Abstract
Computational studies provide support for the involvement of intermolecular π–interactions in the chiral recognition of secondary benzylic alcohols by the enantioselective acyl transfer catalyst CF3-PIP.
Nonenzymatic enantioselective acyl transfer catalysis has been an active area of research for over a decade.1 Many of the catalysts developed to date have demonstrated varying degrees of enantioselectivity in kinetic resolution2 of secondary alcohols. Secondary benzylic alcohols have enjoyed particular popularity as substrates in this reaction.3,4a–c However, the origin of enantioselectivity in this process has not been elucidated. In this Communication, we present the results of our computational studies, which support the involvement of π–interactions in the chiral recognition of this class of substrates.5
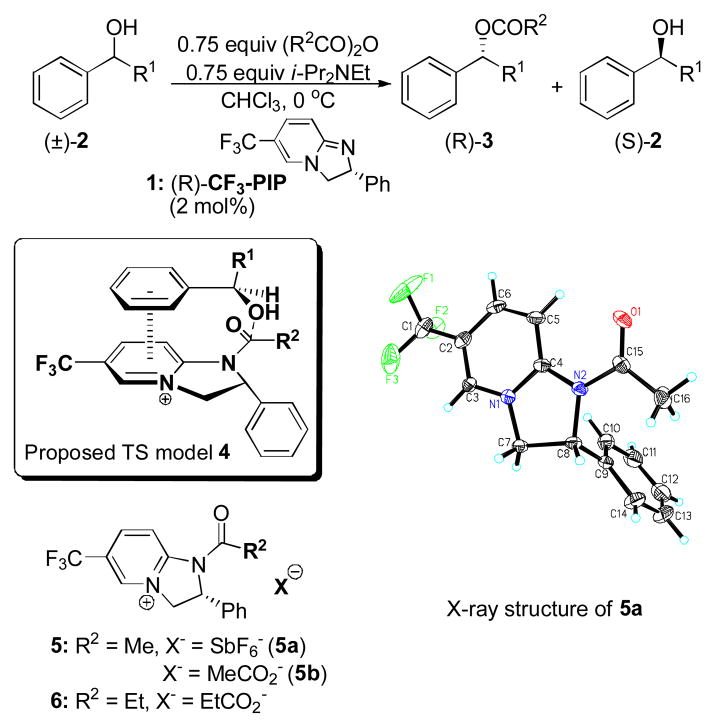
In 2004, we introduced a new class of enantioselective acyl transfer catalysts. Among the first-generation catalysts, CF3-PIP 1 proved to be particularly effective in kinetic resolution of secondary benzylic alcohols (2). Structure-selectivity trends observed in this initial study led us to hypothesize that the chiral recognition depends on π–π and cation-π interactions between the pyridinium ring of the N-acylated catalyst and the benzene ring of the substrate, as shown in the proposed transition state model 4 (Scheme 1).4a Later, this hypothesis proved to be valuable as a guide in the development of subsequent generations of related catalysts.4b,c,f Their application to benzylic,4a–c,f allylic4b and propargylic4d alcohols, 4-aryl-oxazolidinones4e and 2-aryl-cycloalkanols4f produced results that were also consistent with the π–stacking mechanism.
Scheme 1.
CF3-PIP-catalyzed kinetic resolution
Recently, we were able to obtain an X-ray structure of the N-acetylated CF3-PIP in the form of hexafluoroantimonate 5a, which was in accord with the expected conformation. However, the involvement of π–interactions in the transition state is inherently difficult to verify by direct experimental observation. Therefore, we initiated a computational study aimed at elucidating the origin of the enantioselectivity. To the best of our knowledge, the role of intermolecular π–interactions in chiral recognition has not been previously investigated by computational methods. 6, 7
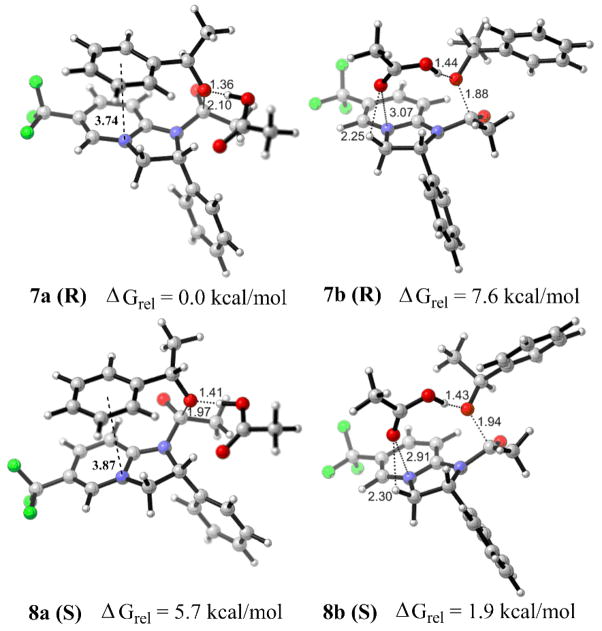
The energy-minimized geometry of N-acetyl-(R)-CF3-PIP+ (5, X omitted) obtained at the B3LYP/6-31G* level of theory8,9 was consistent with the X-ray structure of 5a, the acyl carbonyl being nearly coplanar with the pyridine ring. Transition state geometries for reactions of 5b and the R- and S-enantiomers of 1-phenylethanol (2, R1 = Me) were investigated next. The acetate anion hydrogen-bound to the hydroxyl group of the substrate was included in the calculations, as suggested by the recent computational studies on achiral acyl transfer catalysis.10 Each enantiomer of 1-phenylethanol was attached to the unencumbered β–face of 5b and all accessible conformations were explored.
(R)-1-phenylethanol, which is the fast-reacting enantiomer in kinetic resolutions with (R)-1, preferred the slipped-stacked geometry, with the phenyl of the substrate centered approximately over the pyridinium N. In conformer 7a, representing the global energy minimum, the distance between the center of the phenyl ring and the pyridinium N is 3.74 A, and the planes of the pyridinium and the benzene rings are at an 8.5° dihedral angle.11 The lowest-energy splayed conformer 7b was 7.6 kcal/mol less stable than 7a. For the diastereomeric transition states with the slow-reacting (S)-1-phenylethanol, the situation was reversed. The stacked conformer 8a was less energetically favorable than the splayed conformer 8b, presumably due to the A1,3-strain introduced by the methyl group virtually coplanar with the benzene ring in the former.
Finally, we confirmed that the approach of either the R- or the S-enantiomer of the substrate to the α-face of the N-acylated catalyst encumbered by the phenyl substituent at C2, is disfavored relative to the aforementioned β–face conformers 7a and 8b (by 6.6 kcal/mol and 10.1 kcal/mol, respectively).
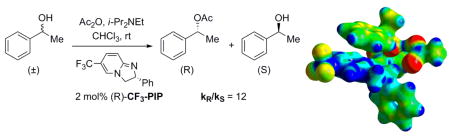
The energy difference between the lowest-energy conformers for the R- and S-enantiomers of the substrate (7a and 8b) is 1.9 kcal/mol. This value was adjusted to 1.6 kcal/mol by introducing solvent correction (CHCl3, CPCM model (UFF radii)), which is in excellent agreement with the experimental data (selectivity factor s = 12 obtained in chloroform at room temperature corresponds to ΔGrel = 1.5 kcal/mol) (Table 1, column 1, entries 1 and 5). Encouraged by these findings, we examined the transition states of the R- and S-enantiomers of 1-phenylethanol with N-propionyl-(R)-CF3-PIP propionate 6 (R2=Et), operating in kinetic resolutions with propionic anhydride (Figure 2). The computed increase in the free energy difference between the energy minimized diastereomeric transition states 9a and 10b (ΔGrel = 3.5 kcal/mol in gas phase, or 2.8 kcal/mol in chloroform) is qualitatively consistent with the experimentally observed enhanced enantioselectivity (s = 26, ΔGrel = 1.9 kcal/mol) (column 2, entries 1 and 5). Apparently, it reflects the greater steric repulsion between the ethyl group of the acyl substituent and the phenyl of the substrate in the splayed conformer 10b.
Table 1.
Comparison of calculation methods
| Entry | method | ΔGrel(8b - 7a)b kcal/mol | ΔGrel (10b - 9a)b kcal/mol |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | B3LYP/6-31G* | 1.9 (1.6) | 3.5 (2.8) |
| 2 | MP2/6-31G*// | 4.5 (5.3) | 6.0 (6.3) |
| B3LYP/6-31G* | |||
| SCS-MP2/6- | |||
| 3 | 31G*// | 3.7 (4.5) | 5.4 (5.7) |
| B3LYP/6-31G* | |||
| 4 | M05-2X/6-31G*// | 2.9 (2.7) | 4.9 (4.2) |
| B3LYP/6-31G* | |||
| 5 | Experimental dataa | 1.5 | 1.9 |
Conditions: 0.25 M 1-phenylethanol, 0.19 M (MeCO)2O or (EtCO)2O, 0.19 M i-Pr2Net, CDCl3, 23 °C.
Data given in paretheses have been computed using CPCM solvent model (UFF radii, CHCl3).
Figure 2.
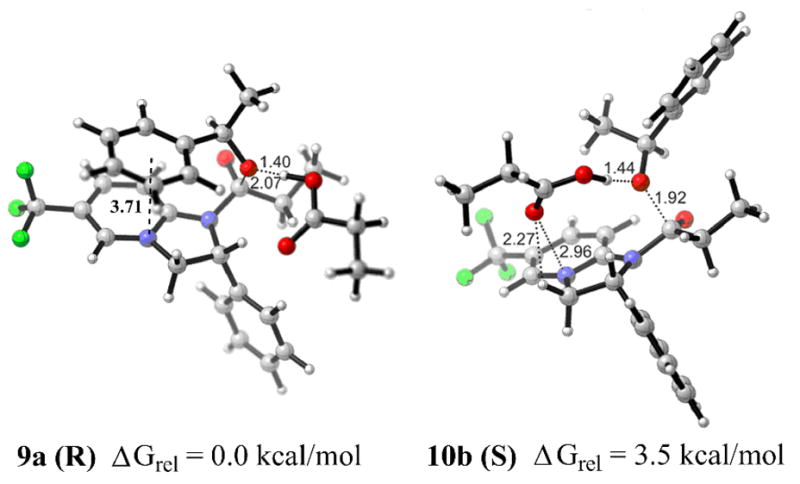
Transition states for reactions of (R)- and (S)-phenylethanol with 6
Since B3LYP may underestimate the dispersion interactions that would stabilize 7a, 8a, and 9a,10 we also calculated these energy differences with methods that are expected to treat such interactions more accurately.12 Single point calculations by MP2,13a SCS-MP2,13b and M05-2X13c performed on the real system using B3LYP-optimized geometries overestimated the energy differences by 1~3 kcal/mol compared to the experiment and the B3LYP results (Table 1).
In summary, our computational study lends theoretical support to the π–interaction hypothesis of chiral recognition in the KR of secondary benzylic alcohols catalyzed by CF3-PIP and provides a more accurate and detailed description of the transition state. The enantioselectivity depends upon two factors: steric repulsion between the methyl and the ortho-hydrogen (7a≪7b; 8b≪8a)), and the electrostatic attraction between the phenyl and pyridinium in the slipped-parallel geometry (7a<8a). The results of this investigation are expected to be applicable to our more advanced catalysts and may also shed light on the mechanism of chiral recognition achieved by enantioselective acylation catalysts developed by other groups.
Supplementary Material
Figure 1.
Transition states for reactions of (R)- and (S)-phenylethanol with 5b.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Glaser (University of Missouri-Columbia) for collaboration and helpful discussions during the early phase of this project. X-ray analysis was performed by Dr. Rath (University of Missouri-St. Louis). The financial support of this study by NIGMS (GM072682 for V. B. B. and X. L.; GM 36700 for K. N. H. and P. L.) is gratefully acknowledged.
Footnotes
Supporting Information Available: Kinetic resolution, computational and X-ray data. These materials are available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.For recent reviews, see: Denmark SE, Beutner GL. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2008;47:1560. doi: 10.1002/anie.200604943.Vedejs E, Jure M. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2005;44:3974. doi: 10.1002/anie.200460842.Dalko PI, Moisan L. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2004;43:5138. doi: 10.1002/anie.200400650.Jarvo ER, Miller SJ. Asymmetric Acylation, Chapter 43. In: Jacobsen EN, Pfaltz A, Yamamoto H, editors. Comprehensive Asymmetric Catalysis, Supplement 1. Springer-Verlag; Berlin, Heidelberg: 2004.
- 2.Kagan HB, Fiaud JC. Top Stereochem. 1988;18:249. [Google Scholar]
- 3.See, e.g., Ruble JC, Tweddell J, Fu GC. J Org Chem. 1998;63:2794.Copeland GT, Miller SJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:6496. doi: 10.1021/ja0108584.Vedejs E, Daugulis O. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:4166. doi: 10.1021/ja021224f.Kano T, Sasaki K, Maruoka K. Org Lett. 2005;7:1347. doi: 10.1021/ol050174r.
- 4.(a) Birman VB, Uffman EW, Jiang H, Li X, Kilbane CJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:12226. doi: 10.1021/ja0491477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Birman VB, Jiang H. Org Lett. 2005;7:3445. doi: 10.1021/ol051063v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Birman VB, Li X. Org Lett. 2006;8:1351. doi: 10.1021/ol060065s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Birman VB, Jiang H, Li X, Guo L, Uffman EW. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:6536. doi: 10.1021/ja061560m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Birman VB, Guo L. Org Lett. 2006;8:4859. doi: 10.1021/ol061906y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Birman VB, Li X. Org Lett. 2008;10:1115. doi: 10.1021/ol703119n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.For reviews of π–π and cation-π interactions, see: Hunter CA, Lawson KR, Perkins J, Urch CJ. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 2. 2001:651.Ma JC, Dougherty DA. Chem Rev. 1997;97:1303. doi: 10.1021/cr9603744.
- 6.The importance of intermolecular π–interactions between an N-acylated catalyst and a substrate containing a π–system was apparently first recognized by Kawabata T, Nagato M, Takasu K, Fuji K. J Am Chem Soc. 1997;119:3169.
- 7.For a computational study of intramolecular cation–π interactions in the structures of enantioselective acylation catalysts, see: Wei Y, Held I, Zipse H. Org Biomol Chem. 2006;4:4223. doi: 10.1039/b610140b.
- 8.Becke ADJ. Chem Phys. 1993;98:5648. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Frisch MJ, et al. Calculations were performed in Gaussian 03 (Revision E.01) Gaussian, Inc; Pittsburgh, PA: 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Xu S, Held I, Kempf B, Mayr H, Steglich W, Zipse H. Chem Eur J. 2005;11:4751. doi: 10.1002/chem.200500398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.3.75 Å was found to be the optimal distance between benzene and the desphenyl analogue of cation 5. See Supporting Information. It is also close to the optimum previously calculated for pyridinium-benzene π–interactions: Tsuzuki S, Mikami M, Yamada S. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:8656. doi: 10.1021/ja071372b.
- 12.On a simplified model system, calculations of ΔGrel by B3LYP produced good agreement with MP2 and M05-2X (typically within 1 kcal/mol). See Supporting Information for details.
- 13.(a) Head-Gordon M, Pople JA, Frisch M. J Chem Phys Lett. 1988;153:503. [Google Scholar]; (b) Grimme S. J Chem Phys. 2003;118:9095. [Google Scholar]; (c) Zhao Y, Schultz NE, Truhlar DG. J Chem Theory Comput. 2006;2:364. doi: 10.1021/ct0502763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.