Abstract
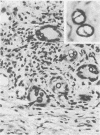
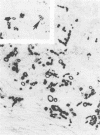
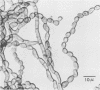
The first human phaeohyphomycotic infection caused by Xylohypha emmonsii is described. The patient, an 83-year-old woman, developed a purpuric lesion on her left arm. The pale brown fungal elements observed in biopsy tissue consisted of thin- to thick-walled, oval to spherical, yeastlike cells with single and, occasionally, multiple buds; chains of budding cells; cells with internal septations in one and, rarely, two planes; and septate hyphae. In culture, X. emmonsii grew moderately fast at 25 degrees C, showed minimal growth at 37 degrees C, and failed to grow at 40 degrees C. It produced acropetal chains of one-celled (rarely two-celled) conidia laterally and terminally directly from vegetative hyphal cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ajello L., Georg L. K., Steigbigel R. T., Wang C. J. A case of phaeohyphomycosis caused by a new species of Phialophora. Mycologia. 1974 May-Jun;66(3):490–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ajello L. Hyalohyphomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis: two global disease entities of public health importance. Eur J Epidemiol. 1986 Dec;2(4):243–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00419488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honbo S., Padhye A. A., Ajello L. The relationship of Cladosporium carrionii to Cladophialophora ajelloi. Sabouraudia. 1984;22(3):209–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshi G., Anandi V., Kurien M., Kirubakaran M. G., Padhye A. A., Ajello L. Nasal phaeohyphomycosis caused by Bipolaris hawaiiensis. J Med Vet Mycol. 1987 Dec;25(6):397–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., de Vries G. A. Comparative study of an isolate resembling Banti's fungus with Cladosporium trichoides. Sabouraudia. 1983 Mar;21(1):59–72. doi: 10.1080/00362178385380091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariat F., Segretain G., Destombes P., Darrasse H. Kyste sous-cutané mycosique (phaeo-sporotrichose) à Phialophora gougerotii (Matruchot 1910) Borelli 1955, observé au Sénégal. Sabouraudia. 1967 Feb;5(3):209–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis M. R., Borelli D., Padhye A. A., Ajello L. Reclassification of Cladosporium bantianum in the genus Xylohypha. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1148–1151. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1148-1151.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis M. R. Chromoblastomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis: new concepts, diagnosis, and mycology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983 Jan;8(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(83)70001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis M. R., McKenzie R. A., Connole M. D. Phaeosclera dematioides, a new etiologic agent of phaeohyphomycosis in cattle. Sabouraudia. 1985 Apr;23(2):133–135. doi: 10.1080/00362178585380211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padhye A. A., McGinnis M. R., Ajello L., Chandler F. W. Xylohypha emmonsii sp. nov., a new agent of phaeohyphomycosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):702–708. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.702-708.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]