Abstract
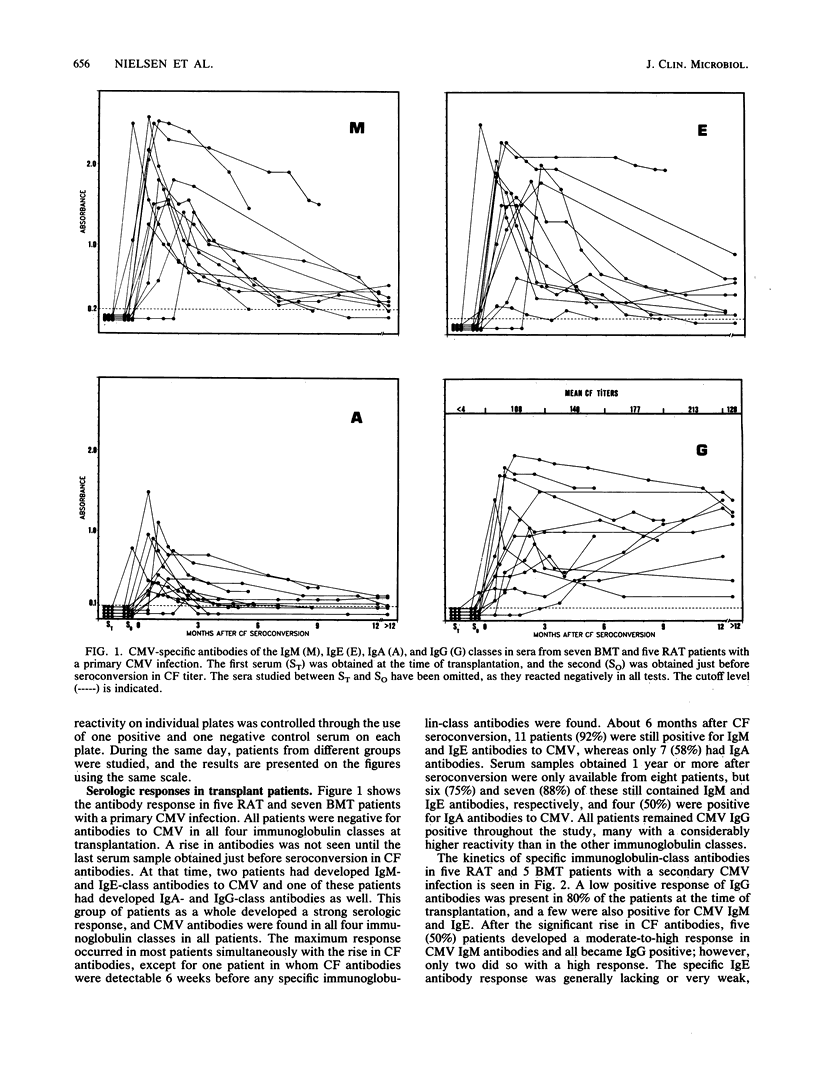
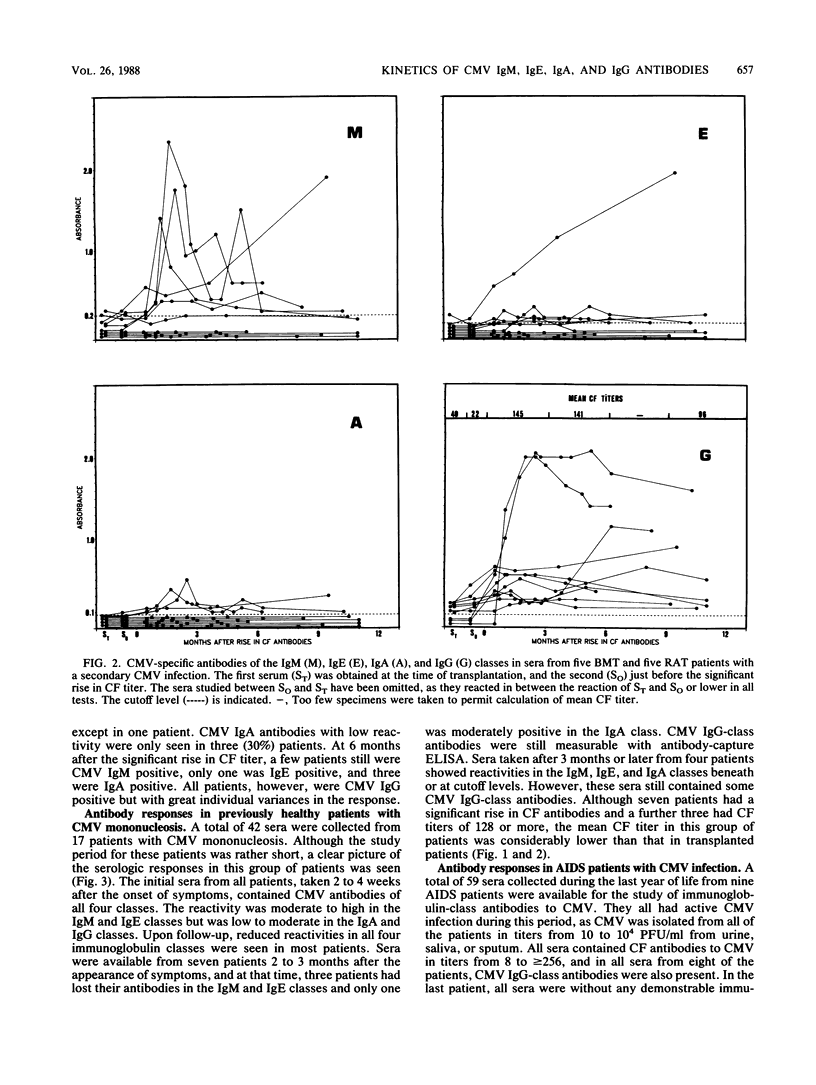
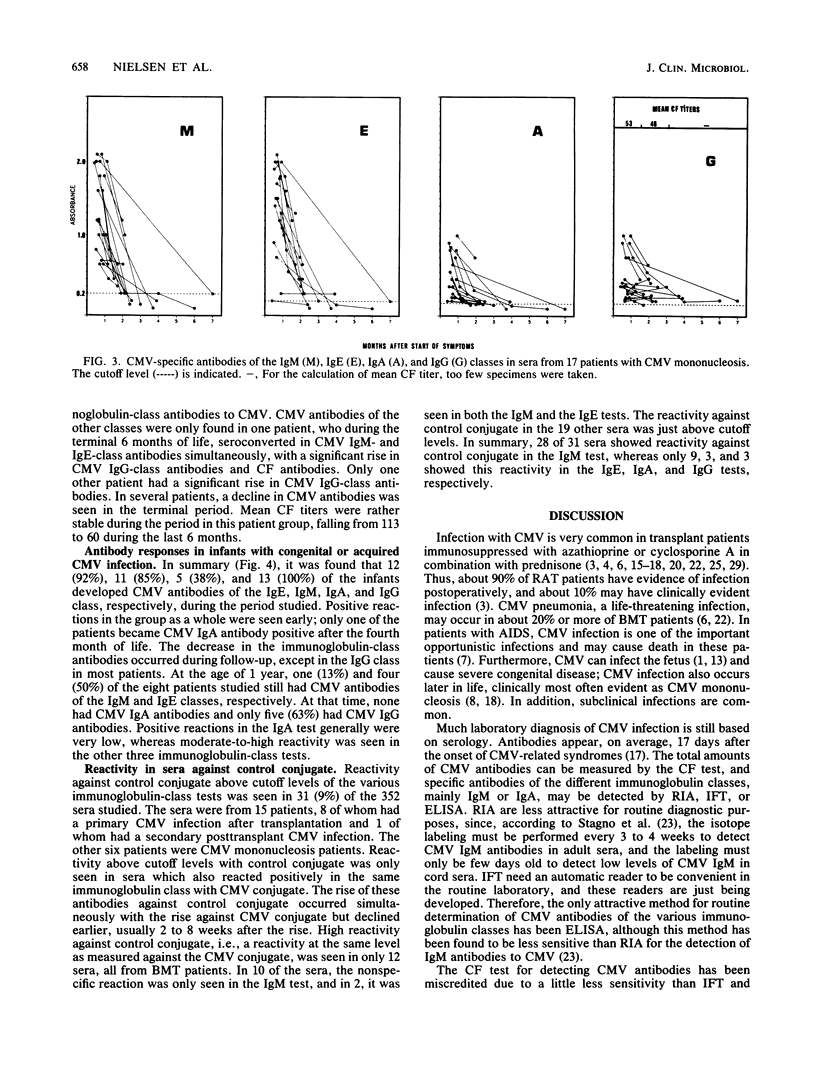
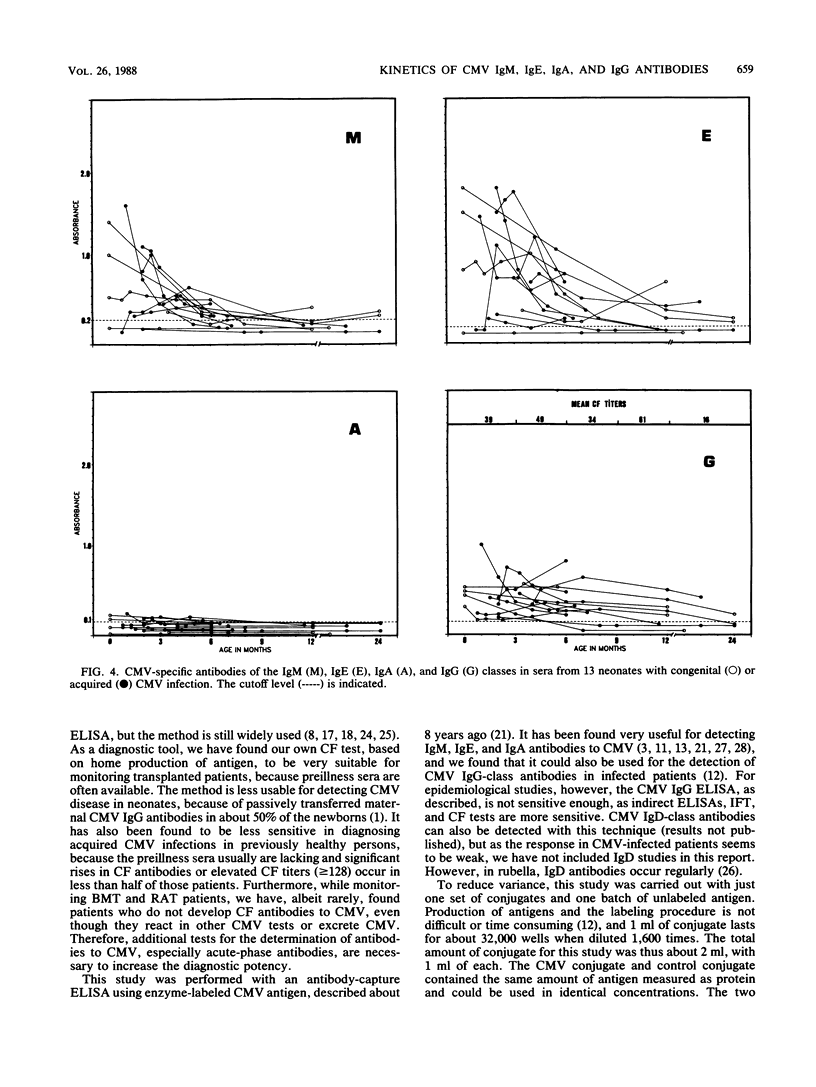
Antibody-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using enzyme-labeled cytomegalovirus (CMV) nuclear antigen is a reliable and easily performed test suitable for routine use. As the serologic response to CMV infection may, however, vary considerably among patients, we have studied the kinetics of CMV-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM), IgE, IgA, and IgG antibodies in 352 sera from 61 patients by using antibody-capture ELISA and complement fixation (CF) tests. In a CMV mononucleosis group (n = 17), most patients had antibodies of all four immunoglobulin classes, but antibody levels decreased rapidly, with half the patients having a borderline-positive or a negative reaction for all classes, except IgG, 2 months after the appearance of symptoms. Twelve patients with a primary CMV infection after renal or bone marrow transplantation also developed all immunoglobulin-class antibodies. In only two patients did CMV IgM and IgE antibodies precede seroconversion of CF antibodies, and in one patient, these antibodies lagged months behind. Most patients had all classes of CMV antibodies, except IgA, for a year or more. Among 10 transplant patients with a secondary CMV infection, 50% had long-lasting IgM antibodies, and very few had IgE or IgA antibodies, but all had IgG antibodies to CMV. In 13 infected infants, the CMV-specific serologic response was also characterized by long-lasting IgM, IgE, and IgG antibodies. Two patients did not develop detectable IgM antibodies, and one of these did not show IgE antibodies either. The IgA response in infants as a whole was lacking; a few, however, were borderline positive. Of the nine acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients with CMV infection studied during their last year of life, only one had antibodies in all four classes, the rest had only CF antibodies, and all except for one had IgG-class antibodies. All sera studied were also tested against a control antigen produced from noninfected cell nuclei. It was found that some patients developed antibodies to nuclear antigens in parallel with the rise in specific antibodies. The nonspecific antibodies occurred in all four classes, but most often they were of the IgM class. Addition of unlabeled control antigen to the conjugates was not always sufficient to abort this nonspecific reaction.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen H. K., Brostrøm K., Hansen K. B., Leerhøy J., Pedersen M., Osterballe O., Felsager U., Mogensen S. A prospective study on the incidence and significance of congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 May;68(3):329–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb05015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Andersen H. K. Smooth-muscle antibodies and other tissue antibodies in cytomegalovirus infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Oct;22(1):22–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnfred J., Nielsen C. M., Spencer E. S., Andersen H. K. A prospective study on infection with cytomegalovirus in renal allograft recipients immunosuppressed with cyclosporine A and low dose prednisone. Scand J Infect Dis. 1987;19(3):297–302. doi: 10.3109/00365548709018474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S., Kim D. Y., Scott K. M., Sewell D. L. Immunoglobulin M to cytomegalovirus in primary and reactivation infections in renal transplant recipients. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):52–55. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.52-55.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demmler G. J., Six H. R., Hurst S. M., Yow M. D. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of IgM-class antibodies to cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1152–1155. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbeek A., Brummelhuis G. J., Donkers A., Dumas A. M., ten Haaft A., Schaap B. J., Sizoo W., Löwenberg B. Rapid clearance of cytomegalovirus-specific IgG after repeated intravenous infusions of human immunoglobulin into allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipients. J Infect Dis. 1987 May;155(5):897–902. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.5.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert S. P., Kiefer D. J., Friedman-Kien A. E., Poiesz B. Antibody levels for cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus, and rubella in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;23(2):318–321. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.2.318-321.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M. J., Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Leary P. L., Zaia J. A., Hirsch M. S. Immune response to herpesvirus antigens in adults with acute cytomegaloviral mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):851–857. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Sarov I. Determination of IgA antibodies to human cytomegalovirus by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). J Med Virol. 1980;6(3):249–257. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890060308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. E., Coleman R. M., Best J. M., Benetato B. B., Nahmias A. J. Persistence of serum IgA antibodies to herpes simplex, varicella-zoster, cytomegalovirus, and rubella virus detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J Med Virol. 1985 Aug;16(4):343–349. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890160407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen C. M., Hansen K., Andersen H. M., Gerstoft J., Vestergaard B. F. An enzyme labelled nuclear antigen immunoassay for detection of cytomegalovirus IgM antibodies in human serum: specific and non-specific reactions. J Med Virol. 1987 May;22(1):67–76. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890220109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S. L., Rønholm E., Sørensen I., Andersen H. K. Detection of immunoglobulin G antibodies to cytomegalovirus antigens by antibody capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):998–1003. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.998-1003.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S. L., Rønholm E., Sørensen I., Jaeger P., Andersen H. K. Improvement of serological diagnosis of neonatal cytomegalovirus infection by simultaneously testing for specific immunoglobulins E and M by antibody-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1406–1410. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1406-1410.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole C. M., Gray J. J., Maher P., Wreghitt T. G. Persistent excretion of cytomegalovirus in heart transplant patients correlates with inversion of the ratio of T helper/T suppressor-cytotoxic cells. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1160–1162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberender H., Straube E., Kunkel M., Gärtner L., Morfiadakis I. Epstein-Barr virus-specific immunoglobulin A in patients with infectious mononucleosis, an age-dependent factor. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;5(2):173–174. doi: 10.1007/BF02013981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panjwani D. D., Ball M. G., Berry N. J., Wimperis J. Z., Blacklock H. A., Prentice H. G., Hoffbrand A. V., Griffiths P. D. Virological and serological diagnosis of cytomegalovirus infection in bone marrow allograft recipients. J Med Virol. 1985 Aug;16(4):357–365. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890160409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pass R. F., Griffiths P. D., August A. M. Antibody response to cytomegalovirus after renal transplantation: comparison of patients with primary and recurrent infections. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):40–46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen L., Kelsall D., Nelson R., Carney W., Hirsch M., Winston D., Preiksaitis J., Merigan T. C. Virus-specific IgG and IgM antibodies in normal and immunocompromised subjects infected with cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):191–199. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Hovi T., Meurman O., Vesikari T., Vaheri A. Kinetics of specific IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM antibody responses in rubella. J Med Virol. 1985 May;16(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890160102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov I., Levy E., Aymard M., Chardonnet Y., Bosshard S., Revillard J. P., Friedman M., Nord E., Greiff M., Haikin H. Detection of virus-specific IgA antibodies in serum of kidney transplant patients with recurrent cytomegalovirus infection by enzymeimmuno and radioimmunoassay techniques. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 May;48(2):321–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinhøj P., Andersen H. K., Møller J., Jacobsen N. Cytomegalovirus infection after bone marrow transplantation: relation of pneumonia to postgrafting immunosuppressive treatment. J Med Virol. 1984;14(2):91–99. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Tinker M. K., Elrod C., Fuccillo D. A., Cloud G., O'Beirne A. J. Immunoglobulin M antibodies detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and radioimmunoassay in the diagnosis of cytomegalovirus infections in pregnant women and newborn infants. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):930–935. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.930-935.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand O. A., Hoddevik G. M. The diagnostic significance of specific serum IgA detection in cytomegalovirus infections. Arch Virol. 1984;82(3-4):173–180. doi: 10.1007/BF01311161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland S., Briggs J. D. The detection of antibodies to cytomegalovirus in the sera of renal transplant patients by an IgM antibody capture assay. J Med Virol. 1983;11(2):147–159. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890110209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torfason E. G., Källander C., Halonen P. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of serum IgG, IgM, and IgA antibodies to cytomegalovirus. J Med Virol. 1981;7(2):85–96. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890070202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wreghitt T. G., Gray J. J., Chandler C. Prognostic value of cytomegalovirus IgM antibody in transplant recipients. Lancet. 1986 May 17;1(8490):1157–1158. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91874-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. M., Heessen F. W., van der Logt J. T., van der Veen J. Direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay that uses peroxidase-labeled antigen for determination of immunoglobulin M antibody to cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Mar;13(3):416–422. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.3.416-422.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. M., van der Logt J. T., Heessen F. W., van der Veen J. Quantitation of immunoglobulin E antibody to cytomegalovirus by antibody capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):558–561. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.558-561.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


