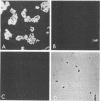
Abstract
A semiquantitative indirect immunofluorescence assay to detect coproantibody secretory IgA (SIgA) was established to investigate the human intestinal immune response to Yersinia species. This assay was based on microagglutination of SIgA in fecal specimens with the patient's homologous organism. Two populations of patients were defined, those who produced an agglutinating (2+) SIgA response and those who did not. A comparison between SIgA production and standard in vitro virulence-related characteristics of infecting organisms, including autoagglutination, calcium dependence, plasmid carriage, and absorption of Congo red, mouse virulence, and clinical presentation, was performed. A positive (2+) SIgA result was associated with acute enteric illness (positive predictive value, 78.6%) and mouse virulence (positive predictive value, 85.7%). When patients with active inflammatory bowel disease were excluded, the positive predictive value of SIgA for mouse virulence and acute enteric disease became 100%. In addition to strains of Yersinia enterocolitica 4,O:3, strains generally characterized as nonpathogenic, including Yersinia frederiksenii, were found to be associated with acute disease, mouse virulence, and stimulation of SIgA. The indirect immunofluorescence assay for detection of SIgA response appears to be a useful indicator of pathogenic strains of yersiniae recovered from enteric specimens.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARKSDALE W. L., GHODA A., OKABE K. Coproagglutinins in ulcerative colitis. J Infect Dis. 1951 Jul-Aug;89(1):47–51. doi: 10.1093/infdis/89.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakour R., Balligand G., Laroche Y., Cornelis G., Wauters G. A simple adult-mouse test for tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica strains of low experimental virulence. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Apr;19(2):237–246. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-2-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J., Sheehan D. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: guidelines for serologic diagnosis of human infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5(5):898–906. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.5.898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cancellieri V., Fara G. M. Demonstration of specific IgA in human feces after immunization with live Ty21a Salmonella typhi vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):482–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corridori S., Negretti F. Immunomicrobiological monitoring of orovaccinal therapy in acute intestinal infections. Dev Biol Stand. 1983;53:285–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Toivanen A. IgA-anti-yersinia antibodies in yersinia triggered reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Jul;45(7):561–565. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.7.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönblad E. A., Mäkelä O. Salivary and serum antibodies in patients with Yersinia enterocolitica infection. Microb Pathog. 1986 Dec;1(6):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. VI. A differential plating medium for the estimation of the mutation rate to avirulence. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:605–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.605-608.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock G. E., Schaedler R. W., MacDonald T. T. Yersinia enterocolitica infection in resistant and susceptible strains of mice. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):26–31. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.26-31.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. E., Banvard J. Coproantibody Excretion During Enteric Infections. Science. 1947 Aug 29;106(2748):188–189. doi: 10.1126/science.106.2748.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay B. A., Wachsmuth K., Gemski P. New virulence-associated plasmid in Yersinia enterocolitica. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1161–1163. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1161-1163.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W. J., Cavanaugh D. C. Correlation of autoagglutination and virulence of yersiniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):430–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.430-432.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. H., Hartzen S. H., Parm M. The determination of specific IgA-antibodies to Yersinia enterocolitica and their role in enteric infections and their complications. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Oct;93(5):331–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., McGrath P. P., Carter P. H., Eide E. L. The ability of some Yersinia enterocolitica strains to invade HeLa cells. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Dec;23(12):1714–1722. doi: 10.1139/m77-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leino R., Granfors K., Havia T., Heinonen R., Lampinen M., Toivanen A. Yersiniosis as a gastrointestinal disease. Scand J Infect Dis. 1987;19(1):63–68. doi: 10.3109/00365548709032379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leino R., Kalliomäki J. L. Yersiniosis as an internal disease. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Oct;81(4):458–461. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-4-458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro E., Fossey J., Shiner M., Drasar B. S., Allison A. C. Antibacterial antibodies in rectal and colonic mucosa in ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 1971 Feb 6;1(7693):249–250. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90997-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble M. A., Barteluk R. L., Freeman H. J., Subramaniam R., Hudson J. B. Clinical significance of virulence-related assay of Yersinia species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):802–807. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.802-807.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Ichikawa H., Kawamoto Y., Miyama A., Yoshii S. Heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Yersinia enterocolitica isolated from patients. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(5):401–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpic J. K., Robins-Browne R. M., Davey R. B. Differentiation between virulent and avirulent Yersinia enterocolitica isolates by using Congo red agar. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):486–490. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.486-490.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpic J. K., Robins-Browne R. M., Davey R. B. In vitro assessment of virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica and related species. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):105–110. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.105-110.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. P., Williams R. C., Jr Intestinal immunoglobulins in shigellosis. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jul;61(1):35–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds S. D., Noble M. A., Freeman H. J. Gastrointestinal features of culture-positive Yersinia enterocolitica infection. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jan;92(1):112–117. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90846-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toivanen A., Granfors K., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Leino R., Ståhlberg T., Vuento R. Pathogenesis of Yersinia-triggered reactive arthritis: immunological, microbiological and clinical aspects. Immunol Rev. 1985 Aug;86:47–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink D. L., Feeley J. C., Wells J. G., Vanderzant C., Vickery J. C., Roof W. D., O'Donovan G. A. Plasmid-mediated tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):224–226. doi: 10.1038/283224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]