Abstract
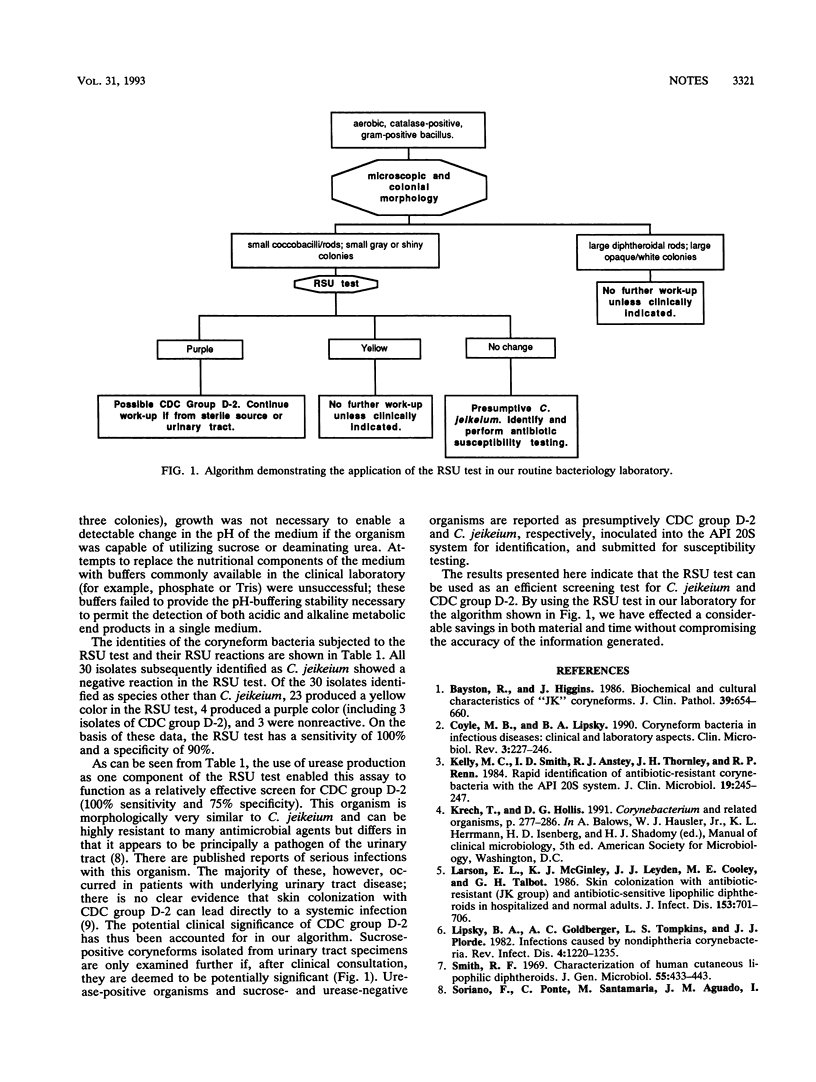
Corynebacterium jeikeium causes systemic infections, particularly in immunocompromised hosts. A minitube assay has been developed for the presumptive identification of C. jeikeium. With our rapid sucrose-urea test and conventional biochemical tests, sixty isolates of gram-positive, catalase-positive bacilli were identified in our laboratory. Results indicated that our assay has a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 90%.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayston R., Higgins J. Biochemical and cultural characteristics of "JK" coryneforms. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jun;39(6):654–660. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.6.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle M. B., Lipsky B. A. Coryneform bacteria in infectious diseases: clinical and laboratory aspects. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jul;3(3):227–246. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. C., Smith I. D., Anstey R. J., Thornley J. H., Rennie R. P. Rapid identification of antibiotic-resistant corynebacteria with the API 20S system. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):245–247. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.245-247.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson E. L., McGinley K. J., Leyden J. J., Cooley M. E., Talbot G. H. Skin colonization with antibiotic-resistant (JK group) and antibiotic-sensitive lipophilic diphtheroids in hospitalized and normal adults. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):701–706. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky B. A., Goldberger A. C., Tompkins L. S., Plorde J. J. Infections caused by nondiphtheria corynebacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Nov-Dec;4(6):1220–1235. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.6.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F. Characterization of human cutaneous lipophilic diphtheroids. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Mar;55(3):433–443. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-3-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano F., Ponte C., Santamaria M., Aguado J. M., Wilhelmi I., Vela R., Delatte L. C. Corynebacterium group D2 as a cause of alkaline-encrusted cystitis: report of four cases and characterization of the organisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):788–792. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.788-792.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano F., Rodriguez-Tudela J. L., Fernández-Roblas R., Aguado J. M., Santamaría M. Skin colonization by Corynebacterium groups D2 and JK in hospitalized patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1878–1880. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1878-1880.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wichmann S., Wirsing von Koenig C. H., Becker-Boost E., Finger H. Isolation of Corynebacterium group JK from clinical specimens with a semiselective medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):204–206. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.204-206.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


