Abstract
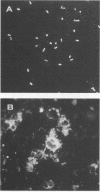
A total of 1,897 clinical specimens (1,019 aspirates and 876 swabs) were studied by indirect immunofluorescence (IF) with a mouse monoclonal antibody (MAb) against a D-galactose oligomer of Bacteroides fragilis lipopolysaccharide. The MAb has been shown to react with 96% of clinical B. fragilis isolates and with about 50% of Bacteroides ovatus and Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron isolates but not with other aerobic or anaerobic organisms tested. The sensitivity of IF in comparison with culturing was 78.9% for all three species. Of the 32 strains originating from culture-positive, IF-negative specimens, 13 lacked the target determinant for the MAb. Sensitivity was highest with specimens taken from the perineal area (87.1%) and lowest with those taken from undefined sites (56.6%). Sensitivity was better with aspirates (86.8%) than with swabs (72.6%). The specificity of IF was 95.6% for all of the material. Positive and negative predictive values were 51.1 and 98.0%, respectively. Neither long transportation times of specimens nor antimicrobial therapy seemed to correlate with the occurrence of IF-positive, culture-negative specimens. This study shows that a single MAb can be used to establish an IF assay that can complement isolation in the detection of these three members of the B. fragilis group.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DeGirolami P. C., Mepani C. P. Evaluation of a direct fluorescent antibody staining method for rapid identification of members of the bacteroides fragilis group. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Jul;76(1):78–82. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/76.1.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Bartlett J. G. Anaerobic infections (second of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1237–1245. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Mayhew J. W., Bartlett J. G., Thadepalli H., Onderdonk A. B. Rapid diagnosis of anaerobic infections by direct gas-liquid chromatography of clinical speciments. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):478–484. doi: 10.1172/JCI108300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin M. H. Fluorescent antibody techniques in the identification of the gram-negative nonsporeforming anaerobes. Health Lab Sci. 1970 Apr;7(2):78–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L. Chemical and biological characterization of the lipopolysaccharide of Bacteroides fragilis subspecies fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jul;134(1):59–66. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Fiddian A. P., Tabaqchali S. Rapid diagnosis of Bacteroides infections by indirect immunofluorescence assay of clinical specimens. Lancet. 1979 Feb 3;1(8110):239–242. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90768-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Seiler M. W. Immunochemical characterization of the outer membrane complex of Bacteroides fragilis subspecies fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1975 Oct;132(4):440–450. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.4.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé M., Delamare N., Pepersack F., Crokaert F., Yourassowsky E. Detection of Bacteroides fragilis and Bacteroides melaninogenicus by direct immunofluorescence. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;33(12):1189–1192. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.12.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linko-Kettunen L., Arstila P., Jalkanen M., Jousimies-Somer H., Lassila O., Lehtonen O. P., Weintraub A., Viljanen M. K. Monoclonal antibodies to Bacteroides fragilis lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):519–524. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.519-524.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linko L., Weintraub A., Arstila P., Pelliniemi L. J., Viljanen M. K. Characterization of the common immunodominant antigenic determinant in the lipopolysaccharide of Bacteroides fragilis by a monoclonal antibody. Scand J Immunol. 1987 May;25(5):469–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston S. J., Kominos S. D., Yee R. B. New medium for selection and presumptive identification of the Bacteroides fragilis group. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 May;7(5):448–453. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.5.448-453.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack M. P., Griffiths D. T., Johnston H. H. The Fluoretec system for rapid diagnosis of bacteroides infections by direct immunofluorescence of clinical specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Dec;34(12):1381–1384. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.12.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer L. R., Hill E. O., Holland J. W., Altemeier W. A. Indirect fluorescent antibody procedure for the rapid detection and identification of Bacteroides and Fusobacterium in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Oct;2(4):337–344. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.4.337-344.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub A., Lindberg A. A., Kasper D. L. Characterization of Bacteroides fragilis strains based on antigen-specific immunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):780–780. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub A., Lindberg A. A., Nord C. E. Identification of Bacteroides fragilis by indirect immunofluorescence. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1979;167(4):223–230. doi: 10.1007/BF02120807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]