Abstract
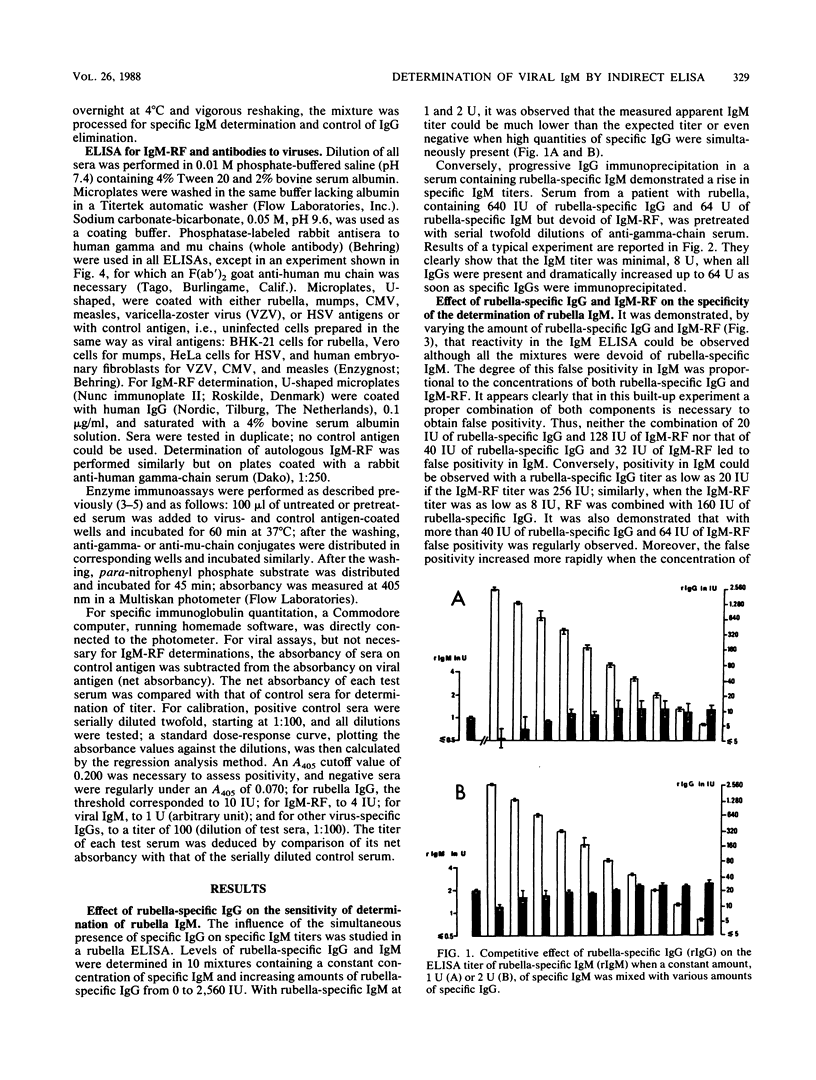
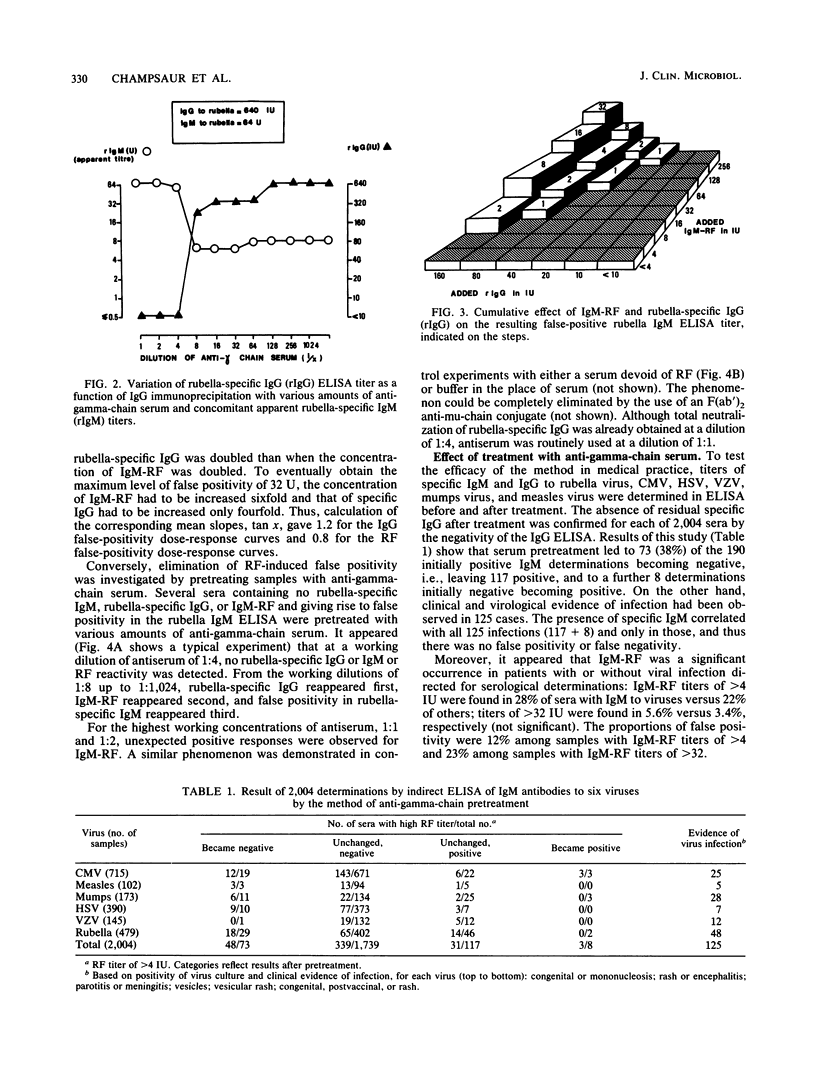
Four sources of error associated with virus-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) determination by indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were recognized and analyzed. First, competitive inhibition due to specific IgG was demonstrated by experiments involving addition and subtraction of rubella-specific IgG. Second, the interference due to rheumatoid factors (RFs) of the IgM class (IgM-RFs) was studied thoroughly, and it appeared that the level of false positivity was more dependent on specific IgG titers than on IgM-RF titers. Third, it was found that some IgM-RFs, differing from conventional IgM-RFs in that they reacted only with isologous IgG, were responsible for further cases of false positivity. Fourth, the interference of an IgM reacting with some virus-unmasked cellular antigens was demonstrated for some uninfected individuals. All four interfering factors could be readily eliminated by simply premixing serum samples with a sheep anti-human gamma-chain serum. This single pretreatment was shown to eliminate false-negatives as well as false-positives in a further 2,004 sera tested for six viruses. These results also emphasize the frequency of RFs and their heterogeneity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonfanti C., Meurman O., Halonen P. Detection of specific immunoglobulin M antibody to rubella virus by use of an enzyme-labeled antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):963–968. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.963-968.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerny E. H., Farshy C. E., Hunter E. F., Larsen S. A. Rheumatoid factor in syphilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):89–94. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.89-94.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champsaur H., Dussaix E., Tournier P. Hemagglutination inhibition, single radial hemolysis, and ELISA tests for the detection of IgG and IgM to rubella virus. J Med Virol. 1980;5(4):273–286. doi: 10.1002/1096-9071(1980)5:4<273::aid-jmv1890050403>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champsaur H., Henry-Amar M., Goldszmidt D., Prevot J., Bourjouane M., Questiaux E., Bach C. Rotavirus carriage, asymptomatic infection, and disease in the first two years of life. II. Serological response. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):675–682. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champsaur H., Iscaki S., Bernard O., Dodin A. Induction of Vibrio cholerae specific biliary antibodies after oral immunisation with a cholera cell-wall fraction. Lancet. 1985 Jun 1;1(8440):1276–1277. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunliffe D. A., Cox K. O. IgM-autoantibodies against isologous erythrocytes also react with isologous IgG(Fc). Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):720–722. doi: 10.1038/286720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser K. B., Shirodaria P. V., Stanford C. F. Fluorescent staining and human IgM. Br Med J. 1971 Sep 18;3(5776):707–707. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5776.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gispen R., Nagel J., Brand-Saathof B., De Graaf S. Immunofluorescence test for IgM rubella antibodies in whole serum after absorption with anti-gammaFc. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Dec;22(3):431–437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekker A. C., Brand-Saathof B., Vis J., Meijers R. C. Indirect immunofluorescence test for detection of IgM antibodies to cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):596–600. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinikki P. O., Shekarchi I., Dorsett P., Sever J. L. Determination of virus-specific IgM antibodies by using ELISA: elimination of false-positive results with protein A-Sepharose absorption and subsequent IgM antibody assay. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Dec;92(6):849–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Barnett E. V., Remington J. S. Method for avoiding false-positive results occurring in immunoglobulin M enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays due to presence of both rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):73–78. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.73-78.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Cleveland P. H., Redfield D. C., Oxman M. N., Wahl G. M. Rapid viral diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):298–310. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Vaheri A., Suni J., Wager O. Rheumatoid factor in acute viral infections: interference with determination of IgM, IgG, and IgA antibodies in an enzyme immunoassay. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):250–255. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Shimizu H., Kampa D., Doerr H. W. Rapid method to detect rubella immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin A antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Feb;1(2):132–135. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.2.132-135.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodaria P. V., Fraser K. B., Stanford F. Secondary fluorescent staining of virus antigens by rheumatoid factor and fluorescein-conjugated anti-IgM. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Jan;32(1):53–57. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torfason E. G., Diderholm H. False RIA IgM titres to herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus: factors causing them, and their absorption by protein A-Sepharose/IgG-protein A-Sepharose. J Med Virol. 1982;10(3):157–170. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890100302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegelmaier R., Behrens F., Enders G. Class-specific determination of antibodies against cytomegalo (CMV) and rubella virus by ELISA. J Biol Stand. 1981 Jan;9(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(81)80062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziola B., Meurman O., Matikainen M. T., Salmi A., Kalliomäki J. L. Determination of human immunoglobulin M rheumatoid factor by a solid-phase radioimmunoassay which uses human immunoglobulin G in antigen-antibody complexes. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):134–141. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.134-141.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


