Abstract
Two recombinant antigens of the larval stages of Echinococcus granulosus and Echinococcus multilocularis, termed EG55 and EM10, respectively, were applied for serodiagnosis and serological differentiation between parasitic infections caused by the metacestode tissue of both tapeworms. Antigen EM10 is synthesized by E. multilocularis larvae. Antigen EG55 represents the recombinant form of the low-molecular-weight subunit of antigen B, which is an Echinococcus genus-specific antigen. Both recombinant antigens were expressed as glutathione S-transferase fusion proteins. A sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal antibodies against EM10 and EG55 as capture reagents for the recombinant antigens was established and was evaluated with 74 serum samples from patients with histologically confirmed alveolar echinococcosis and 63 serum samples from patients with histologically confirmed cystic echinococcosis. A sensitivity of 93.2% and a specificity of 96.8% were achieved for the serodiagnosis of alveolar echinococcosis. Cystic echinococcosis could be detected with a sensitivity of 89.1% and a specificity of 98.6%.
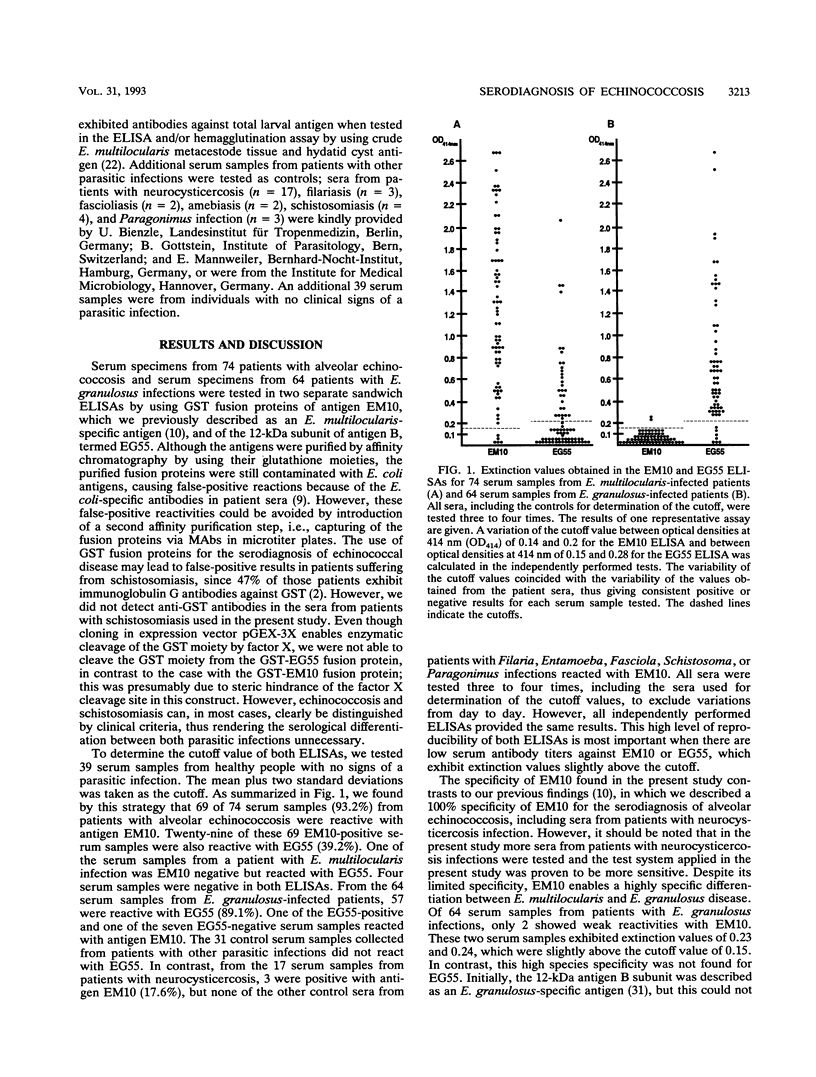
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auriault C., Gras-Masse H., Pierce R. J., Butterworth A. E., Wolowczuk I., Capron M., Ouma J. H., Balloul J. M., Khalife J., Neyrinck J. L. Antibody response of Schistosoma mansoni-infected human subjects to the recombinant P28 glutathione-S-transferase and to synthetic peptides. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1918–1924. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1918-1924.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamekh M., Gras-Masse H., Bossus M., Facon B., Dissous C., Tartar A., Capron A. Diagnostic value of a synthetic peptide derived from Echinococcus granulosus recombinant protein. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):458–464. doi: 10.1172/JCI115606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chemtai A. K., Bowry T. R., Ahmad Z. Evaluation of five immunodiagnostic techniques in echinococcosis patients. Bull World Health Organ. 1981;59(5):767–772. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facon B., Chamekh M., Dissous C., Capron A. Molecular cloning of an Echinococcus granulosus protein expressing an immunogenic epitope of antigen 5. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Apr;45(2):233–239. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90090-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch P. M., Frosch M., Pfister T., Schaad V., Bitter-Suermann D. Cloning and characterisation of an immunodominant major surface antigen of Echinococcus multilocularis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Oct;48(2):121–130. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90108-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch P. M., Geier C., Kaup F. J., Müller A., Frosch M. Molecular cloning of an echinococcal microtrichal antigen immunoreactive in Echinococcus multilocularis disease. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Apr;58(2):301–310. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90052-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B., Eckert J., Fey H. Serological differentiation between Echinococcus granulosus and E. multilocularis infections in man. Z Parasitenkd. 1983;69(3):347–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00927876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B., Jacquier P., Bresson-Hadni S., Eckert J. Improved primary immunodiagnosis of alveolar echinococcosis in humans by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using the Em2plus antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):373–376. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.373-376.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B. Molecular and immunological diagnosis of echinococcosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1992 Jul;5(3):248–261. doi: 10.1128/cmr.5.3.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B. Purification and characterization of a specific antigen from Echinococcus multilocularis. Parasite Immunol. 1985 May;7(3):201–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1985.tb00070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings L., McManus D. P. The diagnostic value and molecular characterisation of an Echinococcus multilocularis antigen gene clone. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Jan;44(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90220-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings L., McManus D. P. The isolation, by differential antibody screening, of Echinococcus multilocularis antigen gene clones with potential for immunodiagnosis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Mar 1;33(2):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hira P. R., Shweiki H. M., Siboo R., Behbehani K. Counterimmunoelectrophoresis using an arc 5 antigen for the rapid diagnosis of hydatidosis and comparison with the indirect hemagglutination test. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 May;36(3):592–597. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagiko M. M., Gathuma J. M., Lindqvist K. J. Serological diagnosis of hydatid disease by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using partially purified hydatid cyst fluid antigens. Int J Zoonoses. 1986 Dec;13(4):241–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar J. R., Kaushik S. P., Sawhney I. M., Kamboj M. S., Mehta S. K., Vinayak V. K. Specific antibodies in serum of patients with hydatidosis recognised by immunoblotting. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Jan;36(1):46–51. doi: 10.1099/00222615-36-1-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch J., Lederer I., Mannweiler E. Species-specific immunodiagnosis of human echinococcosis with crude antigens. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;3(6):554–555. doi: 10.1007/BF02013618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightowlers M. W., Liu D. Y., Haralambous A., Rickard M. D. Subunit composition and specificity of the major cyst fluid antigens of Echinococcus granulosus. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Dec;37(2):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddison S. E., Slemenda S. B., Schantz P. M., Fried J. A., Wilson M., Tsang V. C. A specific diagnostic antigen of Echinococcus granulosus with an apparent molecular weight of 8 kDA. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Apr;40(4):377–383. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.40.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller N., Gottstein B., Vogel M., Flury K., Seebeck T. Application of a recombinant Echinococcus multilocularis antigen in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunodiagnosis of human alveolar echinococcosis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Sep;36(2):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriol R., Williams J. F., Pérez Esandi M. V., Oriol C. Purification of lipoprotein antigens of Echinococcus granulosus from sheep hydatid fluid. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Jul;20(4):569–574. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1971.20.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella M., Galli C., Vullo V., Zennaro F., Delia S., Sorice F. Echinococcus granulosus antigens: comparative analysis of human, bovine and ovine hydatid fluids. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1984 Oct;78(5):549–551. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1984.11811863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. C., Aitken A., McManus D. P. A protein secreted in vivo by Echinococcus granulosus inhibits elastase activity and neutrophil chemotaxis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Jan;44(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90223-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. C., McManus D. P. Specific and cross-reactive antigens of Echinococcus granulosus hydatid cyst fluid. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Sep;25(2):143–154. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusano A., Ioppolo S., Notargiacomo S., Ortona E., Riganó R., Teggi A., De Rosa F., Vicari G. Detection of antibodies against Echinococcus granulosus major antigens and their subunits by immunoblotting. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1991 Mar-Apr;85(2):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(91)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verastegui M., Moro P., Guevara A., Rodriguez T., Miranda E., Gilman R. H. Enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot test for diagnosis of human hydatid disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1557–1561. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1557-1561.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel M., Gottstein B., Müller N., Seebeck T. Production of a recombinant antigen of Echinococcus multilocularis with high immunodiagnostic sensitivity and specificity. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Nov;31(2):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattal C., Malla N., Khan I. A., Agarwal S. C. Comparative evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the diagnosis of pulmonary echinococcosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):41–46. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.41-46.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., Liu J. P., Efstratiadis A. Cloning of PCR-amplified total cDNA: construction of a mouse oocyte cDNA library. Genet Anal Tech Appl. 1990 Feb;7(1):5–17. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(90)90038-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarzabal L. A., Dupas H., Bout D., Naquira F., Capron A. Echinococcus granulosus: the distribution of hydatid fluid antigens in the tissues of the larval stage. II. Localization of the thermostable lipoprotein of parasitic origin (antigen B). Exp Parasitol. 1977 Jun;42(1):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Yaman F. M., Knobloch J. Isolation and partial characterization of species-specific and cross-reactive antigens of Echinococcus granulosus cyst fluid. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Nov;37(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Amelio R., Pontesilli O., Dayal R., de Rosa F., Barnet M., Teggi A., Brighouse G., Lambert P. H. Characterization of parasite antigens from human hydatid cyst fluid by SDS-PAGE and IEF. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1985;174(1):43–50. doi: 10.1007/BF02123670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de StGroth S. F., Scheidegger D. Production of monoclonal antibodies: strategy and tactics. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(1-2):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


