from Peptococcus asaccharolyticus (Distaso) Douglas. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):157–162. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.157-162.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. Enzymatic characterization of some oral and nonoral gram-negative bacteria with the API ZYM system. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):288–294. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.288-294.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenson M. J., Lee D. T., Rosenblatt J. E., Contezac J. M. Evaluation of the AnIdent system for the identification of anaerobic bacteria. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 May;5(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(86)90086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. C., Strzempko M. N., Belsky C. A., McKinley G. A. API ZYM and API An-Ident reactions of fastidious oral gram-negative species. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):333–335. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.333-335.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tharagonnet D., Sisson P. R., Roxby C. M., Ingham H. R., Selkon J. B. The API ZYM system in the identification of Gram-negative anaerobes. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jun;30(6):505–509. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.6.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


